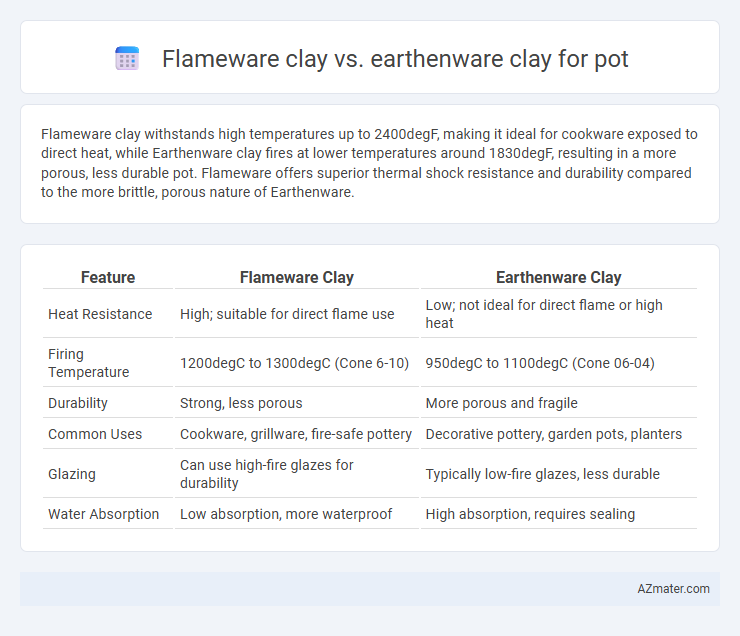
Flameware clay withstands high temperatures up to 2400degF, making it ideal for cookware exposed to direct heat, while Earthenware clay fires at lower temperatures around 1830degF, resulting in a more porous, less durable pot. Flameware offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability compared to the more brittle, porous nature of Earthenware.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flameware Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | High; suitable for direct flame use | Low; not ideal for direct flame or high heat |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC to 1300degC (Cone 6-10) | 950degC to 1100degC (Cone 06-04) |
| Durability | Strong, less porous | More porous and fragile |
| Common Uses | Cookware, grillware, fire-safe pottery | Decorative pottery, garden pots, planters |
| Glazing | Can use high-fire glazes for durability | Typically low-fire glazes, less durable |
| Water Absorption | Low absorption, more waterproof | High absorption, requires sealing |
Introduction to Flameware and Earthenware Clay
Flameware clay is a high-fire ceramic material designed to withstand extreme temperatures, making it ideal for cookware and functional pottery that requires durability and heat resistance. Earthenware clay, a low-fire ceramic, is porous and less durable but favored for decorative pottery and traditional artisan crafts due to its warm, natural texture. Understanding the firing temperature ranges--flameware typically matures between 1200degC and 1300degC, whereas earthenware fires at 1000degC to 1150degC--highlights their suitability for different pottery applications.
What is Flameware Clay?
Flameware clay is a high-fire ceramic material designed to withstand direct flame and extreme heat, making it ideal for functional cookware such as pots and baking dishes. Unlike earthenware clay, which is typically fired at lower temperatures and remains porous and less durable, flameware can endure thermal shock without cracking. This durability allows flameware pots to be used safely on stovetops, ovens, and even open flames, offering superior heat retention and resistance compared to traditional earthenware cookware.
What is Earthenware Clay?
Earthenware clay is a porous, low-fire clay typically fired between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, making it ideal for decorative pots and pottery that do not require water-tight durability without glazing. Unlike flameware clay, which is designed to withstand high temperatures and thermal shock for cooking or heating applications, earthenware is softer and more porous, lending a rustic appearance perfect for ornamental and traditional pottery. Its composition usually includes a higher amount of iron and other impurities, contributing to its characteristic reddish or brownish color after firing.
Key Differences Between Flameware and Earthenware
Flameware clay is specifically formulated to withstand direct flame and thermal shock, making it ideal for cookware like pots and baking dishes. Earthenware clay, by contrast, is more porous and less heat-resistant, often requiring glazing to prevent liquid absorption but is not suitable for high-temperature cooking. The key differences lie in flameware's enhanced durability and thermal stability, whereas earthenware is prized for its rustic aesthetic but limited heat tolerance.
Heat Resistance and Cooking Performance
Flameware clay is specifically formulated to withstand direct flame and high temperatures up to 1200degF, making it ideal for cooking vessels used on stovetops or open flames. Earthenware clay generally has lower heat resistance, typically up to 2100degF but is more porous and less durable under rapid temperature changes, which may affect performance in cooking applications. Flameware's dense composition ensures even heat distribution and reduces thermal shock, enhancing cooking performance and durability compared to earthenware.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Flameware clay, known for its high iron content and vitrification at higher firing temperatures, offers superior durability and resistance to thermal shock compared to earthenware clay, which is more porous and fired at lower temperatures. Earthenware's lower firing range (typically 1,000 to 1,150degC) results in less strength and shorter longevity, making it more susceptible to chipping and water absorption over time. Flameware pottery, often reaching durability similar to stoneware, is ideal for functional pots requiring long-lasting performance and resistance to wear.
Safety and Usability for Cookware
Flameware clay offers superior heat resistance and thermal shock durability compared to traditional Earthenware clay, making it safer and more reliable for cookware exposed to direct flames and high temperatures. Earthenware clay, while porous and less heat-resistant, typically requires glazing to prevent leaching of harmful substances, posing potential safety risks if not properly sealed. Flameware's non-porous nature and inherent durability enhance usability for cooking pots by ensuring even heat distribution and reducing the risk of cracking or contaminant absorption during food preparation.
Aesthetic Qualities and Finishes
Flameware clay offers a unique aesthetic with its naturally variegated textures and vibrant, flame-induced color patterns, creating visually striking pots with a rustic, earthy appeal. Earthenware clay provides a classic, smooth surface that readily absorbs glazes, resulting in bright, uniform finishes ideal for decorative pots with polished, glossy appearances. Both clays support distinct artistic expressions, where Flameware emphasizes organic, unpredictable beauty, and Earthenware highlights refined, controlled surface treatments.
Cost and Availability
Flameware clay generally costs more than earthenware clay due to its higher firing temperature and enhanced durability, making it ideal for cookware and pots exposed to direct heat. Earthenware clay is widely available and more affordable, but it requires lower firing temperatures and tends to be more porous and less heat-resistant. For budget-conscious potters, earthenware offers easy access and cost efficiency, while flameware provides long-term value through superior strength and heat tolerance.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Pots
Flameware clay offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for pots exposed to high temperatures or direct flames, unlike earthenware clay which is more porous and less heat-tolerant. Earthenware clay typically fires at lower temperatures, resulting in more porous pots that require sealing to be waterproof, perfect for decorative or low-heat applications. Choosing between flameware and earthenware depends on the pot's functional requirements, with flameware preferred for cooking or high-heat use and earthenware suited for ornamental or indoor plants.
Infographic: Flameware clay vs Earthenware clay for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com