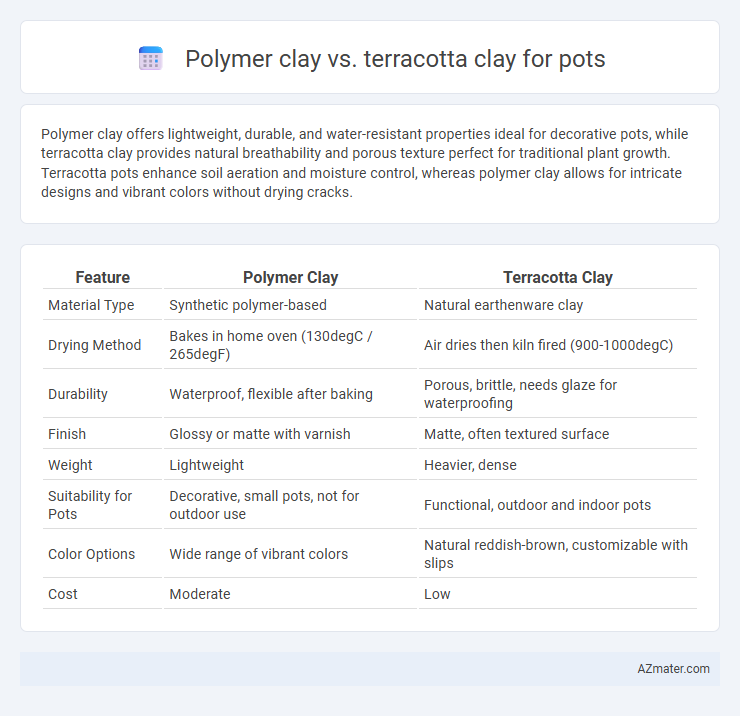
Polymer clay offers lightweight, durable, and water-resistant properties ideal for decorative pots, while terracotta clay provides natural breathability and porous texture perfect for traditional plant growth. Terracotta pots enhance soil aeration and moisture control, whereas polymer clay allows for intricate designs and vibrant colors without drying cracks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polymer Clay | Terracotta Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer-based | Natural earthenware clay |
| Drying Method | Bakes in home oven (130degC / 265degF) | Air dries then kiln fired (900-1000degC) |
| Durability | Waterproof, flexible after baking | Porous, brittle, needs glaze for waterproofing |
| Finish | Glossy or matte with varnish | Matte, often textured surface |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier, dense |
| Suitability for Pots | Decorative, small pots, not for outdoor use | Functional, outdoor and indoor pots |
| Color Options | Wide range of vibrant colors | Natural reddish-brown, customizable with slips |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
Introduction to Polymer Clay and Terracotta Clay
Polymer clay is a versatile, synthetic modeling material composed mainly of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) mixed with plasticizers, allowing it to be easily molded and hardened by baking at low temperatures. Terracotta clay, a natural, porous earthenware made from refined clay minerals, is traditionally used for pottery and fired at higher kiln temperatures to achieve durability and earthy tones. While polymer clay offers vibrant color options and precision for intricate designs, terracotta provides classic, breathable pots ideal for plant health and outdoor use.
Composition and Material Differences
Polymer clay is a synthetic material composed primarily of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) combined with plasticizers, allowing it to remain pliable until cured by heat in a home oven at around 265degF to 275degF (130degC). Terracotta clay is a natural earthenware made from a blend of fine-grained red clay and other minerals, fired at high temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC in a kiln, resulting in a porous, durable ceramic. The major composition difference is that polymer clay is plastic-based and cured by baking, while terracotta clay is mineral-based and hardened through kiln firing, influencing their texture, durability, and suitability for different pot-making techniques.
Workability and Ease of Use
Polymer clay offers superior workability due to its soft, pliable texture and does not require kiln firing, making it ideal for detailed pot crafting and beginners. Terracotta clay, while traditional and breathable, demands precise moisture control and kiln firing, posing challenges for ease of use and longer drying times. The choice hinges on skill level and available equipment, with polymer clay excelling in convenience and terracotta favored for durability and natural finish.
Strength and Durability of Finished Pots
Polymer clay offers superior strength and durability compared to terracotta clay, as it is less prone to cracking and chipping after curing at low temperatures. Terracotta clay, while traditional and breathable, remains porous and fragile, making pots more susceptible to weather damage and breakage over time. For long-lasting, resilient pots, polymer clay provides enhanced impact resistance and water impermeability.
Firing and Curing Processes
Polymer clay cures at low temperatures, typically between 265degF and 275degF (129degC to 135degC) in a conventional oven, eliminating the need for traditional kiln firing and reducing energy consumption. Terracotta clay requires high-temperature firing in a kiln, generally between 1,800degF and 2,100degF (982degC to 1,150degC), which vitrifies the clay, enhancing durability and porosity suitable for outdoor pots. The curing process of polymer clay offers quicker turnaround and less equipment demand, while terracotta's firing ensures structural strength and weather resistance essential for functional pottery.
Color Options and Finishing Techniques
Polymer clay offers a wide range of vibrant color options, allowing artists to mix and match hues for detailed designs, while terracotta clay primarily comes in natural earthy tones like reddish-brown and requires painted finishes to achieve varied colors. Finishing techniques for polymer clay include baking to harden and gloss varnishes to enhance shine and durability, whereas terracotta clay is fired in a kiln and can be glazed for a smooth, waterproof surface or left unglazed for a rustic matte look. Color versatility in polymer clay is superior for intricate, multicolored pots, while terracotta's traditional appeal lies in its natural texture and classical finishes.
Water Resistance and Porosity
Polymer clay is highly water-resistant and non-porous, making it ideal for indoor pots that do not require drainage. Terracotta clay is porous and absorbs water, which helps aerate plant roots but necessitates proper drainage to prevent root rot in pots. For outdoor or watering-intensive use, terracotta's breathability is preferable, whereas polymer clay suits decorative, moisture-sensitive applications.
Suitability for Indoor and Outdoor Use
Polymer clay offers excellent durability for indoor pots, resisting cracking and maintaining vibrant colors without requiring kiln firing, making it ideal for decorative purposes in controlled environments. Terracotta clay, fired at high temperatures, provides porous, breathable qualities suitable for outdoor pots, allowing moisture to evaporate and reducing root rot risk in plants. While terracotta's rugged texture withstands weather fluctuations, polymer clay may degrade under prolonged UV exposure, limiting its outdoor application.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Polymer clay typically costs between $10 to $25 per pound, making it more expensive than terracotta clay, which usually ranges from $1 to $5 per pound. Terracotta clay is widely available in art supply stores, pottery shops, and online, whereas polymer clay is often found in specialty craft stores and may have limited color and brand options depending on location. For pot-making projects, terracotta clay offers a budget-friendly option with broad accessibility, while polymer clay provides more versatility but at a higher cost.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymer clay is a synthetic material derived from petroleum, making its production energy-intensive and less biodegradable, which raises concerns about environmental pollution and long-term sustainability. Terracotta clay, made from natural clay fired at high temperatures, is biodegradable and sourced from abundant earth materials, resulting in a lower carbon footprint and better eco-friendly credentials. Choosing terracotta over polymer clay significantly reduces plastic waste and promotes sustainable pottery practices.
Infographic: Polymer clay vs Terracotta clay for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com