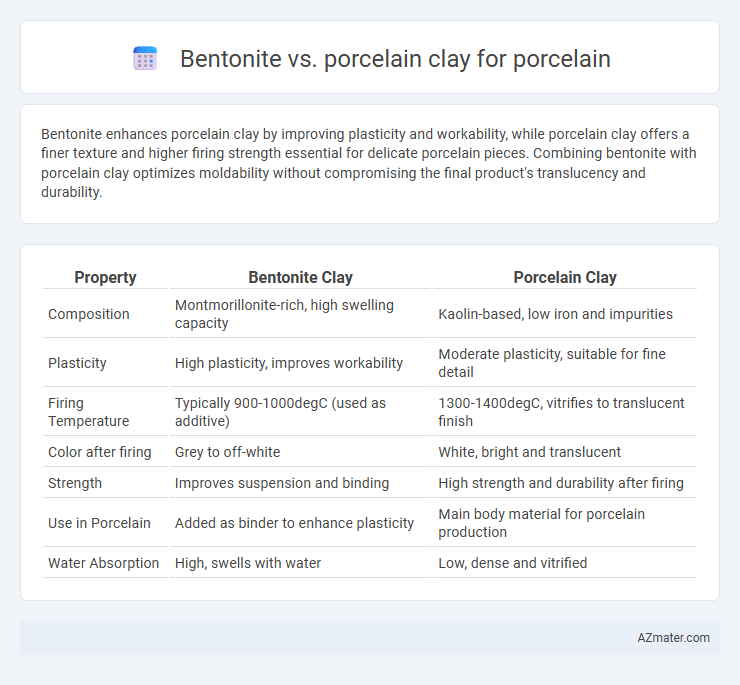
Bentonite enhances porcelain clay by improving plasticity and workability, while porcelain clay offers a finer texture and higher firing strength essential for delicate porcelain pieces. Combining bentonite with porcelain clay optimizes moldability without compromising the final product's translucency and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bentonite Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Montmorillonite-rich, high swelling capacity | Kaolin-based, low iron and impurities |
| Plasticity | High plasticity, improves workability | Moderate plasticity, suitable for fine detail |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 900-1000degC (used as additive) | 1300-1400degC, vitrifies to translucent finish |
| Color after firing | Grey to off-white | White, bright and translucent |
| Strength | Improves suspension and binding | High strength and durability after firing |
| Use in Porcelain | Added as binder to enhance plasticity | Main body material for porcelain production |
| Water Absorption | High, swells with water | Low, dense and vitrified |
Introduction to Bentonite and Porcelain Clay
Bentonite is a highly absorbent clay known for its swelling properties and ability to improve plasticity and strength in ceramic mixtures. Porcelain clay, primarily composed of kaolin, is prized for its whiteness, fine particle size, and high firing temperature, resulting in a dense, vitrified, and translucent final product. The combination of bentonite with porcelain clay enhances workability and durability, making it a preferred blend in fine porcelain production.
Key Differences in Mineral Composition
Bentonite clay primarily consists of montmorillonite, a type of smectite clay mineral known for its high swelling capacity and strong plasticity, making it ideal for enhancing the workability of porcelain clay bodies. Porcelain clay, on the other hand, is rich in kaolinite, a non-plastic mineral that provides strength, whiteness, and translucency after firing, crucial for true porcelain characteristics. The key difference lies in bentonite's ability to improve plasticity through its montmorillonite content, while porcelain clay's dominant kaolinite ensures durability and aesthetic quality in finished porcelain products.
Physical Properties Comparison
Bentonite clay features high plasticity and excellent water absorption, making it ideal for enhancing the workability and strength of porcelain clay bodies. Porcelain clay, composed mainly of kaolin, offers a smoother texture, lower shrinkage rates, and higher firing temperatures, resulting in a denser and more translucent finish. Comparing physical properties, bentonite increases plasticity and green strength while porcelain clay ensures durability, whiteness, and vitrification in the final product.
Plasticity and Workability in Ceramics
Bentonite clay significantly enhances plasticity due to its fine particle size and high swelling capacity, making it an ideal additive for improving workability in porcelain formulations. Porcelain clay itself is less plastic but provides the essential refractory properties and smooth texture that define fine ceramics. Combining bentonite with porcelain clay optimizes the balance between plasticity and strength, enabling easier shaping and better handling during the ceramic forming process.
Firing Temperature and Thermal Behavior
Bentonite enhances porcelain clay bodies by improving plasticity and increasing thermal shock resistance during firing, typically melting and vitrifying between 1200degC to 1300degC. Porcelain clay, composed primarily of kaolin, fires at a higher temperature range of approximately 1250degC to 1400degC, resulting in a dense, glassy, and strong final product with minimal shrinkage. The thermal behavior of bentonite-infused porcelain clay optimizes workability and firing stability, whereas pure porcelain clay requires careful temperature control to avoid warping or cracking.
Impact on Glaze and Surface Quality
Bentonite enhances porcelain's glaze durability by improving suspension and plasticity, resulting in a smoother and more uniform glaze surface. Porcelain clay contributes to a refined texture and higher vitrification, producing a glossy and dense finish with fewer imperfections. Choosing between bentonite and porcelain clay influences the glaze's adhesion, surface strength, and overall aesthetic quality in porcelain production.
Strength and Durability Considerations
Bentonite clay enhances porcelain by improving plasticity and workability, which contributes to fewer cracks and increased strength during the forming process. Porcelain clay, known for its fine particle size and high kaolin content, results in a dense, vitrified final product prized for exceptional hardness and durability. Combining bentonite with porcelain clay optimizes the balance between strength and durability, making it ideal for high-performance porcelain ceramics.
Applications in Porcelain Production
Bentonite enhances porcelain production by improving plasticity and workability, making it ideal for shaping fine, detailed forms. Porcelain clay, characterized by its high kaolin content, contributes to the final product's translucency, whiteness, and strength after firing. Combining bentonite with porcelain clay optimizes the raw material blend, facilitating smoother molding processes and stronger, more durable porcelain articles.
Environmental and Health Impacts
Bentonite and porcelain clay differ significantly in their environmental and health impacts during porcelain production; bentonite, a naturally occurring absorbent clay, enhances plasticity but its mining can lead to land degradation and dust-related respiratory issues. Porcelain clay, typically kaolin, is prized for its purity and whiteness, with relatively lower dust hazard but intensive mining may disrupt ecosystems and consume substantial energy. Both materials require controlled handling to minimize airborne particulates, while sustainable sourcing and proper workplace ventilation reduce health risks and environmental footprints in ceramic manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Project
Bentonite clay enhances plasticity and strength in porcelain, making it ideal for projects requiring durability and fine detail. Porcelain clay offers a smooth, white finish perfect for delicate, high-quality ceramics with a translucent appearance when fired. Selecting the right clay depends on the desired texture, firing temperature, and final aesthetic of your porcelain project.
Infographic: Bentonite vs Porcelain clay for Porcelain
 azmater.com
azmater.com