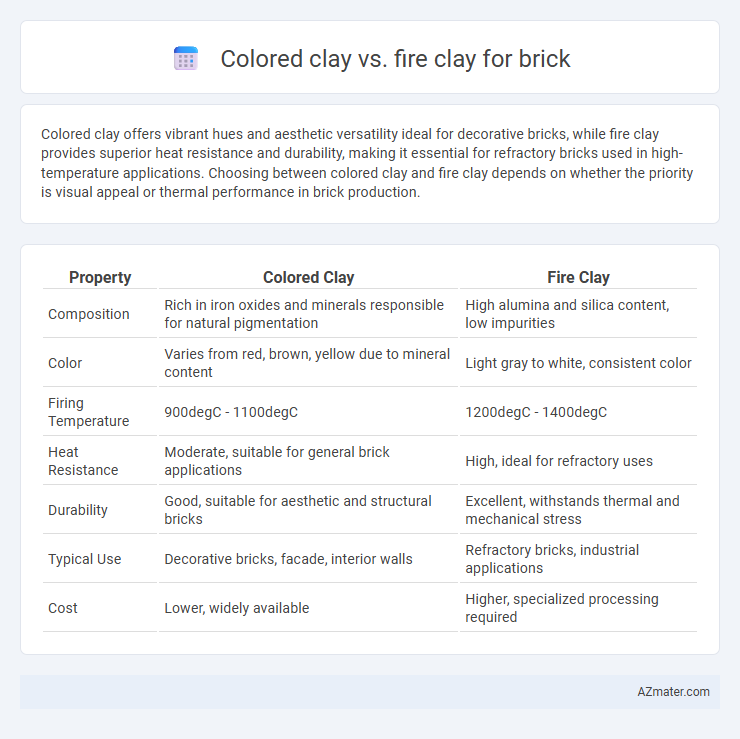
Colored clay offers vibrant hues and aesthetic versatility ideal for decorative bricks, while fire clay provides superior heat resistance and durability, making it essential for refractory bricks used in high-temperature applications. Choosing between colored clay and fire clay depends on whether the priority is visual appeal or thermal performance in brick production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Colored Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Rich in iron oxides and minerals responsible for natural pigmentation | High alumina and silica content, low impurities |
| Color | Varies from red, brown, yellow due to mineral content | Light gray to white, consistent color |
| Firing Temperature | 900degC - 1100degC | 1200degC - 1400degC |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, suitable for general brick applications | High, ideal for refractory uses |
| Durability | Good, suitable for aesthetic and structural bricks | Excellent, withstands thermal and mechanical stress |
| Typical Use | Decorative bricks, facade, interior walls | Refractory bricks, industrial applications |
| Cost | Lower, widely available | Higher, specialized processing required |
Introduction to Colored Clay and Fire Clay
Colored clay contains natural minerals that impart vibrant hues to bricks, enhancing aesthetic appeal and allowing for versatile architectural designs. Fire clay, characterized by its high refractory properties, is ideal for producing durable bricks that withstand extreme heat in industrial and kiln applications. Understanding the distinct mineral compositions and thermal resistances of colored clay and fire clay is essential for selecting the right material based on desired brick function and appearance.
Key Differences Between Colored Clay and Fire Clay
Colored clay exhibits vibrant hues due to its high iron oxide and mineral content, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of bricks, while fire clay contains higher amounts of alumina and silica, providing superior heat resistance and durability. Fire clay bricks can withstand temperatures above 1,500degC, making them ideal for refractory applications, whereas colored clay bricks are primarily used for decorative purposes in construction. The plasticity and firing temperature ranges also differ, with fire clay requiring higher kiln temperatures for strength and colored clay allowing for varied color finishes at lower temperatures.
Composition and Mineral Content
Colored clay contains higher amounts of iron oxides and other metal oxides such as manganese and chromium, which contribute to its vivid hues ranging from red to yellow and green. Fire clay has a dominant composition of kaolinite and high alumina content, typically containing 20-40% alumina (Al2O3) and low iron oxide levels, making it highly refractory and suitable for high-temperature applications. The mineral content in fire clay also includes quartz and mica, enhancing its thermal stability, while colored clay's diverse mineralogy affects its plasticity and firing color.
Color Variations and Aesthetic Appeal
Colored clay bricks offer a wide range of natural hues, including reds, yellows, and browns, achieved through varying mineral content and firing conditions, making them ideal for vibrant and diverse aesthetic applications. Fire clay bricks, known for their superior heat resistance, typically exhibit a more uniform, muted color palette, often in shades of tan or light brown, which lends a rustic and industrial aesthetic appeal. The choice between colored clay and fire clay bricks greatly influences the visual impact and design versatility of brickwork projects.
Thermal Resistance and Durability
Colored clay bricks offer moderate thermal resistance, effectively insulating buildings due to their dense composition and natural mineral content, making them suitable for temperate climates. Fire clay bricks, composed of refractory clays with high alumina content, provide superior thermal resistance and can withstand extreme temperatures up to 1,800degC, ideal for industrial applications like furnaces and kilns. In terms of durability, fire clay bricks exhibit exceptional resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, while colored clay bricks provide good weather resistance and long-lasting structural integrity in everyday construction.
Manufacturing Process and Firing Techniques
Colored clay bricks involve the use of naturally pigmented clays or added mineral oxides, requiring precise blending during the manufacturing process to achieve consistent hues, with firing temperatures generally ranging between 900degC and 1100degC to preserve the color integrity. Fire clay bricks, made from refractory clays rich in alumina and silica, undergo high-temperature firing at around 1400degC to 1600degC to enhance their heat resistance and structural strength, crucial for industrial applications. Manufacturing fire clay bricks demands controlled drying and firing cycles to prevent cracking, whereas colored clay bricks emphasize uniform pigment distribution and lower firing temperatures to maintain aesthetic quality.
Common Applications in Brick Making
Colored clay is primarily used for decorative bricks due to its natural pigmentation, providing vibrant hues without additional coatings. Fire clay is favored in refractory brick production, offering high thermal resistance essential in kilns, furnaces, and fireplaces. Both clays contribute distinct properties: colored clay enhances aesthetic appeal, while fire clay ensures structural durability under extreme heat.
Advantages of Colored Clay Bricks
Colored clay bricks offer superior aesthetic versatility with a wide range of natural hues that enhance architectural design without the need for additional painting or finishing. These bricks exhibit improved weather resistance and reduced fading, maintaining their vibrant color and structural integrity over time. Their high thermal mass also contributes to better energy efficiency by regulating indoor temperatures more effectively than traditional fire clay bricks.
Benefits of Fire Clay Bricks
Fire clay bricks offer superior heat resistance and durability compared to colored clay bricks, making them ideal for high-temperature applications such as furnaces and fireplaces. Their high alumina content enhances thermal stability and reduces deformation when exposed to extreme heat. Fire clay bricks also provide excellent insulating properties, improving energy efficiency and structural longevity.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Brick Project
Colored clay offers natural hues like red, yellow, and brown, ideal for aesthetic brick projects requiring vibrant, consistent tones without additional pigments. Fire clay provides superior heat resistance and durability, making it the preferred choice for structural bricks in high-temperature environments such as fireplaces or kilns. Selecting between colored and fire clay depends on your project's priority for either visual appeal or thermal performance.
Infographic: Colored clay vs Fire clay for Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com