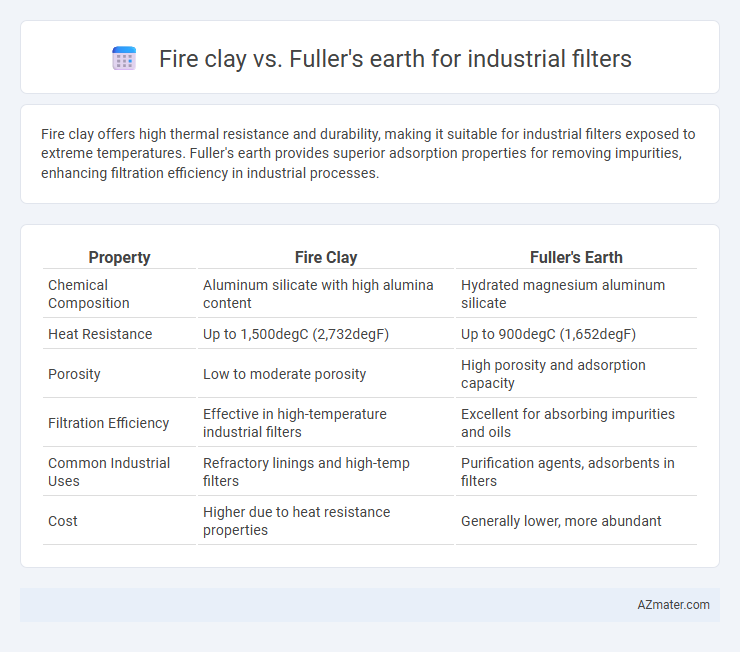
Fire clay offers high thermal resistance and durability, making it suitable for industrial filters exposed to extreme temperatures. Fuller's earth provides superior adsorption properties for removing impurities, enhancing filtration efficiency in industrial processes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fire Clay | Fuller's Earth |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Aluminum silicate with high alumina content | Hydrated magnesium aluminum silicate |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1,500degC (2,732degF) | Up to 900degC (1,652degF) |
| Porosity | Low to moderate porosity | High porosity and adsorption capacity |
| Filtration Efficiency | Effective in high-temperature industrial filters | Excellent for absorbing impurities and oils |
| Common Industrial Uses | Refractory linings and high-temp filters | Purification agents, adsorbents in filters |
| Cost | Higher due to heat resistance properties | Generally lower, more abundant |
Introduction to Industrial Filter Media
Industrial filter media such as fire clay and Fuller's earth play crucial roles in separating impurities in manufacturing processes. Fire clay is valued for its high-temperature resistance, mechanical strength, and ability to withstand chemical corrosion, making it ideal for filtering molten metals and high-viscosity fluids. Fuller's earth excels in adsorptive capacity, effectively removing oils, greases, and impurities in chemical and pharmaceutical industries due to its high surface area and unique mineral composition.
Overview of Fire Clay Properties
Fire clay exhibits high refractory properties with the ability to withstand temperatures exceeding 1500degC, making it ideal for industrial filter applications involving high heat. Its low porosity and excellent chemical resistance ensure durability and stability in harsh industrial environments. The material's strong mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance contribute to efficient filtration performance and long service life compared to Fuller's earth.
Characteristics of Fuller’s Earth
Fuller's earth is a highly absorbent clay material characterized by its fine particle size, large surface area, and strong adsorptive properties, making it ideal for industrial filters. It effectively traps impurities, oils, and heavy metals due to its porous structure and chemical composition rich in montmorillonite and other clay minerals. Compared to fire clay, Fuller's earth offers superior filtration efficiency and regeneration capabilities, enhancing its application in waste treatment and purification processes.
Filtration Efficiency: Fire Clay vs Fuller’s Earth
Fire clay offers high filtration efficiency due to its dense, fine-grained structure that effectively traps fine particles and impurities in industrial processes. Fuller's earth excels in adsorption capabilities, removing oil, grease, and organic contaminants through its porous, absorbent nature, enhancing filtration quality in liquid and gas streams. Comparing both, fire clay provides superior solid particle filtration, while Fuller's earth optimizes removal of chemical and hydrocarbon contaminants, making each suitable for specific industrial filtration applications.
Chemical Resistance and Stability Comparison
Fire clay exhibits superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to Fuller's earth, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial filtration applications involving acidic and alkaline media. Fuller's earth, while effective at adsorbing oils and impurities due to its high porosity, has lower chemical stability and is more prone to degradation in harsh chemical environments. Industrial filters utilizing fire clay benefit from enhanced durability and consistent performance in aggressive chemical conditions, whereas Fuller's earth is preferred for applications requiring high adsorption but less exposure to corrosive substances.
Cost Analysis for Industrial Applications
Fire clay offers a cost-effective solution for industrial filters due to its high thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-temperature environments with lower replacement frequency. Fuller's earth, while typically more expensive upfront, provides superior adsorption properties for removing impurities and contaminants, often reducing operational costs through improved filtration efficiency. In industrial applications, the choice between fire clay and Fuller's earth depends on balancing initial material costs against long-term performance benefits and specific filtration requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fire clay and Fuller's earth differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability when used in industrial filters. Fire clay, composed primarily of kaolinite and other refractory minerals, is abundant and requires less intensive mining processes, resulting in lower ecological disturbance and reduced carbon emissions compared to Fuller's earth. Fuller's earth, known for its high absorbency due to its expandable smectite clay minerals, often involves more invasive extraction methods that can lead to habitat degradation and increased water contamination risks, making fire clay a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious filtration applications.
Typical Industrial Uses of Fire Clay
Fire clay is commonly utilized in industrial filters for its high thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for applications such as metal casting, refractory linings, and furnace insulation. Its fine particle size and plasticity enable efficient filtration of molten metals and slag, enhancing purity and product quality. In contrast, Fuller's earth is primarily used for adsorbing oils and impurities in the filtration of lubricants and industrial wastewater, where its high absorbency is more critical than thermal properties.
Common Applications of Fuller’s Earth
Fuller's earth is widely used in industrial filtration processes to remove oils, greases, and heavy metals from wastewater due to its high absorbency and fine particle structure. It is commonly applied in the purification of edible oils, petroleum refining, and treatment of industrial effluents to enhance clarity and quality. Fire clay, by contrast, is primarily utilized for its thermal resistance in high-temperature filtration systems rather than absorptive filtration needs.
Choosing the Right Filter Media for Your Industry
Fire clay offers high thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for industrial filters exposed to high temperatures and harsh chemicals. Fuller's earth provides excellent adsorption properties and decolorization, suitable for filtering oils, lubricants, and removing impurities in water treatment. Selecting the right filter media depends on factors like operational temperature, chemical exposure, and specific filtration requirements, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in your industrial applications.
Infographic: Fire clay vs Fuller’s earth for Industrial filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com