Engineered clay offers consistent texture and enhanced plasticity, making it ideal for detailed pottery work, while stoneware clay provides higher durability and a natural, rustic finish. Choosing between engineered and stoneware clay depends on the desired pottery strength and aesthetic.
Table of Comparison
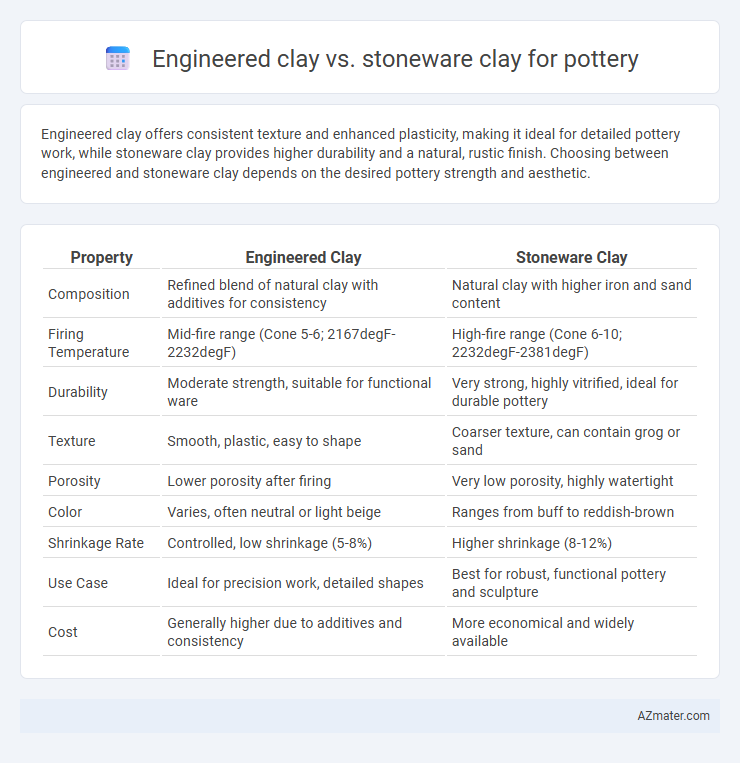
| Property | Engineered Clay | Stoneware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Refined blend of natural clay with additives for consistency | Natural clay with higher iron and sand content |
| Firing Temperature | Mid-fire range (Cone 5-6; 2167degF-2232degF) | High-fire range (Cone 6-10; 2232degF-2381degF) |
| Durability | Moderate strength, suitable for functional ware | Very strong, highly vitrified, ideal for durable pottery |
| Texture | Smooth, plastic, easy to shape | Coarser texture, can contain grog or sand |
| Porosity | Lower porosity after firing | Very low porosity, highly watertight |
| Color | Varies, often neutral or light beige | Ranges from buff to reddish-brown |
| Shrinkage Rate | Controlled, low shrinkage (5-8%) | Higher shrinkage (8-12%) |
| Use Case | Ideal for precision work, detailed shapes | Best for robust, functional pottery and sculpture |
| Cost | Generally higher due to additives and consistency | More economical and widely available |
Introduction to Engineered and Stoneware Clays
Engineered clay is a refined, customized material designed for consistent texture and workability, often incorporating additives that enhance plasticity and firing performance. Stoneware clay is a natural, durable clay that fires at high temperatures, producing a dense, vitrified ceramic ideal for functional pottery. Understanding the distinct compositions and firing properties of engineered versus stoneware clays helps potters select the right medium for specific artistic and utilitarian purposes.
Composition Differences: Engineered vs Stoneware Clays
Engineered clay contains a balanced mixture of synthetic additives and natural clay minerals designed to enhance plasticity, reduce firing shrinkage, and improve workability, whereas stoneware clay primarily consists of natural minerals like kaolin, ball clay, feldspar, and silica, providing durability and high firing temperature resistance. The mineral composition of engineered clay often includes grog or other tempering materials to minimize warping, while stoneware relies on its inherent mineral structure to achieve strength and vitrification. These compositional differences affect the texture, firing range, and final properties critical for pottery applications.
Workability and Handling Properties
Engineered clay offers enhanced plasticity and uniform consistency, making it easier to shape and ideal for intricate pottery designs. Stoneware clay, known for its coarse texture and higher grog content, provides better strength and durability but requires more skillful handling to prevent cracking. The superior workability of engineered clay reduces drying time and warping, while stoneware demands careful moisture control during the forming process.
Firing Temperature Ranges and Effects
Engineered clay typically fires within a temperature range of 1,100degC to 1,200degC, producing a more uniform and durable ceramic body due to controlled composition and additives. Stoneware clay fires at higher temperatures, generally between 1,200degC and 1,300degC, resulting in a vitrified, dense, and non-porous finish ideal for functional pottery. The higher firing range of stoneware clay enhances its strength and water resistance, while engineered clay offers versatility and consistency across varied kiln environments.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Engineered clay offers enhanced durability and consistent strength due to its controlled composition and fewer impurities, making it ideal for intricate pottery projects requiring precision and resilience. Stoneware clay exhibits high strength and thermal shock resistance after firing, with a naturally robust structure suitable for functional ware and everyday use. While engineered clay provides uniformity and reduced shrinkage, stoneware's dense vitrification imparts superior toughness and chip resistance over time.
Color and Surface Finish Variations
Engineered clay offers highly controlled color consistency and uniform surface finishes due to precise mineral blending, ideal for vibrant or muted tones in pottery. Stoneware clay exhibits natural color variations ranging from earthy browns to grays, contributing to rustic aesthetics and organic surface textures. The surface finish of engineered clay can be flawlessly smooth or matte, while stoneware often develops unique glaze pooling and subtle texture differences after firing.
Suitability for Functional vs Decorative Pottery
Engineered clay offers precise consistency and is ideal for functional pottery due to its durability and reduced porosity, making it suitable for items like dinnerware and cookware. Stoneware clay, characterized by its natural texture and strength, is preferred for both functional and decorative pottery, offering versatility with aesthetic appeal and excellent thermal resistance. Functional pottery demands clay that withstands daily use and thermal stress, where engineered clay excels, while stoneware clay often enhances artistic expression in decorative pieces.
Glaze Compatibility and Performance
Engineered clay offers consistent particle size and chemical composition, enhancing glaze adherence and uniform firing results compared to natural stoneware clay. Stoneware clay's variable mineral content can lead to unpredictable glaze behavior, such as variations in color and texture after firing. Both clay types support high-temperature glazes, but engineered clay provides more reliable performance for complex glaze applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Engineered clay for pottery typically involves synthetic additives and processing methods that may increase environmental footprint due to energy consumption and chemical use, while stoneware clay is often naturally sourced with minimal alteration, promoting sustainability. Stoneware clay's durability and high firing temperature result in long-lasting pottery, reducing waste and resource demand. The choice between the two impacts carbon emissions and resource depletion, with stoneware offering a more eco-friendly option when sourced responsibly.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Pottery Project
Engineered clay offers uniform consistency and predictable firing results, making it ideal for beginners or projects requiring detailed precision, while stoneware clay provides greater durability and natural variations suited for functional pottery like mugs and bowls. Consider the firing temperature: engineered clay often fires at lower temperatures, saving energy, whereas stoneware requires higher temperatures for vitrification and strength. Choose engineered clay for smooth surfaces and fine detail, and opt for stoneware when durability and rustic appeal are priorities in your pottery project.
Infographic: Engineered clay vs Stoneware clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com