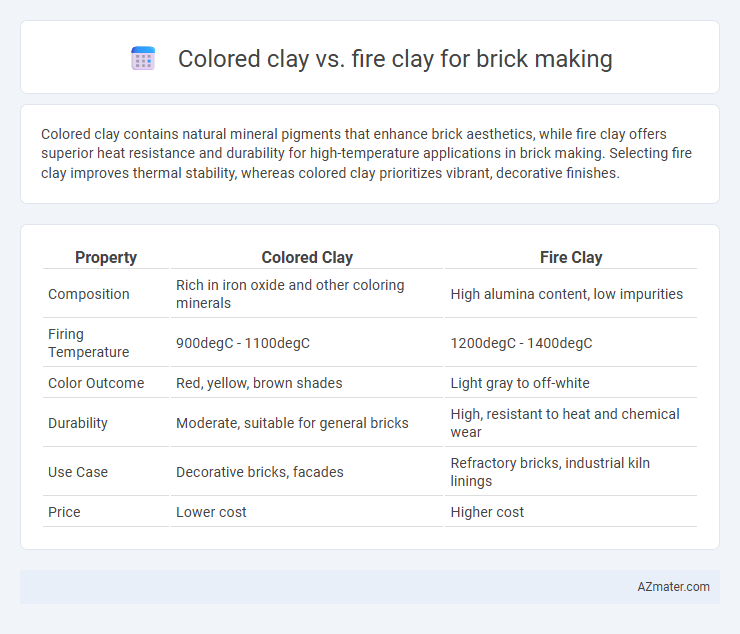
Colored clay contains natural mineral pigments that enhance brick aesthetics, while fire clay offers superior heat resistance and durability for high-temperature applications in brick making. Selecting fire clay improves thermal stability, whereas colored clay prioritizes vibrant, decorative finishes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Colored Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Rich in iron oxide and other coloring minerals | High alumina content, low impurities |
| Firing Temperature | 900degC - 1100degC | 1200degC - 1400degC |
| Color Outcome | Red, yellow, brown shades | Light gray to off-white |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for general bricks | High, resistant to heat and chemical wear |
| Use Case | Decorative bricks, facades | Refractory bricks, industrial kiln linings |
| Price | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Colored Clay and Fire Clay
Colored clay contains natural minerals such as iron, manganese, and copper oxides that impart distinctive hues like red, yellow, and green, making it ideal for decorative brick manufacturing. Fire clay, characterized by its high alumina and silica content, exhibits exceptional heat resistance and is primarily used in refractory bricks for furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces. The mineralogical composition of colored clay emphasizes aesthetic appeal, whereas fire clay prioritizes thermal stability and structural integrity in high-temperature environments.
Understanding the Composition of Colored Clay
Colored clay contains varying amounts of iron oxide, manganese, and other mineral impurities that influence its hue and plasticity, making it ideal for decorative bricks with vibrant colors. Fire clay, in contrast, is rich in alumina and silica, providing high refractory properties but limited color variation, primarily used for heat-resistant bricks. Understanding the mineral composition of colored clay is crucial for achieving specific aesthetic effects and ensuring proper firing temperatures in brick manufacturing.
Key Properties of Fire Clay
Fire clay exhibits exceptional heat resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature applications in brick making. Its high alumina content ensures durability and strength, while low impurity levels contribute to minimal deformation during firing. These properties distinguish fire clay from colored clay, which primarily offers aesthetic appeal but lacks the structural resilience required for refractory bricks.
Differences in Brick-Making Processes
Colored clay requires careful mixing with specific mineral pigments during the molding process to achieve consistent hues, whereas fire clay involves a more standardized molding technique due to its refractory properties. The firing temperature for colored clay bricks is typically lower, around 900-1100degC, to preserve color intensity, while fire clay bricks necessitate much higher firing temperatures, often exceeding 1300degC, to develop heat resistance. Moisture content and plasticity also differ, with colored clay exhibiting higher plasticity for easier shaping, compared to the dense, less plastic fire clay that demands precise moisture control to prevent cracking during firing.
Durability: Colored Clay vs Fire Clay Bricks
Colored clay bricks exhibit moderate durability suitable for standard construction but may be more prone to weathering and surface erosion compared to fire clay bricks. Fire clay bricks, composed of refractory materials, offer exceptional durability with high resistance to heat, chemical corrosion, and mechanical wear, ideal for industrial applications. The intrinsic mineral composition of fire clay ensures superior lifespan and structural integrity, outperforming colored clay in demanding environments.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Colored clay offers a broad spectrum of natural hues, including reds, yellows, and browns, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of bricks with vibrant, earthy tones. Fire clay, primarily used for its heat resistance, typically produces bricks in muted gray or buff shades, limiting color variation but providing a unique industrial look. The choice between colored clay and fire clay for brick making significantly influences the visual character and design versatility of the final product.
Thermal and Structural Performance
Colored clay bricks offer superior thermal insulation due to their mineral composition, which reduces heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency in buildings. Fire clay bricks, characterized by high alumina content, provide exceptional structural strength and resistance to high temperatures, making them ideal for applications requiring durability under thermal stress. The choice between colored clay and fire clay bricks depends on balancing thermal insulation needs with structural performance requirements in construction projects.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Colored clay typically costs more than fire clay due to its specialized mineral content and pigmentation, which enhances aesthetic appeal in brick making. Fire clay is more widely available and economical, often sourced from abundant natural deposits, making it a cost-effective choice for high-temperature-resistant bricks. The availability of fire clay in major brick-producing regions results in lower transportation costs, further reducing overall expenses compared to colored clay.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Colored clay and fire clay differ significantly in their environmental impact and sustainability for brick making, with colored clay typically sourced from surface deposits requiring minimal processing, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced carbon emissions. Fire clay, used for high-temperature applications, often demands deeper extraction and intensive processing, which increases ecological disturbance and energy use. Choosing colored clay for brick production supports eco-friendlier construction by minimizing habitat disruption and promoting resource conservation.
Choosing the Right Clay for Specific Brick Applications
Choosing the right clay for brick making depends on the desired properties and applications of the bricks. Colored clay offers vibrant, natural hues ideal for decorative and architectural bricks, providing aesthetic appeal with moderate strength. Fire clay, characterized by its high alumina content and heat resistance, is essential for refractory bricks used in high-temperature environments such as kilns and furnaces.
Infographic: Colored clay vs Fire clay for Brick making
 azmater.com
azmater.com