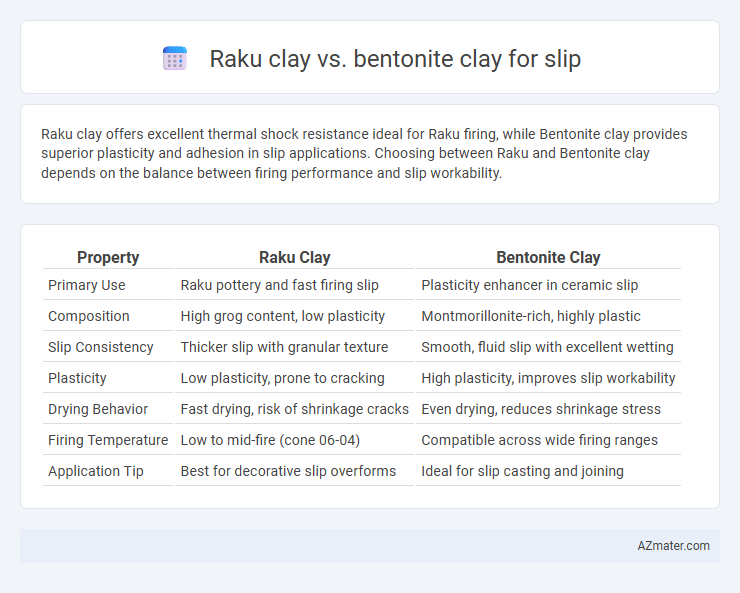
Raku clay offers excellent thermal shock resistance ideal for Raku firing, while Bentonite clay provides superior plasticity and adhesion in slip applications. Choosing between Raku and Bentonite clay depends on the balance between firing performance and slip workability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Raku Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Raku pottery and fast firing slip | Plasticity enhancer in ceramic slip |
| Composition | High grog content, low plasticity | Montmorillonite-rich, highly plastic |
| Slip Consistency | Thicker slip with granular texture | Smooth, fluid slip with excellent wetting |
| Plasticity | Low plasticity, prone to cracking | High plasticity, improves slip workability |
| Drying Behavior | Fast drying, risk of shrinkage cracks | Even drying, reduces shrinkage stress |
| Firing Temperature | Low to mid-fire (cone 06-04) | Compatible across wide firing ranges |
| Application Tip | Best for decorative slip overforms | Ideal for slip casting and joining |
Introduction to Raku Clay and Bentonite Clay
Raku clay, known for its low fire temperature and porous nature, is favored in pottery for its quick drying and thermally reactive properties, making it ideal for raku firing techniques. Bentonite clay, rich in montmorillonite, excels as a slip material due to its high absorbency and plasticity, creating smooth, cohesive suspensions essential for slip casting and decoration. Both clays serve distinct roles in ceramics: Raku clay enhances firing effects while Bentonite clay improves slip consistency and adhesion.
What Is Raku Clay?
Raku clay is a specially formulated clay body designed to withstand the rapid thermal shock of raku firing, making it ideal for decorative pottery with crackled surfaces. It is typically more porous and less plastic than bentonite clay, which enhances its ability to absorb water and dry evenly for slip applications. Unlike bentonite clay, known for its high plasticity and binding properties, raku clay slip is optimized for creating smooth, crack-resistant coatings on raku-fired ceramics.
What Is Bentonite Clay?
Bentonite clay is a natural, highly absorbent clay formed from volcanic ash, prized in pottery for its excellent plasticity and slip suspension qualities. It creates a smooth, fine slip that adheres well to Raku clay surfaces, enhancing the bond between clay layers during the firing process. Bentonite's unique swelling properties improve slip fluidity and workability, making it a preferred additive over Raku clay alone for consistent slip performance.
Key Differences in Composition
Raku clay typically contains grog and sand, providing a coarse texture ideal for thermal shock resistance and slip application in raku firing. Bentonite clay is rich in montmorillonite, offering high plasticity and excellent water absorption, which enhances slip's adhesion and workability. The key compositional difference lies in Raku clay's refractory inclusions versus Bentonite's smectite minerals, affecting slip consistency and drying behavior.
Plasticity and Workability in Slip Applications
Raku clay exhibits moderate plasticity, providing a balance that allows easy shaping while retaining structure in slip applications, making it ideal for hand-building and decorative techniques. Bentonite clay features high plasticity and exceptional workability due to its fine particles and strong water absorption, resulting in a smooth, cohesive slip that enhances adhesion and surface detail. Comparing the two, Raku clay offers better drying flexibility with less shrinkage, whereas Bentonite's superior plasticity improves slip suspension and resistance to cracking during application and firing.
Firing Temperature and Thermal Properties
Raku clay typically fires at lower temperatures, around cone 06 to 04 (1828degF to 1940degF), making it ideal for rapid firing and thermal shock resistance, whereas Bentonite clay is not commonly used alone for firing but as an additive due to its high plasticity and ability to withstand high temperatures without cracking. Raku clay's thermal expansion is suited for quick cooling cycles, minimizing fracture risks during the raku process, while Bentonite enhances the thermal shock resistance when mixed with other clays due to its fine particle size and binding properties. Understanding the firing temperature and thermal behavior of each clay type is crucial for optimizing slip application and ensuring durability in ceramic firing processes.
Behavior and Performance in Slip Casting
Raku clay exhibits rapid drying and lower plasticity compared to Bentonite clay, making it less ideal for smooth slip casting surfaces but better suited for textured finishes. Bentonite clay provides superior suspension properties and high plasticity, enhancing slip stability and reducing settling during casting, which results in more consistent and defect-free ceramic pieces. The high swelling capacity of Bentonite also improves the slip's water retention, ensuring better mold coverage and detail reproduction in slip casting processes.
Color and Surface Finish Comparison
Raku clay typically exhibits a warmer, earth-toned color palette with natural variegation that enhances the visual richness of slip, while bentonite clay offers a brighter, more neutral base that provides consistent color intensity. The surface finish of raku clay slip tends to be more textured and organic, contributing to a rustic aesthetic, whereas bentonite clay slip delivers a smoother, more uniform finish ideal for detailed glazing and fine decorative work. Differences in plasticity and particle size between raku and bentonite clays directly impact the color absorption and surface smoothness of the resulting slip.
Practical Uses: Which Clay for Which Slip Technique?
Raku clay, known for its low firing temperature and thermal shock resistance, is ideal for hand-building and rapid firing slip techniques that require quick drying and firing cycles, such as saggar firing or pit firing slips. Bentonite clay excels in slip casting and surface decoration due to its high plasticity and fine particle size, providing smooth, creamy slips that adhere well and allow for detailed textures or sgraffito work. For practical applications, choose Raku clay slips when working with reduction or hot-smoking slip effects, while Bentonite-based slips suit intricate mold work and layered decorative slips requiring strong suspension and smooth application.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Ceramic Slip
Selecting Raku clay for slip offers low shrinkage and excellent thermal shock resistance, ideal for raku firing techniques. Bentonite clay, rich in montmorillonite, provides superior plasticity and binding properties, enhancing slip adhesion and smooth application. Prioritize Raku clay when durability during rapid firing is essential and Bentonite clay for improved workability and slip consistency in wheel-thrown or hand-built ceramics.
Infographic: Raku clay vs Bentonite clay for Slip
 azmater.com
azmater.com