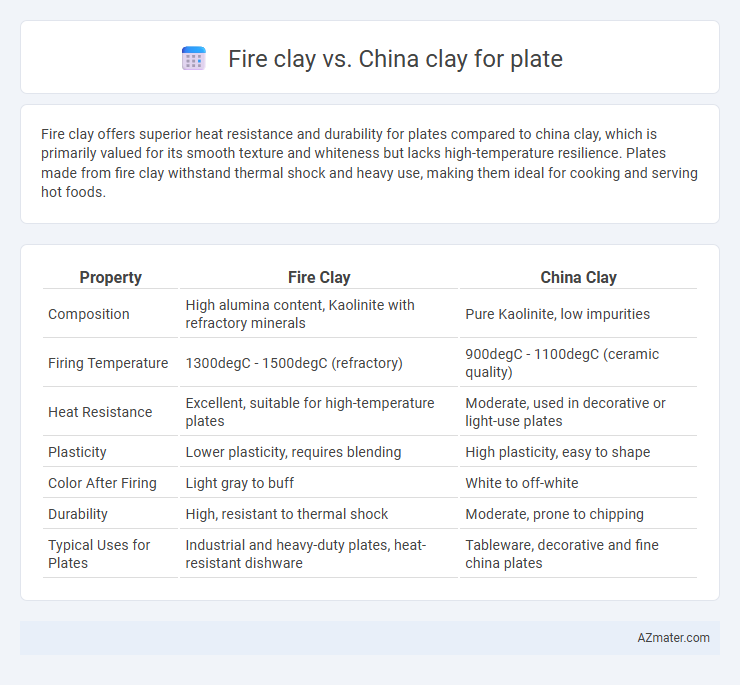
Fire clay offers superior heat resistance and durability for plates compared to china clay, which is primarily valued for its smooth texture and whiteness but lacks high-temperature resilience. Plates made from fire clay withstand thermal shock and heavy use, making them ideal for cooking and serving hot foods.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fire Clay | China Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High alumina content, Kaolinite with refractory minerals | Pure Kaolinite, low impurities |
| Firing Temperature | 1300degC - 1500degC (refractory) | 900degC - 1100degC (ceramic quality) |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent, suitable for high-temperature plates | Moderate, used in decorative or light-use plates |
| Plasticity | Lower plasticity, requires blending | High plasticity, easy to shape |
| Color After Firing | Light gray to buff | White to off-white |
| Durability | High, resistant to thermal shock | Moderate, prone to chipping |
| Typical Uses for Plates | Industrial and heavy-duty plates, heat-resistant dishware | Tableware, decorative and fine china plates |
Introduction to Fire Clay and China Clay
Fire clay, known for its high refractory properties and heat resistance, is primarily composed of kaolinite and is widely used in the manufacture of firebricks and ceramic plates that require durability under extreme temperatures. China clay, also referred to as kaolin, is a fine, white clay primarily used in the production of fine china and porcelain plates due to its purity, plasticity, and whiteness after firing. The key difference lies in fire clay's ability to withstand higher temperatures without deforming, making it ideal for industrial applications, while china clay is preferred for aesthetic and delicate tableware.
Chemical Composition Differences
Fire clay contains higher amounts of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and silica (SiO2), contributing to its refractory properties and heat resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature applications like plates used in kilns. China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), has a higher hydroxyl content and lower impurities, resulting in a smoother texture and better plasticity for fine ceramics and delicate plate finishes. The chemical composition differences significantly affect their thermal stability and workability, with fire clay suited for durability under heat and china clay preferred for aesthetic quality and ease of shaping.
Physical Properties Comparison
Fire clay exhibits higher refractory strength and greater thermal shock resistance compared to China clay, making it ideal for high-temperature applications in plate manufacturing. China clay, or kaolin, has a finer particle size and lower plasticity, resulting in smoother, more delicate plates but with less heat durability. The denser structure of fire clay plates enhances their mechanical strength, whereas China clay plates prioritize whiteness and surface finish.
Suitability for Plate Manufacturing
Fire clay is highly suitable for plate manufacturing due to its high refractory properties and excellent durability under high temperatures, ensuring robust and long-lasting ceramic plates. China clay, also known as kaolin, provides a fine, white, and smooth texture that enhances the aesthetic appeal and finish of plates but lacks the thermal resistance of fire clay. Combining fire clay with china clay can optimize strength and surface quality, making the mixture ideal for producing both practical and visually appealing ceramic plates.
Firing Temperatures and Performance
Fire clay, known for its higher alumina content, typically withstands firing temperatures ranging from 1200degC to 1400degC, making it ideal for heavy-duty ceramic plates that require enhanced thermal shock resistance and durability. In contrast, china clay (kaolin) fires at slightly lower temperatures, around 1100degC to 1300degC, producing smoother, finer ceramics with superior whiteness but less robustness under extreme heat. The choice between these clays impacts plate performance, with fire clay offering better structural integrity and china clay providing a more refined surface finish.
Workability and Shaping Characteristics
Fire clay offers excellent workability with a plastic texture that holds shape well during molding and firing, making it ideal for sturdy plates requiring durability. China clay, known for its fine particle size and smooth consistency, provides superior shaping characteristics, enabling intricate detail and a refined finish on delicate plates. Both clays balance plasticity and rigidity, but fire clay favors robustness while china clay excels in precision shaping.
Color and Aesthetic Outcomes
Fire clay offers a warm, earthy tone with natural reddish or buff hues that enhance rustic and traditional plate designs, while china clay provides a pure white, smooth surface ideal for vibrant glazes and intricate, detailed patterns. Plates made from fire clay exhibit a textured, matte finish that highlights natural imperfections, contributing to a handcrafted aesthetic. China clay's fine particle size enables brilliant translucency and a polished finish, making it perfect for modern, sleek, and brightly colored ceramic plates.
Durability and Strength of Plates
Fire clay exhibits superior durability and strength compared to china clay, making it ideal for plates subjected to high temperatures and heavy use. Fire clay plates possess high refractory properties, withstanding thermal shock and mechanical stress without cracking. China clay plates are smoother and more refined but generally less resistant to impact and heat, limiting their durability in demanding environments.
Cost and Availability
Fire clay, known for its exceptional heat resistance and durability, generally costs more than China clay but offers better performance for high-temperature plate applications. China clay, or kaolin, is more widely available and less expensive, making it a cost-effective option for lower-temperature plates or decorative uses. Availability varies by region, with fire clay deposits being less common and often leading to higher shipping costs compared to abundant China clay.
Environmental Impact Considerations
Fire clay, known for its high refractoriness and durability, typically involves more intensive mining processes that can lead to significant habitat disruption and higher carbon emissions compared to china clay. China clay, or kaolin, extraction generally produces less environmental degradation due to its softer nature and often involves less energy-intensive processing, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing china clay for plates can contribute to reduced environmental footprints, particularly in terms of land disturbance and energy consumption during manufacturing.
Infographic: Fire clay vs China clay for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com