3D printer clay offers precise, customizable shaping with rapid prototyping capabilities, while earthenware clay provides natural texture and traditional firing properties ideal for durable, handcrafted sculptures. Both materials serve distinct artistic purposes depending on detail accuracy and finishing requirements.
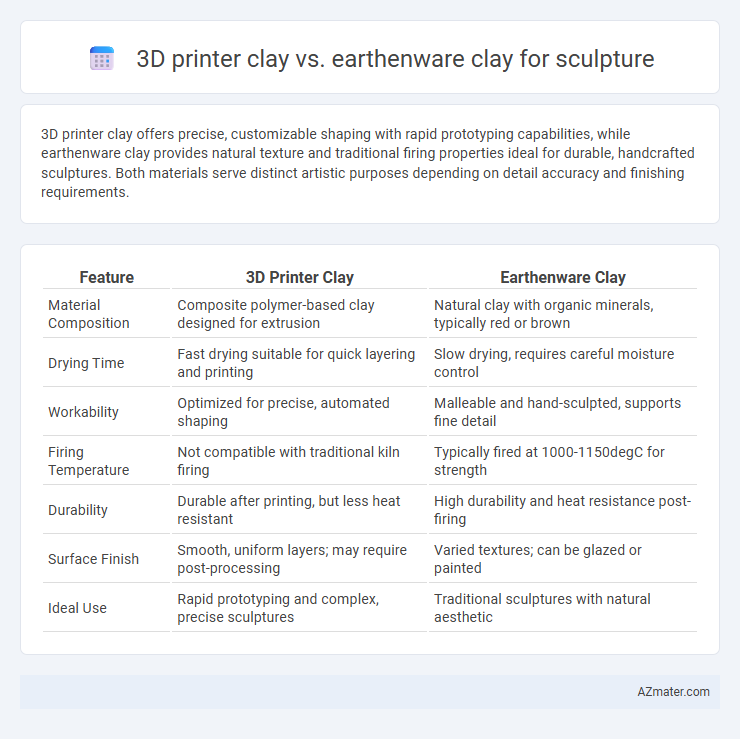
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Composite polymer-based clay designed for extrusion | Natural clay with organic minerals, typically red or brown |
| Drying Time | Fast drying suitable for quick layering and printing | Slow drying, requires careful moisture control |
| Workability | Optimized for precise, automated shaping | Malleable and hand-sculpted, supports fine detail |
| Firing Temperature | Not compatible with traditional kiln firing | Typically fired at 1000-1150degC for strength |
| Durability | Durable after printing, but less heat resistant | High durability and heat resistance post-firing |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, uniform layers; may require post-processing | Varied textures; can be glazed or painted |
| Ideal Use | Rapid prototyping and complex, precise sculptures | Traditional sculptures with natural aesthetic |
Introduction to 3D Printer Clay and Earthenware Clay
3D printer clay offers precise layering and digital customization, enabling artists to create intricate sculptures with consistent detail and reduced material waste. Earthenware clay, a traditional medium, provides a porous, natural texture favored for hand-building and firing in low-temperature kilns, which yields rich, earthy tones. Understanding the distinct properties of both clays is essential for sculptors aiming to combine modern technology with classic craftsmanship in their artistic processes.
Material Composition: 3D Printer Clay vs Earthenware Clay
3D printer clay typically consists of a polymer-based composite that may include plasticizers and binders tailored for extrusion and layer adhesion, enabling precise, repeatable forms ideal for complex sculptures. Earthenware clay is a natural material primarily composed of kaolinite, quartz, and iron oxide, offering organic texture and plasticity suitable for hand-building and wheel-throwing techniques. The differing compositions impact drying, firing temperatures, and final durability, with 3D printer clay favoring fast prototyping and earthenware clay providing traditional, porous finishes after kiln firing.
