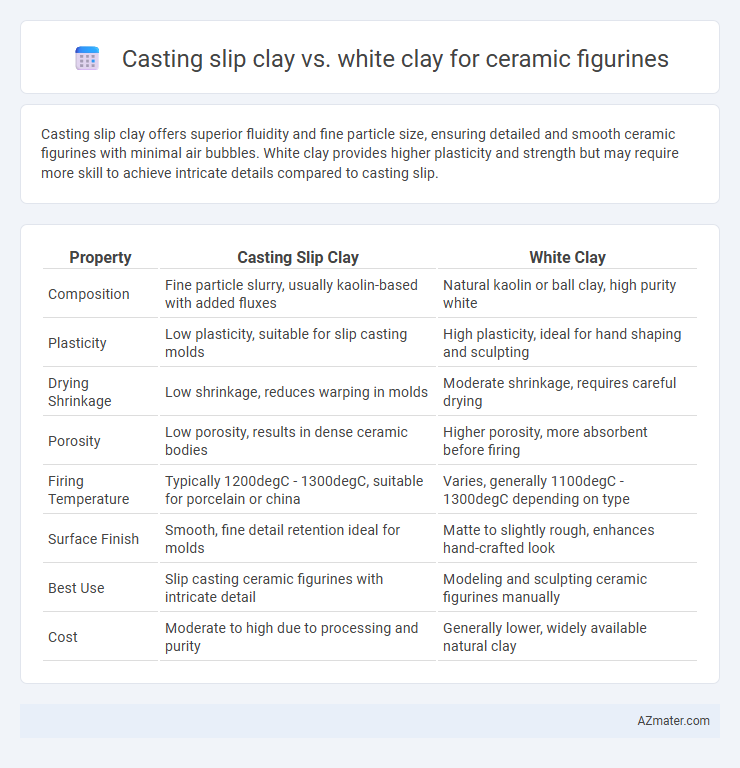
Casting slip clay offers superior fluidity and fine particle size, ensuring detailed and smooth ceramic figurines with minimal air bubbles. White clay provides higher plasticity and strength but may require more skill to achieve intricate details compared to casting slip.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Casting Slip Clay | White Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fine particle slurry, usually kaolin-based with added fluxes | Natural kaolin or ball clay, high purity white |
| Plasticity | Low plasticity, suitable for slip casting molds | High plasticity, ideal for hand shaping and sculpting |
| Drying Shrinkage | Low shrinkage, reduces warping in molds | Moderate shrinkage, requires careful drying |
| Porosity | Low porosity, results in dense ceramic bodies | Higher porosity, more absorbent before firing |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 1200degC - 1300degC, suitable for porcelain or china | Varies, generally 1100degC - 1300degC depending on type |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, fine detail retention ideal for molds | Matte to slightly rough, enhances hand-crafted look |
| Best Use | Slip casting ceramic figurines with intricate detail | Modeling and sculpting ceramic figurines manually |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to processing and purity | Generally lower, widely available natural clay |
Introduction to Ceramic Figurines: Casting Slip Clay vs White Clay
Casting slip clay offers a fluid consistency ideal for intricate molds and fine details in ceramic figurines, ensuring a smooth surface finish and high replicability. White clay, often denser and more plastic, provides durability and a solid texture, making it suitable for hand-sculpted or less detailed figurines. Selecting between casting slip clay and white clay depends on the desired detail, texture, and production method of the ceramic figurine.
Composition and Properties: Casting Slip Clay vs White Clay
Casting slip clay is a liquid mixture of clay and water primarily composed of fine particles that ensure smooth flow and filling of molds, offering high plasticity and minimal shrinkage when fired. White clay, often containing kaolin as its major component, features a coarser particle size, higher refractory properties, and produces a denser, more durable ceramic body with a bright white finish. The fine particle suspension in casting slip optimizes mold casting precision, while white clay's mineral composition enhances strength and whiteness in ceramic figurines.
