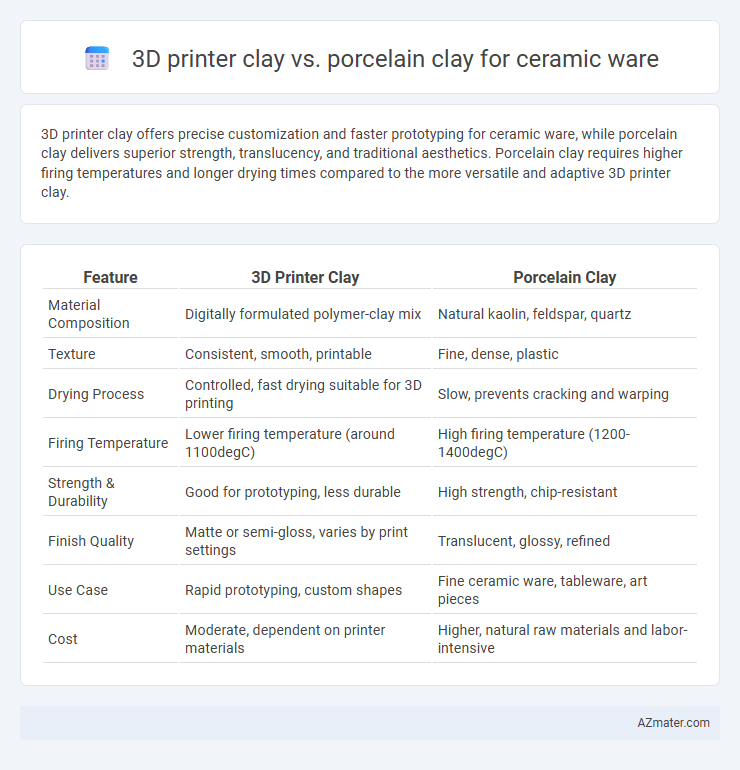
3D printer clay offers precise customization and faster prototyping for ceramic ware, while porcelain clay delivers superior strength, translucency, and traditional aesthetics. Porcelain clay requires higher firing temperatures and longer drying times compared to the more versatile and adaptive 3D printer clay.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Digitally formulated polymer-clay mix | Natural kaolin, feldspar, quartz |
| Texture | Consistent, smooth, printable | Fine, dense, plastic |
| Drying Process | Controlled, fast drying suitable for 3D printing | Slow, prevents cracking and warping |
| Firing Temperature | Lower firing temperature (around 1100degC) | High firing temperature (1200-1400degC) |
| Strength & Durability | Good for prototyping, less durable | High strength, chip-resistant |
| Finish Quality | Matte or semi-gloss, varies by print settings | Translucent, glossy, refined |
| Use Case | Rapid prototyping, custom shapes | Fine ceramic ware, tableware, art pieces |
| Cost | Moderate, dependent on printer materials | Higher, natural raw materials and labor-intensive |
Introduction to 3D Printer Clay and Porcelain Clay
3D printer clay is a specially formulated, plasticized ceramic material designed for additive manufacturing, enabling precise layer-by-layer construction of complex shapes with minimal shrinkage and warping. Porcelain clay, a traditional ceramic material composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, is renowned for its high whiteness, translucency, and strength after firing. While 3D printer clay offers enhanced design flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities, porcelain clay remains favored for producing fine, durable ceramic ware with a classic aesthetic.
Material Composition: 3D Printer Clay vs Porcelain Clay
3D printer clay typically contains a blend of plastic polymers and fine mineral particles designed for extrusion through a nozzle, offering flexibility and ease of shaping in additive manufacturing. Porcelain clay is composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, resulting in a highly refined, dense material that vitrifies to a translucent, durable finish after firing. The fundamental difference in material composition influences the mechanical properties, firing temperature, and aesthetic qualities of the final ceramic ware.
