China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, offers excellent filtration and adsorption properties for oil purification, effectively removing impurities and color contaminants. Smectite clay, known for its high swelling capacity and cation exchange properties, provides superior absorption of polar compounds and heavy metals, making it highly efficient for deep oil refining processes.
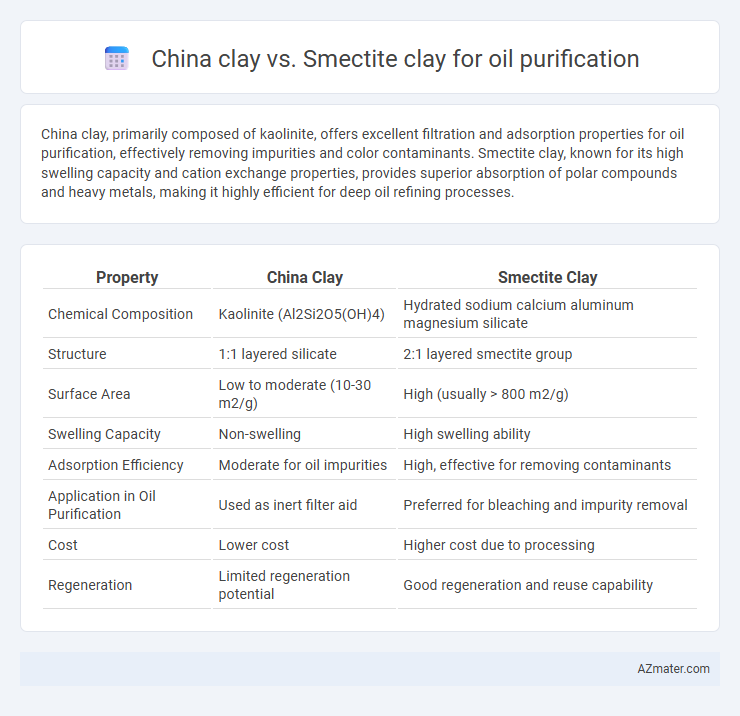
Table of Comparison
| Property | China Clay | Smectite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) | Hydrated sodium calcium aluminum magnesium silicate |
| Structure | 1:1 layered silicate | 2:1 layered smectite group |
| Surface Area | Low to moderate (10-30 m2/g) | High (usually > 800 m2/g) |
| Swelling Capacity | Non-swelling | High swelling ability |
| Adsorption Efficiency | Moderate for oil impurities | High, effective for removing contaminants |
| Application in Oil Purification | Used as inert filter aid | Preferred for bleaching and impurity removal |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to processing |
| Regeneration | Limited regeneration potential | Good regeneration and reuse capability |
Introduction to Clay Types in Oil Purification
China clay and smectite clay are commonly used in oil purification due to their unique adsorptive properties. China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, offers excellent filtration and impurity removal but has limited swelling capacity. Smectite clay, known for its high cation exchange capacity and swelling potential, enhances the adsorption of impurities and heavy metals, making it more effective in deep oil refining processes.
Chemical Structure: China Clay vs Smectite Clay
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite with a 1:1 layer silicate structure, features a simple tetrahedral-octahedral lattice providing low cation exchange capacity, which limits its adsorption capabilities in oil purification. Smectite clay, characterized by a 2:1 layer structure with expandable interlayers and high cation exchange capacity, offers superior adsorption and swelling properties essential for removing impurities and contaminants in oil refining processes. The distinct chemical composition and structural differences between kaolinite-dominant China clay and interlayer-expanding smectite clays critically influence their effectiveness in oil purification applications.
Key Properties Relevant to Oil Purification
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, exhibits low cation exchange capacity (CEC) and moderate surface area, making it effective in adsorbing impurities but less efficient in oil purification compared to smectite clays. Smectite clay, such as bentonite, features high CEC, significant swelling capacity, and a larger surface area, enhancing its ability to remove contaminants, moisture, and polar compounds from crude oil. The superior adsorption and ion exchange properties of smectite clays result in more efficient oil purification and extended catalyst life during refining processes.
Adsorption Capacity Comparison
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, exhibits moderate adsorption capacity for oil purification due to its low cation exchange capacity and limited surface area. Smectite clay, with its expansive layered structure and high cation exchange capacity often exceeding 80 meq/100g, demonstrates superior adsorption performance by effectively capturing oil molecules and impurities. The significantly higher surface area of smectite, sometimes over 600 m2/g compared to around 10-30 m2/g for china clay, enhances its oil adsorption efficiency, making smectite the preferred choice for oil purification applications.
Performance in Removing Impurities
China clay demonstrates moderate effectiveness in oil purification by adsorbing polar compounds and fine impurities, while smectite clay exhibits superior performance due to its high cation-exchange capacity and expansive surface area, enabling enhanced removal of contaminants such as trace metals, moisture, and color bodies. The layered structure and swelling properties of smectite clay facilitate deeper penetration and better retention of impurities compared to the relatively inert kaolinite structure of china clay. Consequently, smectite clay is preferred in industrial applications for achieving higher purity levels and improved stability in refined oils.
Regeneration and Reusability of Both Clays
China clay, primarily kaolinite, exhibits moderate regeneration capacity in oil purification through thermal treatment but tends to experience gradual loss in adsorption efficiency after multiple cycles. Smectite clay, due to its higher cation exchange capacity and swelling properties, demonstrates superior regeneration and reusability by effectively desorbing impurities via chemical or thermal methods, maintaining consistent oil purification performance over repeated uses. Comparative studies highlight smectite's enhanced durability and cost-effectiveness in oil purification applications, emphasizing its advantage for sustainable industrial processes.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
China clay offers a lower raw material cost compared to smectite clay, making it a more budget-friendly option in oil purification processes. Smectite clay, though more expensive, delivers superior adsorption capacity and regeneration potential, which can reduce overall operational costs by extending filter life and improving oil quality. Evaluating total cost-effectiveness requires balancing initial expenditure with long-term performance efficiency and maintenance savings.
Environmental Impact of Each Clay
China clay, also known as kaolin, exhibits lower environmental toxicity and generates less waste during oil purification compared to smectite clay due to its inert chemical properties and minimal swelling behavior. Smectite clay, with its high cation-exchange capacity and swelling potential, can lead to more significant environmental challenges, including increased water usage and disposal concerns from contaminant-laden sludge. The biodegradability and regeneration potential of kaolin further reduce its ecological footprint, making it a more sustainable choice in oil purification applications.
Industrial Applications and Suitability
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite, offers excellent adsorptive properties and fine particle size distribution, making it suitable for oil purification processes requiring mild bleaching and minimal chemical activity. Smectite clay, known for its high swelling capacity and cation exchange capacity, provides superior adsorption of impurities and heavy metals, proving effective in industrial oil refining where aggressive bleaching and contaminant removal are essential. The choice between China clay and Smectite clay depends on specific industrial applications, with China clay favored for delicate oils and Smectite clay preferred in heavy-duty oil purification due to its higher reactivity and adsorption efficiency.
Summary: Choosing the Optimal Clay for Oil Purification
China clay, known for its high purity and fine particle size, excels in oil purification by effectively removing impurities and color bodies. Smectite clay offers superior adsorption properties due to its layered structure, enhancing the removal of polar contaminants and moisture from oils. Selecting the optimal clay depends on the specific oil type and desired purity level, with China clay favored for refining edible oils and smectite clay preferred in industrial oil purification for higher contaminant adsorption.
Infographic: China clay vs Smectite clay for Oil purification
 azmater.com
azmater.com