Workability and Handling Differences
Casting slip clay offers superior fluidity and smooth consistency, making it ideal for detailed molds and fine surface textures in ceramic figurines. White clay, in contrast, tends to be thicker and more plastic, providing better control during hand modeling but requiring more effort to achieve intricate details. The workability of casting slip enables seamless filling of complex shapes, whereas white clay's handling properties favor sculpting and refining by hand.
Mold Compatibility and Techniques
Casting slip clay offers superior fluidity, making it ideal for detailed ceramic figurine molds with intricate textures and sharp edges, ensuring full mold cavity replication. White clay, while less fluid, provides better structural strength and is preferable for slab or hand-building techniques where mold compatibility is less critical. Understanding the drying shrinkage rates and compatibility with plaster molds is essential for both materials to prevent cracking and achieve fine surface resolution.
Shrinkage and Firing Behavior
Casting slip clay typically exhibits lower shrinkage rates around 5-7%, ensuring more dimensional accuracy during drying and firing, while white clay often shrinks more, approximately 7-10%, requiring careful allowance in design. White clay tends to mature at higher temperatures, often cone 5-6 (2167-2232degF), resulting in a denser, more vitrified surface suitable for detailed figurines, whereas casting slip clay matures at slightly lower temperatures, allowing for more flexibility in firing schedules. The differential firing behavior affects the final texture, durability, and color absorption, making casting slip ideal for intricate molds and white clay favorable for finished, high-quality ceramic pieces.
Surface Finish and Detail Reproduction
Casting slip clay offers a smoother surface finish and superior detail reproduction for ceramic figurines due to its fine particle size and fluid consistency, allowing intricate features to be captured with clarity. White clay, while providing a slightly coarser texture, results in a more matte surface and may require additional finishing for sharp detail. Choosing between the two depends on the desired final aesthetic, with casting slip clay favored for high-detail and polished figurines.
Strength and Durability: Material Comparison
Casting slip clay offers superior strength and durability for ceramic figurines due to its fine particle size and homogeneous texture, which reduces porosity and enhances structural integrity during firing. White clay, often kaolin-based, provides excellent whiteness and detail but tends to be more brittle and less resistant to mechanical stress compared to casting slip formulations. Choosing casting slip clay is ideal for figurines requiring enhanced toughness and longevity, while white clay suits applications prioritizing aesthetic purity over robust durability.
Glazing and Coloring Outcomes
Casting slip clay offers a smooth, fine-grained surface ideal for detailed glazing, allowing colors to appear vibrant and uniform on ceramic figurines due to its consistent texture and lower porosity. White clay, often denser and less refined, can result in less predictable glaze absorption, causing colors to sometimes appear muted or uneven, but it provides a traditional aesthetic favored for earthy, natural finishes. Both clays interact differently with glazing compounds, impacting the final hue intensity and surface gloss, making selection critical based on desired visual and tactile outcomes.
Cost and Accessibility: Slip Clay vs White Clay
Casting slip clay offers a cost-effective solution for ceramic figurine production due to its liquid form, enabling easy mold filling and minimal waste, which reduces material expenses. White clay, often firmer and more refined, tends to be pricier and less readily available in bulk quantities, impacting overall accessibility for artists and manufacturers. The widespread availability and economical pricing of slip clay make it a preferred choice for large-scale or budget-conscious ceramic projects.
Best Uses: Choosing the Right Clay for Ceramic Figurines
Casting slip clay is ideal for detailed ceramic figurines due to its fine particle size and smooth texture, allowing precise molds and intricate designs. White clay, known for its durability and strength after firing, is best suited for larger or structural figurines that require robustness and a clean, bright finish. Selecting casting slip clay enhances fine detail work, while white clay offers superior support and a classic aesthetic for ceramic figurines.
Infographic: Casting slip clay vs White clay for Ceramic figurine
 azmater.com
azmater.com