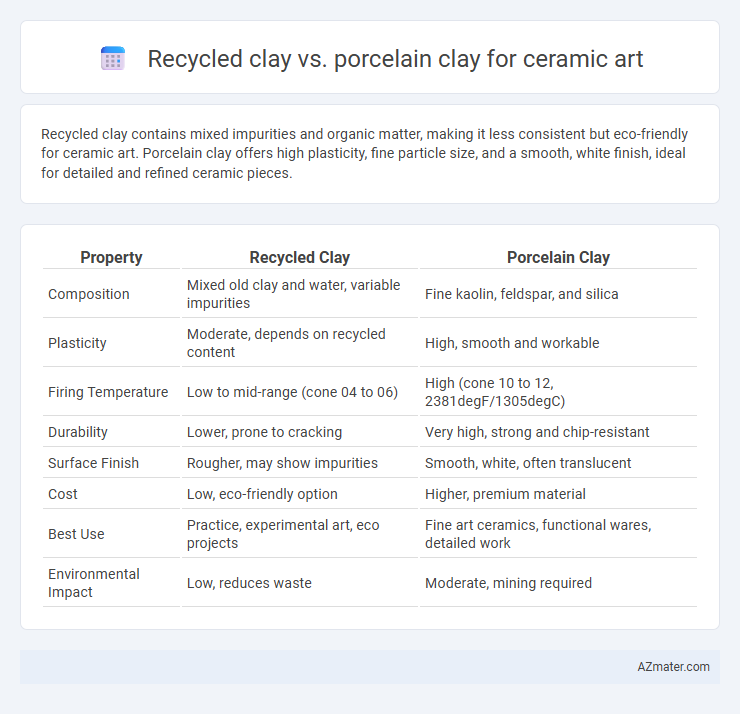
Recycled clay contains mixed impurities and organic matter, making it less consistent but eco-friendly for ceramic art. Porcelain clay offers high plasticity, fine particle size, and a smooth, white finish, ideal for detailed and refined ceramic pieces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Mixed old clay and water, variable impurities | Fine kaolin, feldspar, and silica |
| Plasticity | Moderate, depends on recycled content | High, smooth and workable |
| Firing Temperature | Low to mid-range (cone 04 to 06) | High (cone 10 to 12, 2381degF/1305degC) |
| Durability | Lower, prone to cracking | Very high, strong and chip-resistant |
| Surface Finish | Rougher, may show impurities | Smooth, white, often translucent |
| Cost | Low, eco-friendly option | Higher, premium material |
| Best Use | Practice, experimental art, eco projects | Fine art ceramics, functional wares, detailed work |
| Environmental Impact | Low, reduces waste | Moderate, mining required |
Introduction to Recycled Clay and Porcelain Clay
Recycled clay, derived from previously fired or unused clay scraps, offers an eco-friendly option for ceramic artists by reducing waste and conserving raw materials. Porcelain clay, characterized by its fine, white, and high-kaolin content, provides a smooth texture and high strength, ideal for delicate and refined ceramic art pieces. Understanding the differences in composition, plasticity, and firing temperatures between recycled clay and porcelain clay is essential for selecting the appropriate material for specific artistic techniques and finished ceramic qualities.
Composition Differences: Recycled vs Porcelain Clay
Recycled clay contains a blend of previously fired and unfired clay particles with variable impurities, resulting in less uniform mineral composition compared to porcelain clay, which is primarily composed of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz for a fine, white, and smooth texture. Porcelain clay's high kaolin content provides superior plasticity and strength, enabling delicate and high-fired ceramics with minimal porosity, whereas recycled clay often includes grog or sand to reduce shrinkage and improve workability. The compositional differences directly impact firing temperature, durability, and surface finish, with porcelain requiring higher firing temperatures (around 1200-1400degC) to achieve vitrification, while recycled clay may mature at lower temperatures but often yields less refined results.
Workability and Handling in Ceramic Art
Recycled clay offers a more pliable and forgiving texture, making it ideal for beginners and projects requiring frequent reshaping, while porcelain clay demands precision due to its fine, smooth consistency which can be less tolerant of mistakes. Porcelain's higher plasticity and finer particle size allow for delicate detailing and a refined surface finish but require careful handling to avoid cracking during drying and firing. Recycled clay tends to have variable impurities which can affect consistency, but its robust nature provides easier manipulation during the forming and trimming stages of ceramic art.
Firing Temperatures and Outcomes
Recycled clay typically fires at lower temperatures between Cone 04 (about 1940degF or 1060degC) and Cone 06 (around 1828degF or 998degC), often resulting in more porous and less vitrified ceramic art pieces. Porcelain clay requires higher firing temperatures, generally ranging from Cone 9 to Cone 11 (around 2300degF to 2381degF or 1260degC to 1305degC), producing dense, vitreous, and highly translucent ceramics with superior strength. The choice between recycled clay and porcelain clay significantly impacts the final texture, durability, and aesthetic qualities of the artwork based on their distinct firing protocols.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Recycled clay often contains impurities and inconsistent particle sizes, resulting in lower durability and reduced strength compared to porcelain clay, which is known for its fine, refined texture and high mechanical resistance. Porcelain clay undergoes higher firing temperatures, creating a vitrified, non-porous surface that enhances its structural integrity and longevity in ceramic art. While recycled clay offers eco-friendly benefits, porcelain clay remains the preferred choice for artworks requiring superior strength and long-lasting durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycled clay significantly reduces environmental impact by reusing materials and minimizing landfill waste, conserving natural resources compared to porcelain clay, which typically requires extensive mining and high energy consumption during production. The sustainable use of recycled clay supports circular economy principles by lowering carbon emissions and water usage associated with raw clay extraction and processing. While porcelain clay offers superior durability and translucency, recycled clay remains a preferred choice in eco-conscious ceramic art for its reduced ecological footprint and resource efficiency.
Surface Texture and Finish Quality
Recycled clay often contains impurities and varied particle sizes, resulting in a rougher surface texture that can add a rustic, tactile quality to ceramic art. Porcelain clay, known for its fine, dense composition, produces a smooth, glass-like finish with high translucency and a refined, polished appearance. Artists seeking a high-quality, delicate finish typically prefer porcelain clay, while recycled clay offers unique, textured effects ideal for experimental or eco-conscious projects.
Cost Considerations for Artists
Recycled clay typically offers significant cost savings for artists due to its lower price and reduced waste, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale or experimental projects. Porcelain clay, while more expensive, provides a finer texture and higher durability, often justifying the investment for professional artists aiming for precision and high-quality finishes. Understanding the balance between cost and desired artistic outcome helps ceramicists select the appropriate clay type for their specific needs.
Suitability for Different Ceramic Techniques
Recycled clay is ideal for hand-building and sculptural techniques due to its coarse texture and variable composition, offering greater workability and reduced cost for experimental projects. Porcelain clay, characterized by its fine particle size and high plasticity, excels in wheel-throwing and intricate detailing, providing a smooth surface and translucency after firing. Artists selecting clay should consider the firing temperature, shrinkage rate, and desired finish, as porcelain requires precise kiln control while recycled clay offers more flexibility for mixed media and textured designs.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Art Practice
Recycled clay offers an eco-friendly option with a coarser texture and variable composition, ideal for experimental or large-scale ceramic art projects. Porcelain clay features a smooth, fine grain with high plasticity and translucency, making it perfect for delicate, detailed work and refined finishes. Artists should consider their desired aesthetic, firing temperature, and workability when selecting between recycled and porcelain clay to best support their creative process.
Infographic: Recycled clay vs Porcelain clay for Ceramic art
 azmater.com
azmater.com