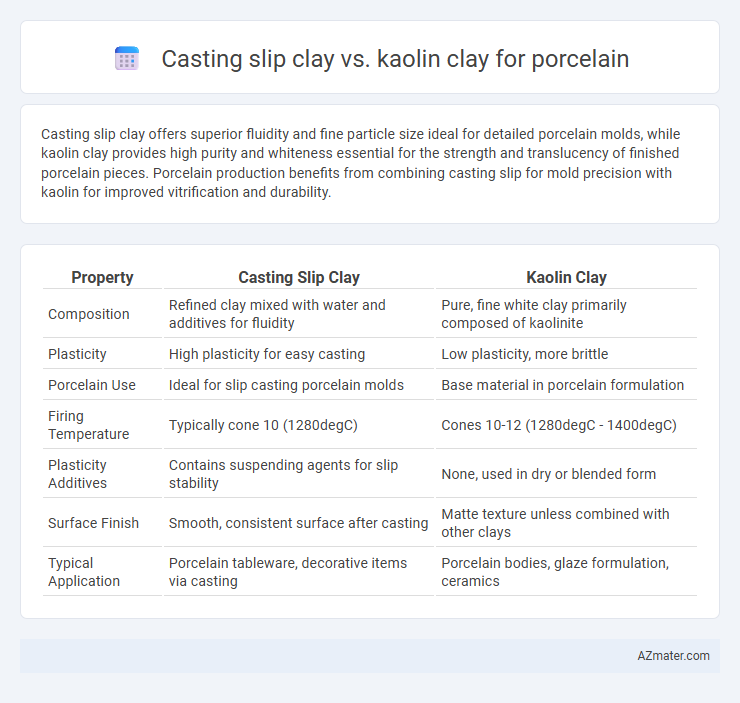
Casting slip clay offers superior fluidity and fine particle size ideal for detailed porcelain molds, while kaolin clay provides high purity and whiteness essential for the strength and translucency of finished porcelain pieces. Porcelain production benefits from combining casting slip for mold precision with kaolin for improved vitrification and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Casting Slip Clay | Kaolin Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Refined clay mixed with water and additives for fluidity | Pure, fine white clay primarily composed of kaolinite |
| Plasticity | High plasticity for easy casting | Low plasticity, more brittle |
| Porcelain Use | Ideal for slip casting porcelain molds | Base material in porcelain formulation |
| Firing Temperature | Typically cone 10 (1280degC) | Cones 10-12 (1280degC - 1400degC) |
| Plasticity Additives | Contains suspending agents for slip stability | None, used in dry or blended form |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, consistent surface after casting | Matte texture unless combined with other clays |
| Typical Application | Porcelain tableware, decorative items via casting | Porcelain bodies, glaze formulation, ceramics |
Introduction to Porcelain Clays
Porcelain clays primarily consist of kaolin, known for its purity, whiteness, and fine particle size, which contribute to porcelain's translucency and strength. Casting slip clay, often a refined kaolin-based slurry, allows for precise shaping and smooth surfaces in ceramic production. The choice between pure kaolin and casting slip depends on the desired porcelain characteristics, with kaolin providing structural integrity and casting slip offering ease of molding and minimal porosity.
What is Casting Slip Clay?
Casting slip clay is a liquid form of clay used in producing fine porcelain items through slip casting, where the fluid slip is poured into plaster molds to create thin, detailed ceramic shapes. Compared to kaolin clay, which is a primary raw material rich in alumina and silica for porcelain, casting slip acts as the work-ready medium tailored for mold shaping and drying control. The key to high-quality porcelain casting slip lies in achieving a balanced particle size distribution and optimal viscosity to ensure smooth flow, minimized defects, and precise mold reproduction.
What is Kaolin Clay?
