Structural ceramic tiles offer superior strength and durability due to their dense, non-porous composition, making them ideal for high-traffic areas. Stoneware tiles, while less dense, provide excellent aesthetic versatility and moisture resistance, suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Table of Comparison
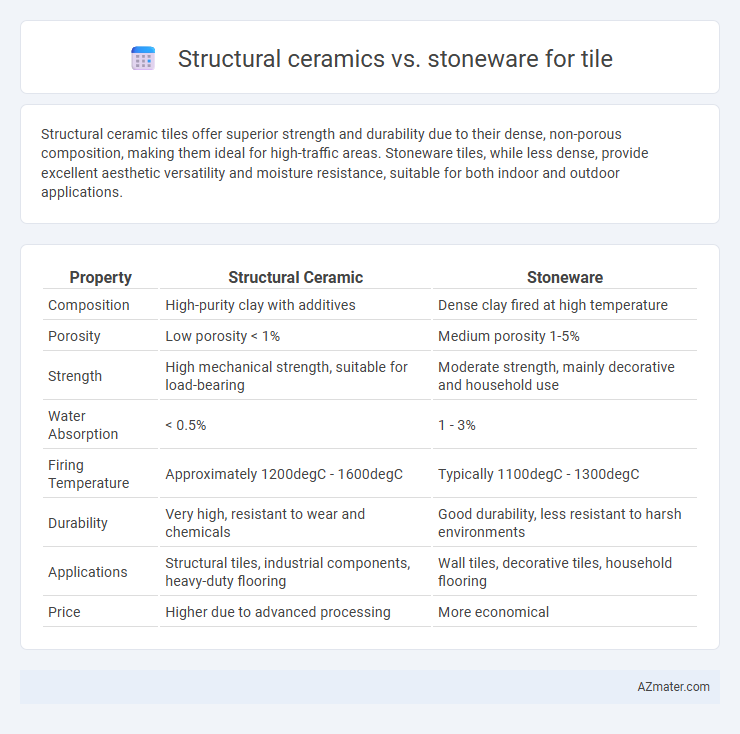
| Property | Structural Ceramic | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High-purity clay with additives | Dense clay fired at high temperature |
| Porosity | Low porosity < 1% | Medium porosity 1-5% |
| Strength | High mechanical strength, suitable for load-bearing | Moderate strength, mainly decorative and household use |
| Water Absorption | < 0.5% | 1 - 3% |
| Firing Temperature | Approximately 1200degC - 1600degC | Typically 1100degC - 1300degC |
| Durability | Very high, resistant to wear and chemicals | Good durability, less resistant to harsh environments |
| Applications | Structural tiles, industrial components, heavy-duty flooring | Wall tiles, decorative tiles, household flooring |
| Price | Higher due to advanced processing | More economical |
Introduction to Structural Ceramic and Stoneware Tiles
Structural ceramic tiles are engineered from dense, high-strength clay mixtures fired at extremely high temperatures, resulting in exceptional durability and low porosity suitable for heavy-duty applications. Stoneware tiles, made from naturally occurring clays and fired at moderate temperatures, offer a balance of hardness and water resistance with a slightly more porous surface, ideal for residential and commercial flooring. Both types provide versatile design options, but structural ceramics excel in environments requiring superior wear resistance and longevity.
Material Composition: Structural Ceramic vs Stoneware
Structural ceramic tiles are primarily composed of dense clay and minerals fired at high temperatures, resulting in a strong, durable material with low porosity. Stoneware tiles feature a mixture of clay and non-clay minerals, such as feldspar and silica, fired at slightly lower temperatures than structural ceramics, producing a more porous but tough tile. The higher firing temperature and refined composition of structural ceramics contribute to enhanced strength and resistance compared to the relatively more absorbent stoneware tiles.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Structural ceramic tiles are produced through high-temperature firing of refined clay with minimal additives, resulting in dense, durable products ideal for heavy-duty applications. Stoneware tiles undergo a similar firing process but utilize a mixture of clay and other natural materials, offering enhanced water resistance and strength due to vitrification. Manufacturing processes for both involve pressing, drying, and firing stages, yet structural ceramics demand more precise control over raw material purity and firing temperatures to achieve optimal mechanical properties.
Durability and Strength Factors
Structural ceramics exhibit superior durability and strength compared to stoneware tiles, making them ideal for high-traffic and industrial applications. Their dense microstructure and low porosity contribute to increased resistance against abrasion, impact, and thermal shock. Stoneware tiles offer good durability but generally have higher porosity and lower mechanical strength, limiting their use in environments requiring extreme wear resistance.
Porosity and Water Absorption Differences
Structural ceramics exhibit significantly lower porosity levels, typically below 0.5%, compared to stoneware which ranges from 0.5% to 3%. This reduced porosity in structural ceramics results in water absorption rates often under 0.5%, enhancing durability and resistance to frost and chemical damage. Stoneware tiles, while more porous, offer moderate absorption rates between 0.5% and 3%, making them suitable for less demanding environments where some moisture exposure is expected.
Aesthetic Options and Surface Finishes
Structural ceramics offer a wide variety of vibrant color palettes and intricate patterns, making them ideal for highly customized tile designs, while stoneware typically provides more earthy and neutral tones with natural textures. Surface finishes for structural ceramics include glossy, matte, and textured options that enhance visual depth and reflectivity, whereas stoneware often features matte or satin finishes that emphasize rustic and organic aesthetics. Both materials can be tailored with specialized glazes and surface treatments, but structural ceramics generally allow for greater precision and complexity in aesthetic detailing.
Cost Considerations: Upfront and Long-Term
Structural ceramic tiles generally have a higher upfront cost compared to stoneware tiles due to their enhanced durability and resistance to wear. Stoneware offers a more budget-friendly initial investment but may incur greater long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating cost efficiency involves balancing structural ceramic's longevity against stoneware's affordability for specific tile applications.
Ideal Applications for Structural Ceramic Tiles
Structural ceramic tiles, known for their high strength and low porosity, are ideal for heavy-duty applications such as industrial flooring, commercial spaces, and areas with high mechanical stress. Unlike stoneware, which is more suitable for residential or decorative uses due to its moderate durability and higher water absorption, structural ceramics withstand abrasion, impact, and chemical exposure effectively. Their superior mechanical properties make them the preferred choice for environments requiring long-lasting, resilient tile solutions.
Best Uses for Stoneware Tiles
Stoneware tiles are best suited for residential flooring, kitchen backsplashes, and bathroom walls due to their durability, water resistance, and variety of finishes. While structural ceramics excel in industrial and exterior applications requiring high mechanical strength, stoneware offers the ideal balance of toughness and aesthetic versatility for indoor environments. Their cost-effectiveness and ability to handle moderate foot traffic make stoneware tiles a practical choice for everyday home use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Structural ceramics and stoneware tiles differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with structural ceramics often sourced from abundant natural clay materials that require high firing temperatures, leading to increased energy consumption and carbon emissions. Stoneware tiles typically utilize dense, durable clay compositions that allow for lower water absorption rates and longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing resource depletion. Both materials can be produced using recycled content and energy-efficient kiln technologies, but stoneware's inherent durability and lower porosity often make it a more sustainable choice for long-term building projects.
Infographic: Structural ceramic vs Stoneware for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com