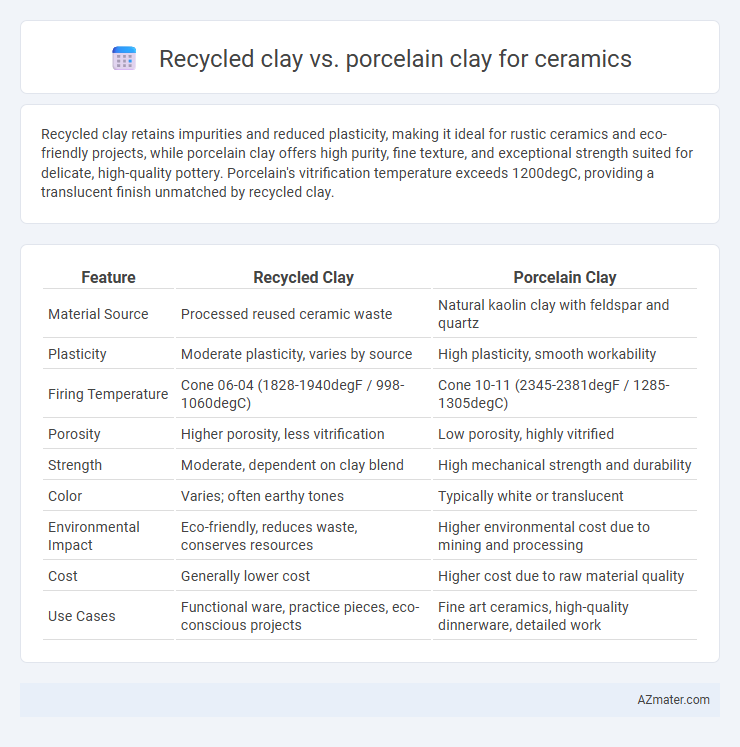
Recycled clay retains impurities and reduced plasticity, making it ideal for rustic ceramics and eco-friendly projects, while porcelain clay offers high purity, fine texture, and exceptional strength suited for delicate, high-quality pottery. Porcelain's vitrification temperature exceeds 1200degC, providing a translucent finish unmatched by recycled clay.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Processed reused ceramic waste | Natural kaolin clay with feldspar and quartz |
| Plasticity | Moderate plasticity, varies by source | High plasticity, smooth workability |
| Firing Temperature | Cone 06-04 (1828-1940degF / 998-1060degC) | Cone 10-11 (2345-2381degF / 1285-1305degC) |
| Porosity | Higher porosity, less vitrification | Low porosity, highly vitrified |
| Strength | Moderate, dependent on clay blend | High mechanical strength and durability |
| Color | Varies; often earthy tones | Typically white or translucent |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces waste, conserves resources | Higher environmental cost due to mining and processing |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to raw material quality |
| Use Cases | Functional ware, practice pieces, eco-conscious projects | Fine art ceramics, high-quality dinnerware, detailed work |
Introduction to Recycled and Porcelain Clays
Recycled clay is made by reclaiming and reprocessing previously fired or dried clay scraps, offering an eco-friendly alternative that reduces waste and conserves raw materials. Porcelain clay is a highly refined, kaolin-based clay known for its smooth texture, durability, and translucent quality when fired at high temperatures. Both clays serve distinct purposes in ceramics, with recycled clay prized for sustainability and porcelain clay valued for its strength and aesthetic appeal in fine pottery.
Material Composition: Recycled vs Porcelain Clay
Recycled clay contains a mixture of previously fired and fragmented clay particles blended with raw clay, resulting in variable mineral content and moisture levels, which can affect plasticity and firing behavior. Porcelain clay primarily consists of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, offering a purer and more consistent mineral composition known for its whiteness, translucency, and high vitrification temperature. The difference in material composition influences the workability, durability, and final appearance of ceramic products made from recycled versus porcelain clay.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Recycled clay reduces the demand for new raw materials, minimizing energy consumption and landfill waste in ceramics production. Porcelain clay, while valued for its purity and fine texture, requires higher firing temperatures, leading to increased carbon emissions. Choosing recycled clay supports circular economy practices and lowers overall environmental footprint in ceramic manufacturing.
Workability and Handling Differences
Recycled clay often contains impurities and varied particle sizes, resulting in less consistent plasticity and increased difficulty during shaping compared to porcelain clay. Porcelain clay exhibits higher plasticity, fine particle consistency, and smoother texture, which enhance workability and precise handling for detailed ceramic projects. The moisture content in recycled clay fluctuates more, requiring frequent adjustments to maintain optimal malleability, whereas porcelain clay retains moisture evenly, facilitating easier manipulation.
Firing Temperatures and Results
Recycled clay typically fires at lower temperatures, around cone 04 to cone 06 (about 1940degF to 2100degF), producing more porous and less vitrified ceramics compared to porcelain clay. Porcelain clay requires higher firing temperatures, generally between cone 10 and cone 11 (2381degF to 2462degF), resulting in a dense, glass-like, and highly durable finished product. The difference in firing temperatures directly impacts the strength, translucency, and water absorption rates of the final ceramic pieces.
Surface Texture and Finish
Recycled clay often exhibits a coarser surface texture due to the presence of small impurities and varied particle sizes, resulting in a more rustic, matte finish in ceramic pieces. Porcelain clay is renowned for its fine, homogenous particle structure that produces a smooth, glass-like surface and a high-quality, glossy finish after firing. The purity and plasticity of porcelain clay allow for delicate detail work and a refined, polished appearance unmatched by recycled clay.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Recycled clay often contains impurities and inconsistencies that can reduce the overall strength and durability of ceramics compared to porcelain clay. Porcelain clay typically exhibits high vitrification, resulting in a denser, harder, and more durable final product with superior resistance to chipping and cracking. The higher kaolin content in porcelain clay contributes to its enhanced mechanical properties, making it the preferred choice for strength-intensive ceramic applications.
Aesthetic Qualities: Color and Translucency
Recycled clay often displays a varied, earthy color palette with natural speckles and imperfections, creating a rustic, organic aesthetic ideal for artisanal ceramics. Porcelain clay is prized for its pure white color and exceptional translucency, enabling delicate, light-permeable pieces with a smooth, refined finish. These contrasting aesthetic qualities make recycled clay suitable for textured, natural designs while porcelain excels in elegant, translucent ceramic art.
Cost Analysis and Accessibility
Recycled clay offers a more cost-effective option for ceramics due to its lower raw material expenses and reduced waste, making it highly accessible for beginner potters and studios operating on tight budgets. Porcelain clay, while more expensive because of its refined composition and firing requirements, provides superior strength and a smooth, translucent finish favored in high-end ceramic production. Accessibility to recycled clay is broader, often sourced from local pottery scraps, whereas porcelain typically requires purchasing from specialized suppliers.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Ceramic Project
Recycled clay and porcelain clay offer distinct advantages depending on the ceramic project's requirements. Recycled clay is environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and ideal for rustic or experimental pieces, providing excellent plasticity and workability. Porcelain clay, known for its fine texture, strength, and translucency, is best suited for detailed, high-quality ceramics requiring a smooth, white finish.
Infographic: Recycled clay vs Porcelain clay for Ceramics
 azmater.com
azmater.com