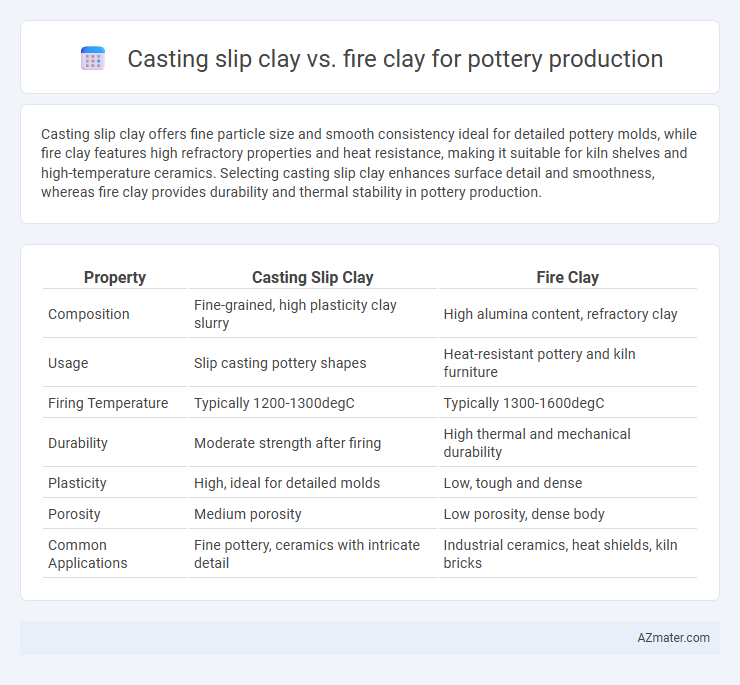
Casting slip clay offers fine particle size and smooth consistency ideal for detailed pottery molds, while fire clay features high refractory properties and heat resistance, making it suitable for kiln shelves and high-temperature ceramics. Selecting casting slip clay enhances surface detail and smoothness, whereas fire clay provides durability and thermal stability in pottery production.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Casting Slip Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fine-grained, high plasticity clay slurry | High alumina content, refractory clay |
| Usage | Slip casting pottery shapes | Heat-resistant pottery and kiln furniture |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 1200-1300degC | Typically 1300-1600degC |
| Durability | Moderate strength after firing | High thermal and mechanical durability |
| Plasticity | High, ideal for detailed molds | Low, tough and dense |
| Porosity | Medium porosity | Low porosity, dense body |
| Common Applications | Fine pottery, ceramics with intricate detail | Industrial ceramics, heat shields, kiln bricks |
Understanding Casting Slip Clay in Pottery
Casting slip clay is a finely ground, liquid form of clay specifically formulated for slip casting, allowing precise molding into detailed shapes and smooth surfaces in pottery production. It contains deflocculants to reduce viscosity, enabling thinner walls and faster drying without cracking compared to fire clay, which is coarser and used for structural or high-temperature applications. Understanding casting slip clay's composition and behavior is essential for achieving consistent quality and intricate designs in ceramic ware manufacturing.
What is Fire Clay? Key Characteristics
Fire clay is a type of refractory clay highly valued in pottery production for its exceptional heat resistance and durability, withstanding temperatures above 1,200degC (2,192degF). It exhibits low plasticity, high alumina content (typically 30-40%), and a coarse particle structure, making it ideal for creating kiln furniture, refractory ware, and high-temperature ceramics. Its stability during firing minimizes shrinkage and warping, ensuring consistent, robust ceramic products suitable for both functional and artistic pottery applications.
Differences in Composition: Casting Slip Clay vs Fire Clay
Casting slip clay primarily consists of finely ground kaolin, ball clay, and feldspar suspended in water, creating a smooth, fluid mixture ideal for slip casting processes in pottery production. Fire clay contains a higher percentage of refractory minerals like alumina and silica, providing superior heat resistance and durability, making it suitable for kiln furniture and high-temperature ceramic applications. The main compositional difference lies in particle size and mineral content, with casting slip clay formulated for workability and detail reproduction, while fire clay emphasizes thermal stability and strength.
Preparation Process: Slip Casting vs Hand-Building
Casting slip clay is prepared as a liquid mixture of finely ground clay and water, ideal for slip casting techniques that require pouring the slip into plaster molds for precise, detailed forms. Fire clay, known for its refractory properties and coarser texture, is typically wedged and shaped by hand in hand-building processes such as coiling or slab construction. Slip casting demands meticulous control of slurry consistency and deflocculant additives, while hand-building with fire clay involves manual manipulation and moisture regulation for structural integrity.
Workability and Handling of Each Clay Type
Casting slip clay offers superior fluidity and ease of pouring, enabling precise mold filling and intricate detail capture, making it ideal for complex pottery production. Fire clay, characterized by its coarse texture and plasticity, provides better structural integrity and workability for hand-building or throwing on the wheel, allowing potters to manipulate thicker forms effectively. While casting slip demands careful control of slurry consistency to prevent defects, fire clay's malleability supports diverse shaping techniques but requires longer drying times to avoid cracking.
Firing Temperatures and Shrinkage Comparison
Casting slip clay typically fires at lower temperatures, ranging from cone 06 (1828degF/998degC) to cone 04 (1940degF/1060degC), making it suitable for low-fire ceramics; it exhibits moderate shrinkage between 5-8% during drying and firing. Fire clay, known for its high refractory properties, is fired at higher temperatures, often between cone 08 (1760degF/960degC) to cone 10 (2345degF/1285degC), with significantly lower shrinkage rates around 1-3% due to its dense particle structure. The higher firing temperature tolerance and minimal shrinkage of fire clay make it ideal for stoneware and high-fire pottery, whereas casting slip clay is preferred for detailed slip casting in low-fire applications.
Surface Texture and Glazing Suitability
Casting slip clay offers a smoother, more uniform surface texture ideal for fine detailed pottery, while fire clay tends to have a coarser texture due to higher refractory content. The smooth surface of casting slip clay allows for better adherence and even distribution of glazes, enhancing the final aesthetic and finish. Fire clay's rougher texture can result in a more rustic glaze appearance but is preferred for its durability in high-temperature firings.
Strength and Durability of Finished Pieces
Fire clay exhibits superior strength and durability compared to casting slip clay, making it ideal for high-temperature pottery production. Its dense, refractory properties enable finished pieces to withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress more effectively. Casting slip clay, while easier to shape, results in less robust pottery suited for decorative or low-impact applications.
Typical Applications: When to Use Casting Slip or Fire Clay
Casting slip is ideal for producing fine, detailed ceramics such as porcelain or delicate figurines due to its fine particle size and fluid consistency, allowing for precise molds and smooth surfaces. Fire clay is best suited for functional pottery requiring high thermal resistance and durability, such as kiln furniture, firebricks, or heat-resistant pottery, because of its refractory properties and coarse texture. Selecting casting slip is preferable for decorative, lightweight pieces, while fire clay excels in applications needing structural strength and heat endurance.
Pros and Cons: Choosing the Right Clay for Your Pottery Project
Casting slip clay offers excellent fluidity and fine particle size, making it ideal for detailed and thin-walled pottery pieces, but it requires precise control during drying to avoid cracking. Fire clay is highly refractory, providing superior heat resistance and durability suited for functional pottery exposed to high temperatures, though it is typically coarser and less smooth in texture. Selecting between casting slip and fire clay depends on the desired pottery characteristics, balancing ease of shaping and surface detail with thermal stability and strength.
Infographic: Casting slip clay vs Fire clay for Pottery production
 azmater.com
azmater.com