Workability and Handling Differences
3D printer clay offers superior workability with its smoother consistency and adaptability to precise layering, making it ideal for complex ceramic designs and rapid prototyping. Porcelain clay provides a denser, more plastic texture that requires careful handling but results in finer, more durable ceramic ware after firing. The differences in handling stem from 3D printer clay's compatibility with digital modeling tools, whereas porcelain demands skilled manual shaping and traditional techniques.
Firing Temperatures and Sintering
3D printer clay typically requires lower firing temperatures, often between 1,000degC and 1,200degC, allowing for faster sintering and reduced energy consumption compared to porcelain clay, which usually demands higher firing temperatures around 1,200degC to 1,400degC to achieve optimal vitrification. Porcelain clay's higher temperature firing results in a denser, more glass-like finish with superior strength and translucency, whereas 3D printer clay sacrifices some of these characteristics for enhanced printability and faster production cycles. The sintering process in porcelain clay promotes particle fusion and minimal porosity, critical for high-quality ceramic ware, while 3D printer clay sinters quickly but may retain more micro-porosity affecting durability and water resistance.
Surface Finish and Texture Comparison
3D printer clay offers a rougher texture and less refined surface finish compared to porcelain clay, which is known for its smooth, translucent, and highly polished appearance. Porcelain clay vitrifies at higher temperatures, resulting in a glass-like, dense surface ideal for fine ceramic ware, while 3D printed clay often requires post-processing to achieve similar smoothness. The inherent porosity and grain size in 3D printer clay typically produce a coarser, matte finish that contrasts with the sleek, glossy texture characteristic of fired porcelain pieces.
Strength and Durability of Final Ware
3D printed clay typically exhibits lower strength and durability compared to porcelain clay due to its coarse particle size and less uniform microstructure. Porcelain clay, known for its fine kaolin content and vitrification during firing, produces ceramic ware with superior mechanical strength and resistance to chipping. The dense, glassy matrix formed in porcelain enhances both the toughness and longevity of the final product, making it ideal for high-quality ceramic applications.
Design Flexibility and Creative Potential
3D printer clay offers superior design flexibility compared to porcelain clay, enabling intricate and complex shapes that are difficult to achieve with traditional hand-building techniques. Its digital fabrication allows for precise customization, rapid prototyping, and seamless replication, expanding creative potential for ceramic artists and designers. Porcelain clay's fine texture and translucency provide elegance and durability but limit design complexity due to its fragile nature and traditional forming methods.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
3D printer clay offers a cost-effective alternative to porcelain clay, with more affordable raw materials and lower operational expenses, making it accessible for hobbyists and small-scale production. Porcelain clay, while more expensive due to its refined composition and firing requirements, provides superior durability and a finer finish ideal for high-quality ceramic ware. Accessibility to 3D printer clay is enhanced by widespread availability at online retailers and compatibility with various desktop 3D printers, whereas porcelain clay often demands specific kiln conditions and specialized supply sources.
Applications in Modern Ceramic Ware
3D printer clay offers precise control and rapid prototyping capabilities, making it ideal for intricate and customized ceramic ware designs in modern applications such as bespoke tableware and decorative art pieces. Porcelain clay, known for its vitrification and translucency, remains preferred for high-quality finished products like fine china and functional ceramics requiring durability and aesthetic elegance. Both materials serve distinct roles, with 3D printer clay enhancing innovative design workflows and porcelain clay ensuring traditional, high-performance results in ceramic ware manufacturing.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
3D printer clay for ceramic ware offers a sustainable alternative by minimizing material waste through precise additive manufacturing, reducing excess clay discard compared to traditional methods. Porcelain clay, while valued for its durability and fine texture, often requires high-energy kilns and involves more resource-intensive processing, contributing to a larger carbon footprint. The shift towards 3D printed clay supports eco-friendly ceramics production by enhancing material efficiency and lowering overall environmental impact.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Porcelain clay for Ceramic ware
 azmater.com
azmater.com