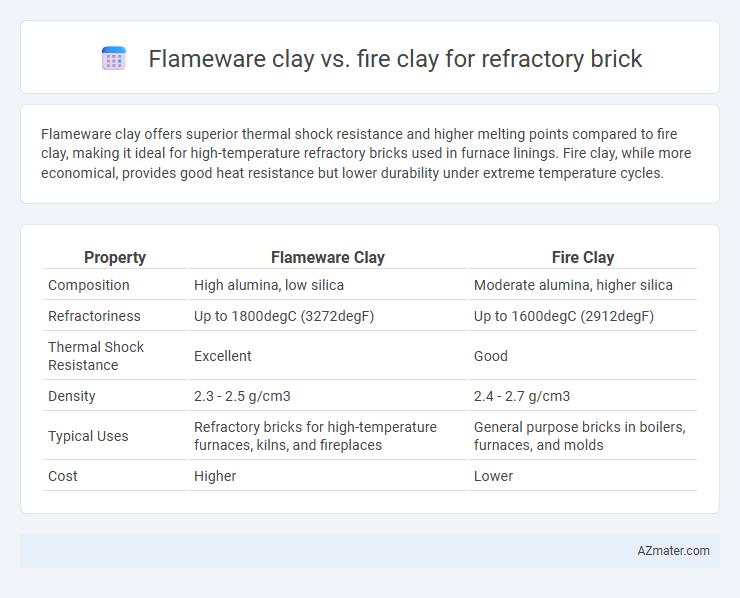
Flameware clay offers superior thermal shock resistance and higher melting points compared to fire clay, making it ideal for high-temperature refractory bricks used in furnace linings. Fire clay, while more economical, provides good heat resistance but lower durability under extreme temperature cycles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Flameware Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High alumina, low silica | Moderate alumina, higher silica |
| Refractoriness | Up to 1800degC (3272degF) | Up to 1600degC (2912degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Density | 2.3 - 2.5 g/cm3 | 2.4 - 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Typical Uses | Refractory bricks for high-temperature furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces | General purpose bricks in boilers, furnaces, and molds |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Refractory Bricks
Refractory bricks, essential for withstanding high temperatures in furnaces and kilns, are primarily composed of materials like Flameware clay and Fire clay. Flameware clay offers enhanced thermal shock resistance and durability at extreme temperatures, making it suitable for high-stress environments. Fire clay provides excellent heat retention and resistance to chemical corrosion, commonly used in industrial applications requiring long-lasting thermal insulation.
What is Flameware Clay?
Flameware clay is a type of refractory clay specifically formulated to withstand rapid temperature changes and intense thermal shock, making it ideal for lining high-temperature industrial furnaces and kilns. This clay exhibits excellent resistance to cracking and deformation at temperatures exceeding 1400degC, which differentiates it from standard fire clay that typically endures slightly lower temperatures up to 1300degC. Its unique mineral composition and fine particle size contribute to superior thermal stability, improved mechanical strength, and enhanced durability under extreme heating and cooling cycles.
What is Fire Clay?
Fire clay is a highly refractory material composed primarily of hydrous aluminum silicates, capable of withstanding temperatures above 1,500degC, making it ideal for manufacturing refractory bricks used in furnaces and kilns. It possesses excellent thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and resistance to chemical attack from slags and fluxes encountered in high-temperature industrial processes. Compared to flameware clay, fire clay offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, contributing to longer service life in demanding refractory applications.
Key Composition Differences
Flameware clay primarily contains high levels of alumina (Al2O3) and low silica content, enhancing its thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength in refractory bricks. Fire clay features a balanced mix of alumina, silica, and kaolin, with higher silica and fluxing agents, providing better plasticity but lower refractory temperature tolerance compared to flameware clay. The key composition difference lies in alumina concentration, where flameware clay ranges between 35-45% alumina, while fire clay typically contains 20-30% alumina, making flameware more suitable for high-temperature furnace linings.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Flameware clay exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to fire clay, withstanding temperatures up to 1,800degC, making it ideal for high-temperature refractory brick applications. Fire clay typically endures temperatures around 1,500degC to 1,700degC, offering adequate resistance for less extreme thermal environments. The higher alumina content in flameware clay enhances its thermal stability and resistance to deformation under intense heat.
Performance in High-Temperature Applications
Flameware clay demonstrates superior thermal shock resistance and higher refractoriness compared to traditional fire clay, making it ideal for extreme high-temperature applications above 1500degC. Its dense microstructure ensures enhanced mechanical strength and durability under rapid temperature fluctuations, outperforming fire clay bricks typically limited to around 1400degC. This performance advantage makes flameware clay bricks the preferred choice for advanced furnaces, kilns, and incinerators requiring prolonged exposure to intense heat.
Durability and Longevity
Flameware clay offers superior durability due to its high alumina content, enhancing resistance to thermal shock and rapid temperature changes in refractory bricks. Fire clay, while also heat-resistant, contains more impurities, resulting in slightly lower lifespan under extreme conditions compared to Flameware. The longevity of refractory bricks made from Flameware clay typically exceeds that of fire clay bricks, making it ideal for applications demanding sustained high-temperature exposure and mechanical stress.
Workability and Shaping Properties
Flameware clay exhibits superior workability and shaping properties compared to fire clay, allowing for easier molding and forming into precise refractory brick shapes. Its finer particle size and plasticity enhance the ability to create intricate designs without cracking during drying. Fire clay, although durable at high temperatures, tends to be less plastic, resulting in more challenges during shaping and increased risk of deformation under mechanical stress.
Cost and Availability
Flameware clay offers a cost-effective solution with moderate availability, suited for less extreme refractory applications where budget constraints are critical. Fire clay, known for its higher alumina content and superior heat resistance, tends to be more expensive but widely available from industrial suppliers specializing in high-temperature materials. Choosing between these clays depends on balancing cost considerations against performance requirements and local material supply conditions.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Project
Flameware clay offers high thermal shock resistance and exceptional durability, making it ideal for applications exposed to rapid temperature changes in refractory bricks. Fire clay provides excellent heat retention and structural stability at high temperatures, suitable for consistent, long-duration heat environments. Selecting the right clay depends on your project's specific thermal demands and mechanical stresses, with Flameware clay preferred for dynamic heat cycles and fire clay for steady, high-heat conditions.
Infographic: Flameware clay vs Fire clay for Refractory brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com