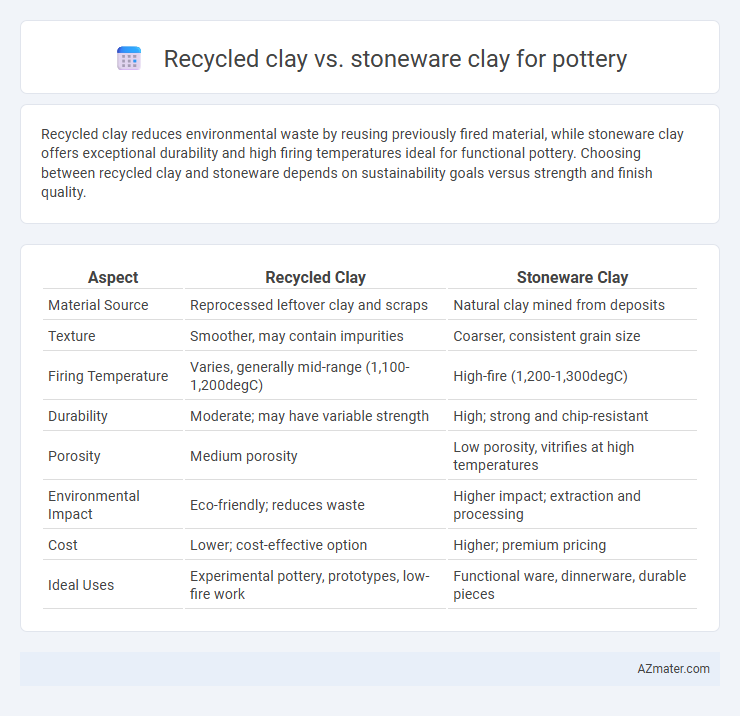
Recycled clay reduces environmental waste by reusing previously fired material, while stoneware clay offers exceptional durability and high firing temperatures ideal for functional pottery. Choosing between recycled clay and stoneware depends on sustainability goals versus strength and finish quality.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Recycled Clay | Stoneware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Reprocessed leftover clay and scraps | Natural clay mined from deposits |
| Texture | Smoother, may contain impurities | Coarser, consistent grain size |
| Firing Temperature | Varies, generally mid-range (1,100-1,200degC) | High-fire (1,200-1,300degC) |
| Durability | Moderate; may have variable strength | High; strong and chip-resistant |
| Porosity | Medium porosity | Low porosity, vitrifies at high temperatures |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; reduces waste | Higher impact; extraction and processing |
| Cost | Lower; cost-effective option | Higher; premium pricing |
| Ideal Uses | Experimental pottery, prototypes, low-fire work | Functional ware, dinnerware, durable pieces |
Introduction to Recycled Clay and Stoneware Clay
Recycled clay is made by reclaiming and reprocessing previously used clay, reducing waste and conserving natural resources in pottery production. Stoneware clay is a durable, non-porous material fired at high temperatures between 1200degC and 1300degC, prized for its strength and versatility. Comparing recycled clay and stoneware clay highlights differences in texture, plasticity, and firing requirements critical for potters choosing materials for sustainable and functional ceramic projects.
Understanding the Composition of Recycled Clay
Recycled clay consists of previously fired or unused clay that has been rehydrated and reprocessed to form a workable material, often containing a mix of grog, impurities, and varying particle sizes that affect its plasticity and firing behavior. Stoneware clay is a dense, non-porous type of clay composed primarily of kaolinite, feldspar, and quartz, which vitrifies at higher temperatures between 1200degC and 1300degC, resulting in a durable, stone-like finish. Understanding the composition of recycled clay is crucial for adjusting firing schedules and moisture content to achieve consistent results comparable to the more stable and naturally vitrifying stoneware clay.
Key Properties of Stoneware Clay for Pottery
Stoneware clay features high plasticity and durability, allowing potters to create functional and robust pottery pieces that withstand daily use. Its ability to vitrify at high firing temperatures results in dense, non-porous ceramics with excellent water resistance. Compared to recycled clay, stoneware clay provides superior strength, making it ideal for both artistic and utilitarian pottery applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Recycled clay significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing raw material extraction and decreasing landfill waste, promoting sustainable pottery practices. Stoneware clay, while durable and often preferred for high-fired ceramics, typically requires more extensive mining and energy-intensive firing processes that contribute to higher carbon emissions. Choosing recycled clay supports circular resource use and lowers the pottery studio's overall ecological footprint compared to traditional stoneware clay.
Workability and Texture Differences
Recycled clay offers a softer, more malleable workability due to its finer particles and added moisture, making it ideal for detailed hand-building techniques. Stoneware clay boasts a denser texture with higher plasticity, providing stronger structural integrity and better resistance to warping during firing. The distinct granular composition of stoneware allows for smoother surface finishes, while recycled clay may retain more impurities affecting texture uniformity.
Firing Temperatures and Performance
Recycled clay typically fires at lower temperatures, around cone 04 to cone 06 (approximately 1940degF to 2167degF), making it suitable for low-fire pottery but less durable compared to stoneware. Stoneware clay matures at higher temperatures, usually between cone 5 and cone 10 (approximately 2167degF to 2345degF), resulting in a denser, more vitrified, and durable ceramic body ideal for functional ware. The higher firing temperature of stoneware enhances its water resistance and strength, whereas recycled clay may remain more porous and fragile if fired beyond its optimal range.
Cost Comparison and Accessibility
Recycled clay generally offers a cost-effective option for pottery due to lower material expenses and the ability to reuse waste clay from previous projects, making it accessible for hobbyists and educators. Stoneware clay, while often more expensive, provides durability and a finer finish favored by professional potters, but its cost and availability can vary depending on quality and local suppliers. Access to recycled clay depends on proximity to pottery studios or recycling programs, whereas stoneware clay typically requires purchasing from specialized ceramic suppliers or stores.
Suitability for Beginners vs. Experienced Potters
Recycled clay offers a cost-effective and eco-friendly option ideal for beginners due to its forgiving texture and lower firing temperature, which reduces the risk of cracking during the learning process. Stoneware clay, known for its durability and high firing temperature, suits experienced potters seeking strength and a professional finish in functional or decorative ware. Beginners benefit from recycled clay's plasticity and ease of handling, while seasoned artisans prefer stoneware's robust properties for advanced techniques and long-term use.
Artistic Results and Surface Finishes
Recycled clay offers unique textural variations and organic imperfections that enhance the artistic appeal of pottery, creating distinctive surface finishes with natural color shifts and varied firing responses. Stoneware clay provides a consistent texture and high plasticity, allowing for smooth, durable surfaces and precise detailing in both functional and decorative pieces. Artists seeking a rustic, earthy aesthetic might prefer recycled clay, while those pursuing refined, polished finishes often choose stoneware for its stability and predictable results.
Choosing the Right Clay: Factors to Consider
Recycled clay offers eco-friendly benefits and cost savings but may contain impurities affecting workability and final product strength compared to stoneware clay, which provides durability and high firing temperature tolerance ideal for functional pottery. Choosing between recycled and stoneware clay depends on factors such as project requirements, firing temperature compatibility, texture preferences, and environmental impact goals. Evaluating clay plasticity, shrinkage rates, and potential contamination ensures selection aligns with desired pottery quality and sustainability considerations.
Infographic: Recycled clay vs Stoneware clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com