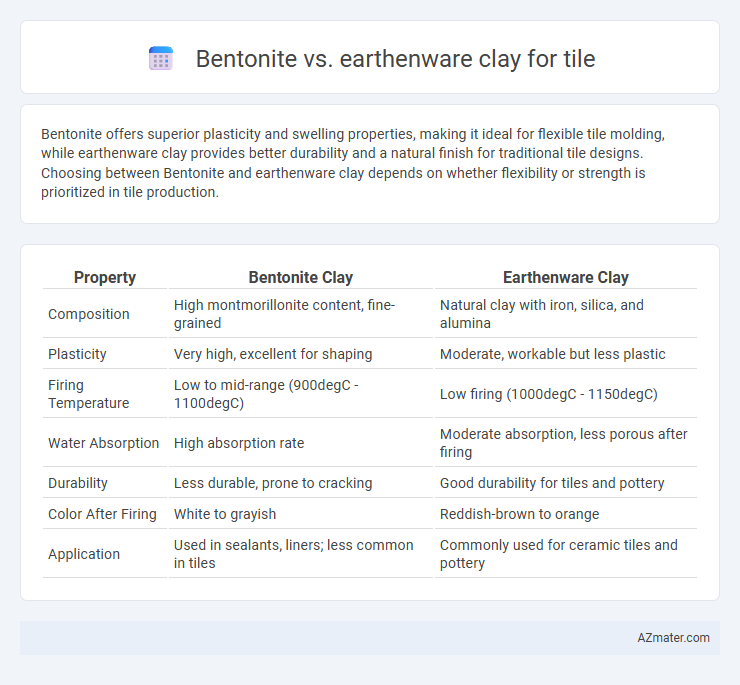
Bentonite offers superior plasticity and swelling properties, making it ideal for flexible tile molding, while earthenware clay provides better durability and a natural finish for traditional tile designs. Choosing between Bentonite and earthenware clay depends on whether flexibility or strength is prioritized in tile production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bentonite Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High montmorillonite content, fine-grained | Natural clay with iron, silica, and alumina |
| Plasticity | Very high, excellent for shaping | Moderate, workable but less plastic |
| Firing Temperature | Low to mid-range (900degC - 1100degC) | Low firing (1000degC - 1150degC) |
| Water Absorption | High absorption rate | Moderate absorption, less porous after firing |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to cracking | Good durability for tiles and pottery |
| Color After Firing | White to grayish | Reddish-brown to orange |
| Application | Used in sealants, liners; less common in tiles | Commonly used for ceramic tiles and pottery |
Introduction to Bentonite and Earthenware Clay
Bentonite is a highly absorbent, fine-grained clay primarily composed of montmorillonite, known for its excellent plasticity and swelling properties, making it ideal for sealing and waterproofing in tile production. Earthenware clay is a porous, red or brown clay fired at lower temperatures, valued for its ease of shaping and rustic finish in decorative and functional tiles. Understanding the distinct mineral compositions and firing requirements of bentonite and earthenware clay is essential for selecting the appropriate material for specific tile applications.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Bentonite primarily consists of montmorillonite, a smectite clay mineral rich in silica, alumina, and water, providing high plasticity and swelling properties ideal for tile shaping. Earthenware clay is composed mainly of kaolinite with varying amounts of iron oxides, quartz, and feldspar, which contribute to its lower plasticity and porous nature after firing. The chemical differences impact their behavior in tile production, with bentonite offering superior moldability and water absorption, while earthenware provides strength and a characteristic reddish hue due to iron content.
Physical Properties and Texture
Bentonite clay exhibits high plasticity and swelling capacity due to its fine particle size and montmorillonite mineral content, making it ideal for applications requiring water retention and flexibility. Earthenware clay has a coarser texture with lower plasticity, resulting in a more porous and less dense tile after firing, suitable for decorative and lightweight tiles. Physical properties of Bentonite provide superior shrinkage resistance and durability compared to the more porous, brittle nature of earthenware tiles.
Water Absorption and Plasticity
Bentonite exhibits high plasticity and low water absorption, making it ideal for tiles requiring flexibility and durability in moist environments. Earthenware clay has higher water absorption rates and lower plasticity, resulting in more porous and less durable tiles suited for decorative rather than structural applications. The water absorption rate for bentonite typically ranges below 5%, whereas earthenware clay can absorb between 15-25%, influencing tile strength and longevity.
Firing Temperatures and Methods
Bentonite typically requires firing between 1200degC and 1300degC, making it suitable for high-fire methods that enhance its strength and durability. Earthenware clay fires at lower temperatures, generally between 900degC and 1100degC, ideal for low-fire techniques that preserve its porous and rustic qualities. Choosing between bentonite and earthenware depends on the desired tile finish, with bentonite offering vitrification for waterproof tiles and earthenware retaining a more porous texture.
Strength and Durability of Finished Tiles
Bentonite clay offers superior strength and durability for finished tiles due to its high plasticity and swelling properties, which enhance tile cohesion and resistance to cracking. Earthenware clay, while easier to shape and fire at lower temperatures, generally produces more porous and less durable tiles prone to chipping and wear over time. For applications demanding long-lasting, robust tiles, bentonite-based formulations provide a stronger structural integrity compared to traditional earthenware clay.
Shrinkage and Warping Potential
Bentonite clay exhibits minimal shrinkage and low warping potential due to its fine particle size and high plasticity, making it ideal for tile production requiring dimensional stability. Earthenware clay, while easier to work with, has a higher shrinkage rate ranging from 5% to 12%, increasing the risk of warping during drying and firing. Controlling moisture content and firing temperature is crucial for earthenware to minimize deformation and ensure tile durability.
Color and Surface Finish Variations
Bentonite clay typically offers a smooth, uniform surface finish with a light gray to pale cream color that can darken upon firing, providing subtle variations ideal for minimalist tile designs. Earthenware clay presents a broader color palette, ranging from warm reds, oranges, and browns to buff tones, with surface finishes that can vary from rough and rustic to smooth and glossy depending on glazing techniques. Color stability and finish texture in bentonite tiles lend themselves to consistent, modern aesthetics, while earthenware tiles deliver more pronounced, organic visual textures suitable for traditional or eclectic styles.
Cost and Availability
Bentonite clay typically costs more than earthenware clay due to its unique swelling properties and specialized industrial uses, making it less commonly available at local art supply stores. Earthenware clay is widely accessible and generally more affordable, making it a preferred choice for tile-making by hobbyists and artisans. The broad availability and lower price of earthenware clay make it ideal for large-scale projects or beginners working with ceramic tiles.
Best Use Cases and Recommendations
Bentonite clay, rich in montmorillonite, excels in tile applications requiring strong binding and water absorption, making it ideal for waterproof coatings and structural tiles in humid environments. Earthenware clay, characterized by its porous nature and lower firing temperature, is best suited for decorative tiles and indoor applications where aesthetic variations and lighter weight are prioritized. For durable, moisture-resistant tile projects, bentonite is recommended, while earthenware clay is preferable for artistic, low-impact tiling needs.
Infographic: Bentonite vs Earthenware clay for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com