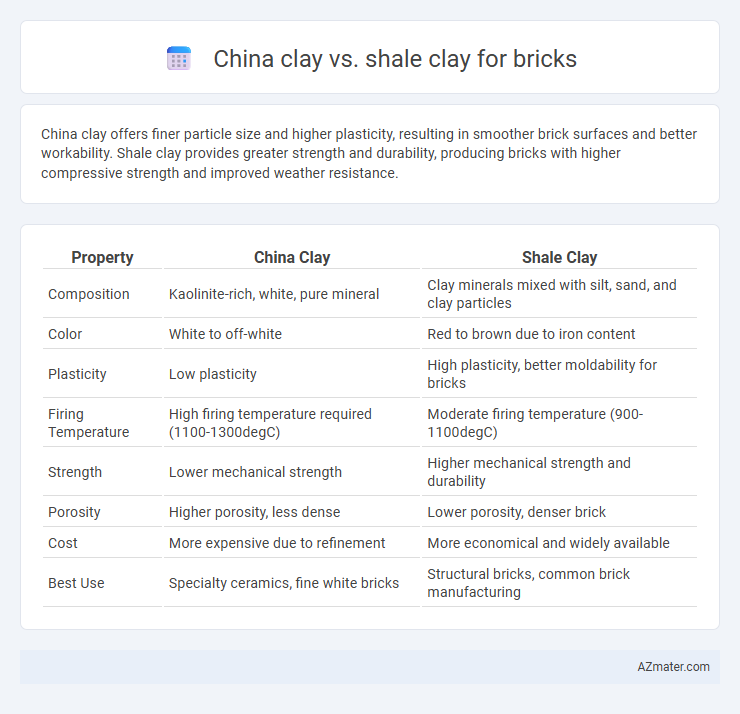
China clay offers finer particle size and higher plasticity, resulting in smoother brick surfaces and better workability. Shale clay provides greater strength and durability, producing bricks with higher compressive strength and improved weather resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | China Clay | Shale Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolinite-rich, white, pure mineral | Clay minerals mixed with silt, sand, and clay particles |
| Color | White to off-white | Red to brown due to iron content |
| Plasticity | Low plasticity | High plasticity, better moldability for bricks |
| Firing Temperature | High firing temperature required (1100-1300degC) | Moderate firing temperature (900-1100degC) |
| Strength | Lower mechanical strength | Higher mechanical strength and durability |
| Porosity | Higher porosity, less dense | Lower porosity, denser brick |
| Cost | More expensive due to refinement | More economical and widely available |
| Best Use | Specialty ceramics, fine white bricks | Structural bricks, common brick manufacturing |
Introduction to Clay Types in Brick Manufacturing
China clay, also known as kaolin, is a highly refined, white clay composed primarily of kaolinite, valued for its purity and plasticity in brick manufacturing, producing smooth, dense bricks with a lighter color. Shale clay, derived from compacted sedimentary rock rich in clay minerals, offers higher silica and alumina content, resulting in bricks with greater strength and durability but a darker, more variable color. The choice between China clay and shale clay significantly influences the physical properties, firing temperature, and final appearance of bricks in construction.
Overview of China Clay and Shale Clay
China clay, also known as kaolin, is a fine, white clay primarily composed of kaolinite mineral, valued for its high plasticity and purity, making it ideal for producing smooth and durable bricks with excellent firing properties. Shale clay, derived from weathered shale rock, contains a mixture of clay minerals, quartz, and silt, offering moderate plasticity and strength but often requiring preprocessing to remove impurities for brick production. The choice between China clay and shale clay depends on their mineral composition, plasticity, and firing behavior, which influence the texture, color, and mechanical properties of finished bricks.
Geological Origins: China Clay vs Shale Clay
China clay, also known as kaolin, originates from the chemical weathering of feldspathic rocks under humid conditions, resulting in a fine, white, and highly pure clay mineral predominantly composed of kaolinite. Shale clay forms from the compaction and lithification of silt and clay-sized particles in sedimentary environments, often containing various impurities and exhibiting a layered structure. The distinct geological origins influence their mineral composition, plasticity, and suitability for brick manufacturing applications.
Chemical Composition Comparison
China clay, primarily composed of kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), contains high levels of alumina and low iron oxide, which contributes to its white firing properties and chemical stability. Shale clay, rich in silica, alumina, and notable iron oxide content, tends to produce bricks with a reddish hue due to iron oxidation during firing. The higher silica and iron oxide concentration in shale clay affects the thermal expansion and color, making it less suitable for producing white or light-colored bricks compared to the purer chemical composition of China clay.
Physical Properties and Workability
China clay exhibits finer particle size and higher plasticity compared to shale clay, resulting in improved moldability and smoother brick surfaces. Shale clay typically has coarser particles and lower plasticity, which can lead to less uniform shaping but higher strength after firing due to greater silica content. The higher water retention and plastic range of China clay enhance workability, whereas shale clay's denser composition requires careful moisture control during brick manufacturing.
Firing Temperature and Energy Requirements
China clay typically requires a firing temperature between 1100degC and 1250degC, resulting in higher energy consumption compared to shale clay, which fires at lower temperatures around 900degC to 1050degC. The chemical composition of china clay, rich in kaolinite, demands more thermal energy to achieve vitrification, while shale clay's mixed mineralogy allows for efficient firing at reduced temperatures. Consequently, bricks made from shale clay offer energy savings and lower production costs without compromising structural integrity.
Color and Texture of Finished Bricks
China clay bricks typically exhibit a bright white to light cream color due to their high kaolinite content, resulting in a smooth and uniform texture that enhances the aesthetic appeal of finished bricks. Shale clay bricks, conversely, often display a range of reddish-brown to deep red hues attributed to higher iron oxide levels and possess a coarser texture with increased density, contributing to their robustness. The color and texture differences in bricks derived from China clay and shale clay significantly influence their selection for architectural and structural applications depending on desired visual and tactile qualities.
Durability and Strength Performance
China clay, known for its fine particle size and high kaolinite content, enhances brick strength and durability by improving plasticity and firing properties. Shale clay, composed of more varied mineral content including silts and fine sands, produces bricks with higher compressive strength but may be more prone to shrinkage and cracking. The choice between China clay and shale clay impacts brick performance based on the balance of strength, durability, and resistance to weathering in construction applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
China clay, or kaolin, is a highly refined material with lower impurities, resulting in cleaner combustion and reduced emissions during brick firing compared to shale clay, which contains heavier minerals and organic matter that can produce more pollutants. The extraction of china clay often involves less environmental disturbance and can be managed with better waste control, while shale clay mining tends to cause significant land degradation and higher energy consumption due to its harder composition. Sustainable brick production favors china clay for its lower carbon footprint and enhanced recyclability, contributing to reduced soil erosion and improved resource efficiency in construction materials.
Practical Applications and Cost Considerations
China clay, known for its high purity and fine particle size, offers excellent plasticity and workability, making it ideal for producing high-quality, smooth bricks with superior strength and durability. Shale clay, composed of compressed sedimentary particles, is abundant and cost-effective, providing good firing characteristics and thermal stability, suitable for standard brick manufacturing at a lower cost. In practical applications, China clay bricks are preferred for premium construction projects requiring enhanced aesthetics and performance, while shale clay bricks dominate large-scale, budget-sensitive construction due to their economic advantage and adequate strength.
Infographic: China clay vs Shale clay for Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com