Paper clay offers enhanced flexibility and lightweight properties due to its fiber content but has lower thermal resistance compared to fire clay. Fire clay, composed of high alumina content minerals, provides superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for refractory brick applications exposed to extreme temperatures.
Table of Comparison
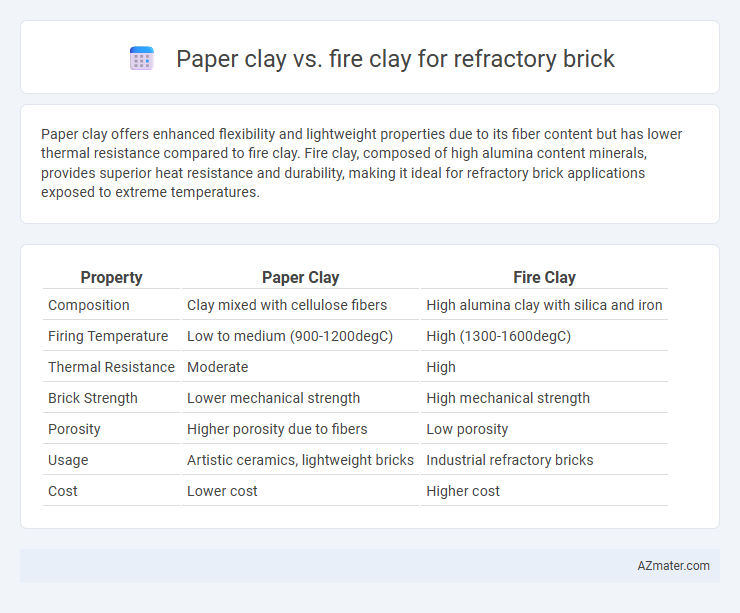
| Property | Paper Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay mixed with cellulose fibers | High alumina clay with silica and iron |
| Firing Temperature | Low to medium (900-1200degC) | High (1300-1600degC) |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Brick Strength | Lower mechanical strength | High mechanical strength |
| Porosity | Higher porosity due to fibers | Low porosity |
| Usage | Artistic ceramics, lightweight bricks | Industrial refractory bricks |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Refractory Bricks
Refractory bricks are essential materials engineered to withstand high temperatures and harsh environments in industrial furnaces, kilns, and reactors. Paper clay and fire clay represent two key types of refractory bricks, differing primarily in their composition and thermal durability; fire clay bricks contain high alumina content enhancing their heat resistance, while paper clay bricks incorporate cellulose fibers for improved plasticity and reduced shrinkage. The choice between paper clay and fire clay refractory bricks depends on specific application requirements such as thermal stability, mechanical strength, and resistance to thermal shock.
What is Paper Clay?
Paper clay is a type of clay mixed with cellulose fibers, typically made from recycled paper, enhancing its strength and workability before firing. It offers improved plasticity, reduced drying shrinkage, and increased surface area, making it easier to shape and less prone to cracking during the drying process. Unlike fire clay, which is naturally high in alumina and silica for heat resistance, paper clay is primarily used for its handling properties and can be combined with fire clay to produce refractory bricks with better durability and reduced defects.
What is Fire Clay?
Fire clay is a heat-resistant material primarily composed of hydrous aluminum silicates, widely used in refractory bricks for its excellent ability to withstand high temperatures and thermal shock. It has a high melting point, typically above 1580degC (2876degF), making it ideal for furnaces, kilns, and fireplaces. Unlike paper clay, which incorporates fibrous additives for lightweight and workability, fire clay offers superior structural integrity and durability under intense heat conditions.
Composition Differences Between Paper Clay and Fire Clay
Paper clay contains a mix of clay minerals combined with cellulose fibers derived from paper pulp, which enhances plasticity and drying strength, whereas fire clay primarily consists of alumina and silica with minimal organic content, designed to withstand high temperatures. The cellulose fibers in paper clay improve workability but burn out during firing, leaving a more porous structure, while fire clay's dense composition offers superior thermal stability and resistance to deformation at extreme heat. These compositional differences dictate their respective suitability for refractory bricks, with fire clay preferred for high-temperature applications and paper clay favored for detailed shaping and lightweight features.
Thermal Properties Comparison
Paper clay exhibits lower thermal conductivity compared to fire clay, enhancing insulation performance in refractory bricks. Fire clay offers superior thermal shock resistance and higher melting points, making it suitable for high-temperature industrial applications. The combination of paper clay's lightweight structure and fire clay's heat endurance results in optimized refractory materials for efficient thermal management.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Paper clay exhibits enhanced plasticity and reduced drying shrinkage compared to fire clay, resulting in improved crack resistance during forming processes. Fire clay refractory bricks are known for their superior high-temperature strength and excellent thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for sustained exposure to extreme heat. Strength and durability analysis indicates fire clay bricks generally maintain structural integrity under prolonged thermal cycling better than paper clay variants, which may suffer from reduced high-temperature mechanical stability.
Workability and Shaping Methods
Paper clay offers superior workability compared to fire clay due to its incorporation of cellulose fibers, which enhance plasticity and reduce cracking during drying. Fire clay, known for its high alumina and silica content, is denser and requires more mechanized shaping methods like pressing or extrusion to achieve precise forms. The fibrous texture of paper clay allows for hand molding and intricate detailing, making it ideal for complex refractory brick shapes with minimal tooling.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Paper clay offers cost efficiency due to its lower raw material cost and reduced firing temperature compared to fire clay, making it ideal for budget-conscious refractory brick production. Fire clay, while generally more expensive, provides superior high-temperature resistance and durability, justifying its cost in demanding industrial applications. Availability of paper clay is typically higher in regions with abundant organic waste, whereas fire clay deposits are geologically specific and less widespread, influencing regional supply and pricing.
Applications in Refractory Brick Making
Paper clay, known for its high plasticity and reinforced fiber content, is primarily used in shaping complex refractory brick forms requiring fine detail and improved drying resistance in kiln linings and furnace walls. Fire clay, rich in alumina and silica, offers superior thermal stability and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature zones in industrial furnaces, kilns, and incinerators where intense heat and mechanical wear occur. Combining paper clay with fire clay in refractory bricks enhances moldability and structural integrity, optimizing performance in diverse refractory applications.
Choosing the Best Clay for Refractory Bricks
Paper clay offers enhanced workability and flexibility for shaping refractory bricks, making it ideal for intricate designs and repairs. Fire clay provides superior heat resistance and durability, essential for high-temperature applications such as furnaces and kilns. Choosing the best clay depends on the required thermal stability and mechanical strength, with fire clay preferred for heavy-duty use and paper clay for precision molding and repair tasks.
Infographic: Paper clay vs Fire clay for Refractory brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com