Workability and Handling Differences
3D printer clay offers precise layer-by-layer construction, allowing intricate details with consistent texture and minimal manual shaping, making it ideal for complex sculptures requiring fine control. Earthenware clay, by contrast, provides more tactile feedback and flexibility during manual modeling but demands skillful handling to achieve smooth surfaces and intricate details, prone to cracking if mishandled. The workability of 3D printer clay favors digital design replication, while earthenware clay excels in traditional, hands-on sculpting with variable moisture content affecting its malleability.
Suitability for Sculptural Techniques
3D printer clay offers precise layering and intricate detailing ideal for complex sculptural techniques such as additive modeling and fine texturing, making it suitable for rapid prototyping. Earthenware clay excels in traditional hand-building methods like coiling, pinching, and slab construction, providing versatility and tactile control for artisans. While 3D printer clay supports digital design integration, earthenware clay allows for more spontaneous, direct manipulation, essential for expressive sculptural forms.
Surface Texture and Detailing Capabilities
3D printer clay offers precision in surface texture control and intricate detailing due to its digital design and layering process, enabling highly consistent finishes ideal for complex sculptures. Earthenware clay provides a naturally tactile texture with organic variations, allowing artists to manually shape and add unique surface nuances that emphasize hand-crafted qualities. While 3D printer clay excels in replicable fine details, earthenware clay supports more expressive, textured surfaces influenced by traditional sculpting techniques.
Drying Times and Shrinkage Comparison
3D printer clay typically exhibits faster drying times compared to traditional earthenware clay, enabling quicker project completion without extensive waiting periods. Earthenware clay undergoes more significant shrinkage during drying and firing processes, often ranging between 5-15%, while 3D printer clay formulations are engineered to minimize shrinkage, maintaining dimensional stability. The reduced shrinkage and accelerated drying of 3D printer clay make it ideal for intricate sculptures requiring high precision and minimal post-processing adjustment.
Firing Temperatures and Final Strength
3D printer clay typically requires lower firing temperatures, around 1000degC to 1100degC, resulting in moderate strength suitable for detailed prototypes and decorative sculptures. Earthenware clay fires at higher temperatures, typically between 1100degC and 1200degC, producing a more porous and less vitrified final product with moderate durability ideal for traditional sculptural applications. The final strength of earthenware is generally lower than stoneware or porcelain but offers greater workability and finish options compared to 3D printer clays.
Artistic Flexibility and Creative Potential
3D printer clay offers unparalleled artistic flexibility by enabling precise, intricate designs through digital modeling, allowing artists to experiment with complex forms that are difficult to achieve with traditional methods. Earthenware clay provides a tactile, hands-on experience that fosters organic creativity and allows for intuitive shaping and texturing, which can result in unique, expressive sculptures. Combining 3D printer clay's precision with earthenware clay's natural characteristics expands creative potential, offering artists a broader range of possibilities in sculptural art.
Cost and Accessibility for Sculptors
3D printer clay offers sculptors higher cost-efficiency due to reduced material waste and the ability to produce complex shapes with minimal manual labor, making it accessible for those with digital design skills. Earthenware clay, while generally less expensive upfront, requires more traditional tools and workspace, which can increase overall costs and limit accessibility for beginners or hobbyists. Sculptors must weigh the investment in 3D printing technology against the ready availability and tactile experience of earthenware clay.
Choosing the Best Clay for Your Sculpture Project
3D printer clay offers precise control and consistency, ideal for detailed sculptures requiring exact dimensions and smooth finishes, while earthenware clay provides a traditional, textured feel with greater natural variation suited for rustic or organic designs. Earthenware clay tends to be more porous and less durable after firing, making it better for decorative pieces, whereas 3D printer clay allows for repeatability and complex geometries through additive manufacturing. Assessing project goals, from fine detail to tactile quality, alongside firing methods and final use, determines whether 3D printer clay or earthenware clay best suits your sculpture.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Earthenware clay for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com