Kaolin clay, also known as china clay, is a key ingredient in porcelain production due to its high purity, whiteness, and fine particle size, which contribute to porcelain's strength and translucency. Unlike casting slip clay, which may contain impurities and coarser particles, kaolin provides a smooth texture that enhances the plasticity and workability of porcelain bodies. Its primary role in porcelain is to improve firing performance, minimize shrinkage, and create a durable, smooth surface ideal for fine ceramics.
Raw Material Composition: Slip Clay vs Kaolin
Casting slip clay for porcelain primarily consists of fine particles suspended in water, featuring a balanced blend of kaolin, ball clay, feldspar, and silica to achieve optimal plasticity and casting properties. Kaolin clay, a primary raw material in porcelain, is a pure, fine white clay rich in kaolinite mineral, known for its high refractory properties and whiteness but with low plasticity and casting suitability on its own. The key compositional difference lies in slip clay's formulated suspension designed for fluidity and mold filling, whereas kaolin provides the fundamental structural and thermal qualities essential to porcelain body development.
Workability and Handling Differences
Casting slip clay offers superior fluidity and ease of pouring, making it ideal for creating intricate porcelain molds with minimal air bubbles, while Kaolin clay provides a stiffer consistency that requires more skill during shaping and handling. The high plasticity of casting slip enhances fine detail reproduction and reduces drying time, whereas Kaolin's lower plasticity demands careful control to prevent cracking and warping. Workability differences between casting slip and Kaolin clay significantly impact the precision and quality of porcelain products in both hand-building and slip-casting techniques.
Firing Performance and Shrinkage
Casting slip clay offers superior workability and is optimized for slip casting processes, exhibiting moderate shrinkage rates between 6-9% during firing, which aids in maintaining dimensional accuracy in porcelain production. Kaolin clay, characterized by its high purity and refractory nature, provides excellent whiteness and strength after firing but typically experiences lower shrinkage values around 5-7%, resulting in a more stable fired body. The choice between casting slip clay and kaolin clay directly impacts firing performance, with kaolin ensuring higher thermal stability and casting slip clay enabling better mold filling and surface finish in porcelain applications.
Porcelain Texture and Whiteness Comparison
Casting slip clay offers a smooth, fine texture ideal for creating thin, delicate porcelain pieces with consistent translucency, while kaolin clay provides a denser, more plastic body contributing to structural strength in porcelain. In terms of whiteness, kaolin clay typically results in a brighter, purer white finish due to its high purity and low impurity content, enhancing porcelain's aesthetic appeal. Combining casting slip with high-quality kaolin can optimize both the delicate texture and brilliant whiteness characteristic of premium porcelain products.
Strength and Durability Outcomes
Casting slip clay and kaolin clay differ significantly in strength and durability outcomes for porcelain production. Casting slip clay, formulated with fine particles and additives, offers enhanced plasticity and uniformity, resulting in stronger, more consistent porcelain pieces after firing. Kaolin clay, a primary component of porcelain, provides exceptional whiteness and thermal stability but requires blending with other clays to achieve comparable strength and durability in finished porcelain products.
Common Applications in Porcelain Creation
Casting slip clay is widely used in the production of thin-walled porcelain wares due to its optimal fluidity and ease of molding, making it ideal for fine tableware and decorative objects. Kaolin clay, a primary ingredient in porcelain, provides the essential plasticity and whiteness required for high-quality porcelain, commonly used in sculptural pieces and high-end dinnerware. Both clays play complementary roles; casting slip enables precise detail and smooth finishes, while kaolin contributes to the porcelain's strength and translucency.
Choosing the Best Clay Type for Your Project
Choosing between casting slip clay and kaolin clay for porcelain hinges on project goals and desired finish quality. Casting slip, a liquid mixture, enables detailed, thin-walled forms through slip casting, ideal for intricate designs and mass production. Kaolin clay, a fine white clay essential for traditional porcelain, offers superior whiteness and plasticity, making it suitable for hand-building or wheel throwing high-quality, translucent porcelain pieces.
Infographic: Casting slip clay vs Kaolin clay for Porcelain
 azmater.com
azmater.com