Colored clay provides vibrant hues and natural pigmentation for decorative tiles, while ball clay offers superior plasticity and workability, enhancing tile strength and durability. Combining colored clay with ball clay can optimize both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity in tile production.
Table of Comparison
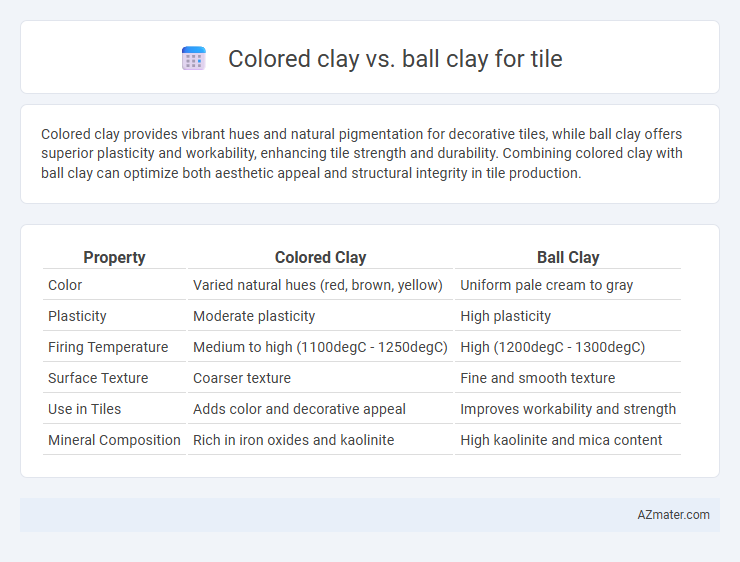
| Property | Colored Clay | Ball Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Varied natural hues (red, brown, yellow) | Uniform pale cream to gray |
| Plasticity | Moderate plasticity | High plasticity |
| Firing Temperature | Medium to high (1100degC - 1250degC) | High (1200degC - 1300degC) |
| Surface Texture | Coarser texture | Fine and smooth texture |
| Use in Tiles | Adds color and decorative appeal | Improves workability and strength |
| Mineral Composition | Rich in iron oxides and kaolinite | High kaolinite and mica content |
Introduction to Colored Clay and Ball Clay
Colored clay exhibits natural pigments such as iron oxide and manganese, providing rich hues like red, yellow, and brown, ideal for decorative tiles with vibrant color variations. Ball clay, characterized by its fine particle size, high plasticity, and strong binding properties, is essential for enhancing the workability and structural integrity of tile bodies. Combining colored clay with ball clay allows tile manufacturers to achieve both aesthetic appeal and optimal performance in ceramic tile production.
Composition Differences Between Colored Clay and Ball Clay
Colored clay primarily contains higher amounts of iron oxides and other natural pigments, giving it its distinctive hues, while ball clay consists mainly of kaolinite, mica, and quartz, resulting in a finer texture and higher plasticity. The mineral content in colored clay affects the fired color and strength of tiles, whereas ball clay enhances workability and bonding due to its fine particle size and plastic properties. These compositional differences influence the tile's aesthetic qualities and mechanical performance during shaping and firing processes.
Physical Properties: Strength, Plasticity, and Texture
Colored clay typically exhibits higher plasticity and a coarser texture, making it ideal for decorative tiles that require intricate shaping and vibrant finishes. Ball clay, known for its fine particles and exceptional plasticity, provides superior strength and workability, enhancing tile durability and smoothness. The choice between colored clay and ball clay significantly impacts tile performance, as ball clay offers higher tensile strength while colored clay contributes unique aesthetic textures.
Color Variations and Their Impact on Tiles
Colored clay offers a wide range of natural color variations, from reds to yellows and browns, which directly influence the aesthetic appeal and design flexibility of tiles. Ball clay, typically white or light gray, provides a neutral base that enhances glaze brightness and allows for more precise color control through finishes. The choice between colored and ball clay affects tile color vibrancy, durability, and suitability for different architectural styles.
Firing Behavior: Shrinkage and Maturity Temperatures
Colored clay exhibits lower shrinkage rates and matures at higher temperatures, making it suitable for durable, vibrant tiles with consistent dimensional stability during firing. Ball clay shows higher plasticity with increased shrinkage, maturing at lower temperatures, which aids in shaping but requires precise control to avoid warping or cracking. Understanding these differences in firing behavior informs optimal kiln settings to achieve desired tile quality and performance.
Workability and Shaping for Tile Production
Colored clay offers enhanced workability due to its balanced plasticity, making it ideal for intricate tile shaping and detailed designs. Ball clay provides superior plasticity and fine particle size, enabling excellent moldability and smooth surface finishes in tile production. The choice between colored clay and ball clay depends on the desired tile texture and ease of shaping during manufacturing.
Glaze Compatibility and Surface Finish
Colored clay offers excellent glaze compatibility due to its inherent pigments that react uniquely with various glazes, producing vibrant and diverse surface finishes. Ball clay, known for its high plasticity and fine particle size, enhances glaze adhesion and contributes to a smooth, consistent surface finish on tiles. Selecting the appropriate clay type directly influences glaze behavior and the final aesthetic quality of ceramic tiles.
Environmental Considerations in Sourcing Clays
Colored clay typically involves natural mineral pigments requiring minimal processing, resulting in lower carbon emissions during extraction and preparation compared to ball clay, which often demands intensive beneficiation and drying processes. The environmental impact of sourcing colored clay is generally reduced due to localized deposits, limiting transportation-related pollution, whereas ball clay mining can involve extensive soil disruption and water usage in refining stages. Sustainable clay sourcing prioritizes reducing habitat disturbance and optimizing resource efficiency, with colored clay presenting advantages in preserving ecological balance for tile manufacturing.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Colored clay typically costs more than ball clay due to the natural pigmentation and limited regional deposits, making it less readily available in bulk. Ball clay, prized for its plasticity and fine particle size, is more abundant globally and generally offers a lower-cost option for tile production. Manufacturers often balance cost and availability by blending ball clay with minimal amounts of colored clay to achieve desired tile aesthetics while maintaining budget efficiency.
Best Use Cases: When to Choose Colored Clay vs Ball Clay for Tiles
Colored clay offers natural pigmentation and is ideal for decorative tiles requiring vibrant hues and unique textures, enhancing aesthetic appeal without additional coloring agents. Ball clay provides excellent plasticity and strength, making it best suited for tiles that demand high durability and precise molding, especially in structural or high-traffic applications. Selecting colored clay benefits artistic, low-impact surfaces, while ball clay is preferred for functional tiles needing robust performance and uniformity.
Infographic: Colored clay vs Ball clay for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com