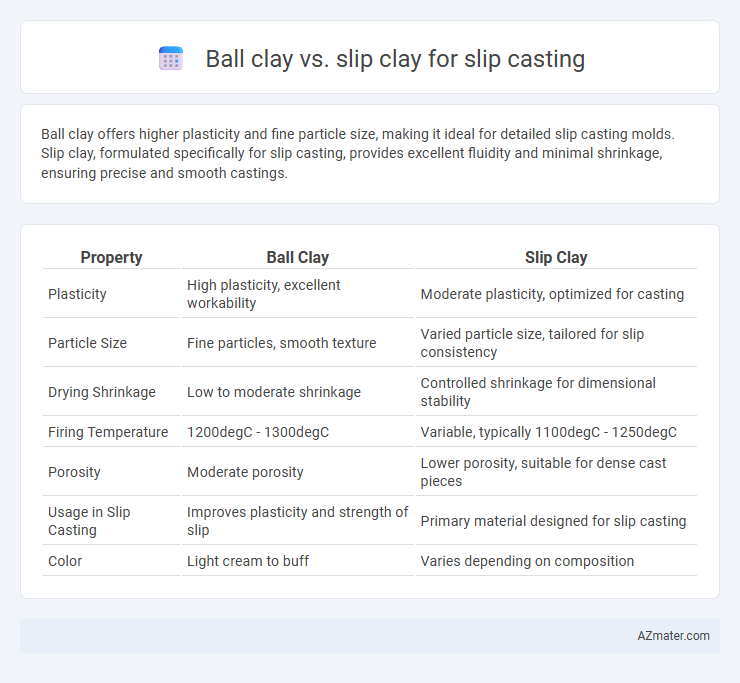
Ball clay offers higher plasticity and fine particle size, making it ideal for detailed slip casting molds. Slip clay, formulated specifically for slip casting, provides excellent fluidity and minimal shrinkage, ensuring precise and smooth castings.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ball Clay | Slip Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Plasticity | High plasticity, excellent workability | Moderate plasticity, optimized for casting |
| Particle Size | Fine particles, smooth texture | Varied particle size, tailored for slip consistency |
| Drying Shrinkage | Low to moderate shrinkage | Controlled shrinkage for dimensional stability |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC - 1300degC | Variable, typically 1100degC - 1250degC |
| Porosity | Moderate porosity | Lower porosity, suitable for dense cast pieces |
| Usage in Slip Casting | Improves plasticity and strength of slip | Primary material designed for slip casting |
| Color | Light cream to buff | Varies depending on composition |
Introduction to Ball Clay and Slip Clay
Ball clay is a highly plastic, fine-grained sedimentary clay containing kaolinite, mica, and quartz, known for its excellent workability and binding properties in ceramic formulations. Slip clay, specifically formulated as a liquid suspension of clay particles in water, is tailored for slip casting processes to achieve smooth pouring and uniform drying characteristics. Understanding the distinct physical and chemical properties of ball clay and slip clay is essential for optimizing slip casting performance and final product quality.
Key Properties of Ball Clay
Ball clay exhibits high plasticity, fine particle size, and excellent workability, making it ideal for slip casting due to its ability to form smooth, cohesive slips. Its low shrinkage and good green strength enhance the integrity of unfired ceramic pieces compared to slip clay, which may vary in plasticity and particle composition. The high kaolinite content in ball clay contributes to superior binding properties, ensuring precise mold filling and detailed surface finishes in ceramic production.
Key Properties of Slip Clay
Slip clay for slip casting is characterized by high plasticity, fine particle size, and excellent suspension stability, enabling smooth flow and consistent mold filling. It contains a controlled water content and deflocculants that reduce viscosity while maintaining workability, essential for precise casting. Unlike ball clay, which is denser and less refined, slip clay optimizes shrinkage rates and drying times to minimize warping and cracking in cast ceramics.
Differences in Plasticity and Workability
Ball clay exhibits higher plasticity due to its fine particle size and mineral composition, making it ideal for slip casting by providing excellent mold-filling ability and shape retention. Slip clay, while also suitable for slip casting, generally has lower plasticity but offers improved workability and reduced shrinkage during drying and firing. The choice between ball clay and slip clay depends on the desired balance between forming ease and final product stability in ceramic production.
Particle Size and Its Impact on Slip Casting
Ball clay features fine particles typically ranging from 0.5 to 5 microns, enhancing plasticity and green strength, which is crucial for slip casting precision. Slip clay, often containing a wider particle size distribution, provides a balance between fluidity and suspension stability necessary for smooth mold filling. The smaller particle size in ball clay improves slip casting by promoting better particle packing and reduced settling, resulting in a denser, more uniform cast.
Suitability for Slip Casting Applications
Ball clay offers excellent plasticity and fine particle size, making it highly suitable for slip casting by creating smooth, consistent slips that form detailed molds. Slip clay, engineered specifically for slip casting, provides optimal viscosity and drying characteristics to ensure minimal shrinkage and cracking during the casting process. Both clays excel in slip casting, but ball clay's natural plasticity is ideal for intricate shapes, while slip clay is preferred for improved processing control and faster production cycles.
Influence on Casting Rate and Strength
Ball clay offers finer particle size and higher plasticity, enhancing slip viscosity and resulting in a more controlled casting rate during slip casting. Slip clay, often coarser with lower plasticity, promotes faster water drainage, increasing the casting rate but potentially reducing the strength and uniformity of the cast piece. Optimizing the balance between ball clay and slip clay directly influences green strength and drying durability, crucial for achieving high-quality ceramic components.
Color and Firing Characteristics
Ball clay typically exhibits a creamy to off-white color with high plasticity and fires to a warm beige or light gray tone, making it ideal for porcelain and whiteware production. Slip clay, often formulated for slip casting, has a more neutral color and is designed to maintain stability during firing, reducing shrinkage and warping. The firing characteristics of slip clay emphasize smooth surface finish and translucency, while ball clay enhances strength and plasticity in the casting slip.
Common Uses in Ceramics Industry
Ball clay is favored in the ceramics industry for its plasticity and strength, making it ideal for shaping complex slip-cast molds and improving green strength. Slip clay, characterized by fine particles and smooth texture, is primarily used in slip casting to produce detailed, thin-walled ceramic products with excellent surface finishes. Both clays enhance the slip casting process, but ball clay contributes to durability during molding, while slip clay optimizes fluidity and detail replication.
Choosing the Right Clay for Slip Casting
Selecting the right clay for slip casting hinges on the specific properties of ball clay and slip clay. Ball clay offers excellent plasticity and fine particle size, making it suitable for detailed mold reproduction, while slip clay provides better workability and faster drying times due to its balanced composition. Understanding these differences helps optimize casting quality, ensuring the chosen clay meets the requirements of strength, shrinkage, and surface finish.
Infographic: Ball clay vs Slip clay for Slip casting
 azmater.com
azmater.com