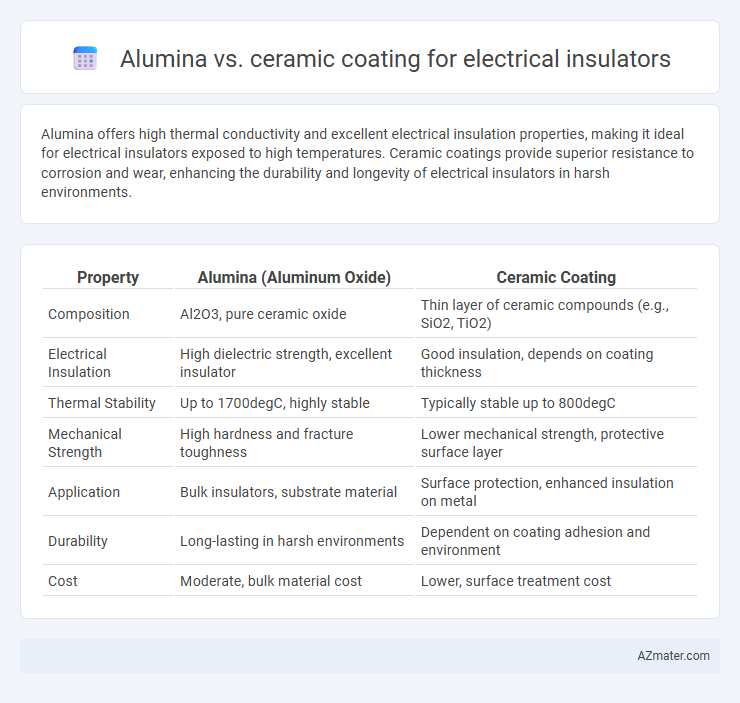
Alumina offers high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for electrical insulators exposed to high temperatures. Ceramic coatings provide superior resistance to corrosion and wear, enhancing the durability and longevity of electrical insulators in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Al2O3, pure ceramic oxide | Thin layer of ceramic compounds (e.g., SiO2, TiO2) |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength, excellent insulator | Good insulation, depends on coating thickness |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1700degC, highly stable | Typically stable up to 800degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High hardness and fracture toughness | Lower mechanical strength, protective surface layer |
| Application | Bulk insulators, substrate material | Surface protection, enhanced insulation on metal |
| Durability | Long-lasting in harsh environments | Dependent on coating adhesion and environment |
| Cost | Moderate, bulk material cost | Lower, surface treatment cost |
Introduction to Electrical Insulator Coatings
Electrical insulator coatings such as alumina and ceramic play a critical role in enhancing the performance and durability of electrical components by providing high dielectric strength and thermal stability. Alumina coatings offer excellent electrical insulation, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength, making them suitable for high-voltage applications and harsh environments. Ceramic coatings provide superior thermal resistance, chemical inertness, and electrical insulation, often used in advanced electrical systems requiring long-term reliability and protection against extreme conditions.
Overview of Alumina Coatings
Alumina coatings, primarily composed of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), provide superior electrical insulation and thermal stability for electrical insulators, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. These coatings exhibit excellent resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and high temperatures, which enhances the durability and lifespan of insulators in harsh environments. Alumina's high dielectric strength and chemical inertness contribute to reliable performance in power transmission and electronic insulation systems compared to generic ceramic coatings.
Overview of Ceramic Coatings
Ceramic coatings for electrical insulators provide superior dielectric strength and thermal stability compared to alumina, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. These coatings exhibit excellent resistance to environmental degradation, including moisture, UV radiation, and chemical exposure, enhancing insulator longevity and performance. Their nanostructured composition ensures enhanced surface hardness and reduced electrical conductivity, minimizing leakage currents and improving overall insulation reliability.
Material Properties Comparison
Alumina (Al2O3) offers superior thermal conductivity and excellent mechanical strength compared to traditional ceramic coatings, enhancing electrical insulator durability under high temperatures. Ceramic coatings, typically composed of materials like silicon carbide or zirconia, provide exceptional chemical resistance and electrical insulation but generally have lower thermal conductivity than alumina. The choice between alumina and ceramic coatings depends on the required balance between thermal management, mechanical robustness, and chemical stability in electrical insulator applications.
Electrical Performance Analysis
Alumina coatings exhibit superior electrical insulation properties due to their high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity, making them ideal for high-voltage insulators. Ceramic coatings, often composed of silicon carbide or zirconia, offer excellent thermal stability and mechanical durability but generally have slightly lower dielectric strength compared to alumina. Electrical performance analysis shows alumina's consistent resistivity and breakdown voltage outperform typical ceramic coatings in preventing leakage currents and dielectric failure under operational stresses.
Durability and Lifespan
Alumina coatings provide excellent durability and withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments, making them ideal for electrical insulators in harsh conditions. Ceramic coatings offer superior resistance to wear, chemical attack, and electrical stress, extending the insulator's lifespan significantly in demanding applications. Both materials enhance insulation performance, but ceramics typically deliver longer operational life due to their robustness against environmental degradation.
Thermal Conductivity and Resistance
Alumina offers high thermal conductivity ranging from 20 to 30 W/m*K, making it efficient for heat dissipation in electrical insulators. Ceramic coatings, typically based on silica or zirconia, exhibit lower thermal conductivity values around 1 to 3 W/m*K but provide excellent electrical resistance and thermal insulation. The choice between alumina and ceramic coatings depends on balancing the need for effective heat transfer versus superior electrical insulation and thermal resistance in high-voltage applications.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Alumina coatings provide a cost-effective solution for electrical insulators due to the lower raw material and processing expenses compared to advanced ceramic coatings. Manufacturing alumina coatings typically involves simpler techniques like plasma spraying or thermal spraying, reducing production time and equipment complexity. Ceramic coatings offer superior dielectric properties and enhanced durability but require more specialized fabrication methods such as chemical vapor deposition, which increases manufacturing costs and complexity.
Application Suitability: Alumina vs. Ceramic
Alumina offers excellent mechanical strength and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-voltage electrical insulators in power transmission and distribution systems. Ceramic coatings provide superior surface hardness, chemical resistance, and weatherability, enhancing insulator lifespan in outdoor and harsh environmental applications. The choice between alumina and ceramic coatings depends on specific operational conditions, with alumina favored for structural integrity and ceramic coatings preferred for protective surface performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Insulator Coating
Alumina offers excellent thermal conductivity and high dielectric strength, making it ideal for high-voltage electrical insulators requiring robust heat dissipation. Ceramic coatings provide superior chemical resistance and mechanical durability, enhancing insulator lifespan in harsh environments. Selecting the best insulator coating depends on specific operational conditions, prioritizing alumina for thermal management and ceramics for environmental protection.
Infographic: Alumina vs Ceramic coating for Electrical insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com