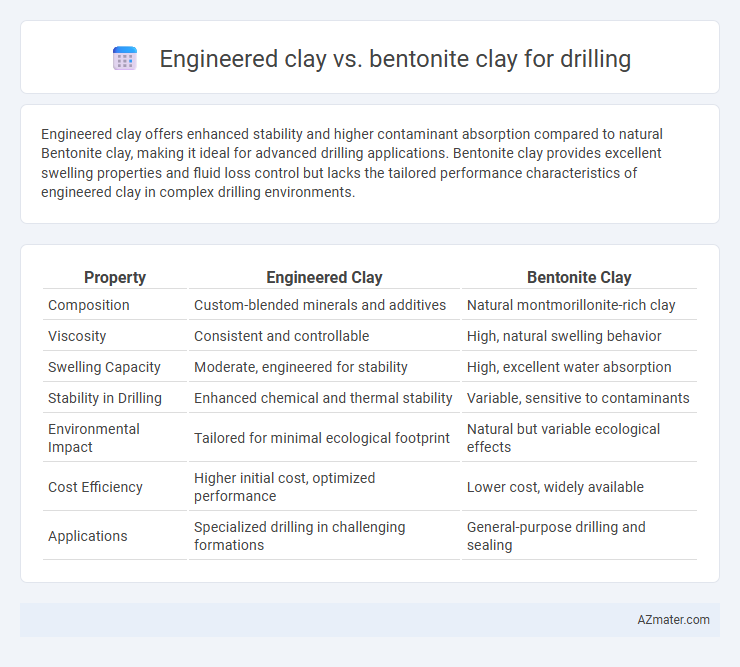
Engineered clay offers enhanced stability and higher contaminant absorption compared to natural Bentonite clay, making it ideal for advanced drilling applications. Bentonite clay provides excellent swelling properties and fluid loss control but lacks the tailored performance characteristics of engineered clay in complex drilling environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Engineered Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Custom-blended minerals and additives | Natural montmorillonite-rich clay |
| Viscosity | Consistent and controllable | High, natural swelling behavior |
| Swelling Capacity | Moderate, engineered for stability | High, excellent water absorption |
| Stability in Drilling | Enhanced chemical and thermal stability | Variable, sensitive to contaminants |
| Environmental Impact | Tailored for minimal ecological footprint | Natural but variable ecological effects |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost, optimized performance | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Specialized drilling in challenging formations | General-purpose drilling and sealing |
Introduction to Drilling-Grade Clays
Drilling-grade clays such as engineered clay and bentonite clay play crucial roles in drilling fluid formulations to enhance wellbore stability and minimize fluid loss. Engineered clay, often modified to improve rheological properties and contamination resistance, offers tailored performance for specific drilling conditions. Bentonite clay, primarily composed of montmorillonite, provides excellent swelling and thixotropic characteristics that facilitate efficient cuttings suspension and hole cleaning during rotary drilling operations.
What is Engineered Clay?
Engineered clay is a specially formulated drilling fluid additive designed to improve borehole stability and fluid loss control by enhancing the rheological properties of drilling muds. Unlike natural bentonite clay, engineered clay is chemically modified to offer superior swelling capacity, thermal stability, and hardness, making it more effective in high-temperature and high-pressure drilling environments. Its use in drilling operations results in enhanced wellbore integrity, reduced formation damage, and optimized drilling performance.
Understanding Bentonite Clay
Bentonite clay is a highly absorbent, swelling clay composed primarily of montmorillonite, making it essential for drilling mud due to its superior viscosity and fluid loss control properties. Engineered clay, while designed with specific additives to enhance performance, often lacks the natural swelling capacity and rheological balance of bentonite, limiting its effectiveness in stabilizing boreholes and sealing permeable formations. Understanding the mineralogical composition and hydration behavior of bentonite clay is critical for optimizing drilling fluid formulations and ensuring efficient, cost-effective drilling operations.
Composition Differences: Engineered vs Bentonite Clay
Engineered clay for drilling typically consists of a customized blend of minerals and additives designed to enhance specific properties such as viscosity, fluid loss control, and thermal stability, whereas bentonite clay is a natural, primarily montmorillonite-rich clay known for its high swelling capacity and thixotropic behavior. The compositional differences affect drilling performance: engineered clay formulations often include polymers, weighting agents, and chemical conditioners to optimize drilling fluid characteristics, while bentonite offers natural rheological properties and filtration control but may require modification for extreme conditions. These distinctions in mineralogy and additive inclusion lead to varied applications and efficiencies in drilling operations depending on geological and operational requirements.
Performance in Drilling Fluid Applications
Engineered clay offers enhanced rheological properties and improved thermal stability compared to bentonite clay, making it more effective in maintaining borehole stability and reducing fluid loss in drilling fluid applications. Bentonite clay, particularly sodium bentonite, provides excellent swelling capacity and viscosity but may suffer from decreased performance in high-temperature environments and saline conditions. Selecting engineered clay delivers superior suspension capabilities and higher resistance to contamination, optimizing drilling fluid performance under demanding downhole scenarios.
Rheological Properties Comparison
Engineered clay exhibits superior rheological properties compared to bentonite clay, offering enhanced shear thinning behavior and higher yield stress, which improves cuttings suspension during drilling operations. Bentonite clay tends to have higher viscosity at low shear rates but loses stability under high shear, leading to potential viscosity breakdown and reduced hole cleaning efficiency. The tailored particle size distribution and chemical modifications in engineered clay provide more consistent rheological performance, optimizing drilling fluid behavior for varying downhole conditions.
Filtration Control Capabilities
Engineered clay offers superior filtration control capabilities compared to Bentonite clay, as it is specifically formulated to maintain wellbore stability and reduce fluid loss in challenging drilling environments. Bentonite clay, while effective in creating a gel-like suspension and sealing formation pores, tends to have higher filtration rates and less control over fluid invasion in high-temperature or high-pressure conditions. Optimized engineered clays integrate additives that enhance viscosity and filter cake quality, resulting in improved wellbore integrity and reduced formation damage during drilling operations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Engineered clay offers enhanced stability and reduced leakage in drilling operations, minimizing environmental contamination compared to bentonite clay, which can swell excessively and disrupt ecosystems. Bentonite's natural swelling properties can lead to increased water usage and potential soil salinization, raising sustainability concerns in sensitive drilling areas. Utilizing engineered clay formulations with controlled rheological properties improves waste management and reduces ecological footprint, supporting more sustainable drilling practices.
Cost Considerations in Drilling Operations
Engineered clay offers tailored properties that can reduce overall drilling fluid formulation costs by enhancing performance and minimizing additives compared to standard bentonite clay. Bentonite clay remains a cost-effective and widely available option, but variability in quality and higher consumption rates can increase total expenses in prolonged drilling operations. Evaluating the balance between initial clay cost and long-term operational efficiency is crucial for optimizing drilling budgets.
Choosing the Right Clay: Key Factors to Consider
When selecting between engineered clay and bentonite clay for drilling applications, prioritize factors such as viscosity, swelling capacity, and filtration control to ensure optimal borehole stability. Engineered clay offers tailored rheological properties and enhanced chemical resistance, making it suitable for complex drilling environments, whereas bentonite clay provides excellent natural swelling and sealing capabilities critical for wellbore integrity. Evaluating site-specific geological conditions, fluid compatibility, and environmental regulations will guide the decision to maximize drilling efficiency and minimize formation damage.
Infographic: Engineered clay vs Bentonite clay for Drilling
 azmater.com
azmater.com