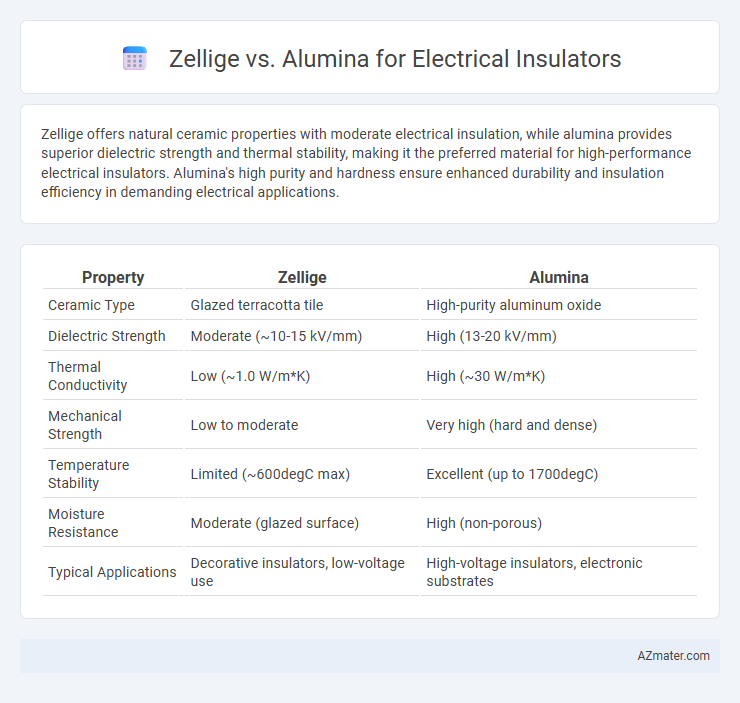
Zellige offers natural ceramic properties with moderate electrical insulation, while alumina provides superior dielectric strength and thermal stability, making it the preferred material for high-performance electrical insulators. Alumina's high purity and hardness ensure enhanced durability and insulation efficiency in demanding electrical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zellige | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Type | Glazed terracotta tile | High-purity aluminum oxide |
| Dielectric Strength | Moderate (~10-15 kV/mm) | High (13-20 kV/mm) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (~1.0 W/m*K) | High (~30 W/m*K) |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate | Very high (hard and dense) |
| Temperature Stability | Limited (~600degC max) | Excellent (up to 1700degC) |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate (glazed surface) | High (non-porous) |
| Typical Applications | Decorative insulators, low-voltage use | High-voltage insulators, electronic substrates |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators, crucial for preventing unwanted electrical current flow, are materials characterized by high resistivity and dielectric strength. Zellige, a traditional Moroccan mosaic tile made from clay, offers moderate insulation but is primarily decorative with limited application in high-voltage environments. Alumina (Al2O3), a ceramic material, exhibits superior electrical insulation properties, high thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance electrical insulators in industrial and electronic applications.
What is Zellige?
Zellige is a traditional Moroccan ceramic tile made from natural clay, known for its intricate geometric patterns and glossy, glazed surface that provides excellent electrical insulation properties due to its high dielectric strength. Alumina, or aluminum oxide, is a synthetic ceramic material widely used in electrical insulators for its superior thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and high electrical resistivity. Comparing the two, Zellige offers aesthetic appeal and decent insulation but lacks the high-temperature resistance and robustness of alumina in demanding electrical applications.
What is Alumina?
Alumina, also known as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), is a widely used ceramic material for electrical insulators due to its excellent dielectric strength, high thermal conductivity, and outstanding mechanical properties. It offers superior resistance to electrical breakdown, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion compared to traditional materials like Zellige, making it ideal for high-voltage insulator applications. Alumina's high purity and uniform microstructure contribute to its reliability and durability in demanding electrical environments.
Material Composition: Zellige vs Alumina
Zellige, a natural ceramic material with a high content of silica and clay minerals, offers moderate electrical insulation due to its heterogeneous microstructure. Alumina (Al2O3), a synthetic oxide ceramic composed primarily of aluminum oxide, provides superior electrical insulating properties attributed to its high purity and crystalline structure. The dense, uniform composition of alumina enhances dielectric strength and thermal stability, making it more efficient than zellige for electrical insulator applications.
Electrical Properties Comparison
Zellige, a traditional Moroccan ceramic, exhibits moderate electrical insulating properties with dielectric strength typically around 10-15 kV/mm, suitable for low to medium voltage applications. Alumina (Al2O3) offers superior electrical insulation due to its high dielectric strength exceeding 20 kV/mm and excellent dielectric constant of approximately 9.8, making it ideal for high-performance and high-frequency electrical insulators. The low electrical conductivity and high resistivity of alumina (above 10^14 O*cm) outperform zellige, ensuring better insulation reliability and thermal stability in demanding electrical environments.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Zellige ceramic insulators exhibit superior thermal resistance with a high melting point around 1100degC, enabling stable performance in high-temperature environments, whereas alumina offers exceptional thermal conductivity and withstands temperatures up to 1700degC, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. Alumina's inherent electrical insulation combined with its thermal stability ensures minimal thermal expansion and enhanced durability under thermal cycling, while Zellige provides a unique aesthetic but with comparatively lower thermal and mechanical performance. For electrical insulation demanding rigorous thermal management and longevity, alumina is generally preferred due to its optimized balance of thermal resistance and electrical insulation properties.
Durability and Longevity
Zellige tiles, made from natural clay, exhibit moderate electrical insulating properties but tend to have lower durability and shorter longevity compared to alumina. Alumina (aluminum oxide) boasts exceptional mechanical strength, high thermal stability, and superior resistance to wear and corrosion, making it ideal for long-term electrical insulation applications. The superior hardness and chemical inertness of alumina ensure prolonged service life in harsh industrial environments, outperforming zellige in durability and sustained insulation performance.
Cost Effectiveness Analysis
Zellige, a traditional Moroccan ceramic tile, offers lower initial material costs compared to high-purity alumina, making it a budget-friendly option for certain electrical insulation applications. Alumina's superior thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and high dielectric strength justify its higher price for performance-critical scenarios, reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs. Cost-effectiveness analysis favors Zellige in low-demand environments, while alumina ensures reliability and durability in high-voltage and industrial insulators.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Zellige, a natural ceramic material made from clay, offers superior environmental benefits compared to alumina, as it is biodegradable, sourced from abundant raw materials, and requires less energy-intensive processing. Alumina, although widely used for its excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength, involves energy-heavy manufacturing and mining processes that contribute significantly to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Choosing Zellige supports sustainability initiatives by reducing environmental impact throughout production while maintaining effective electrical insulation properties.
Which is Better: Zellige or Alumina?
Alumina offers superior electrical insulation performance compared to Zellige, with a higher dielectric strength and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. Zellige, a traditional Moroccan ceramic tile, has limited electrical insulating properties and is not typically used in advanced electrical components. For demanding electrical insulator applications, alumina's mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and consistent manufacturing standards make it the better choice over Zellige.
Infographic: Zellige vs Alumina for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com