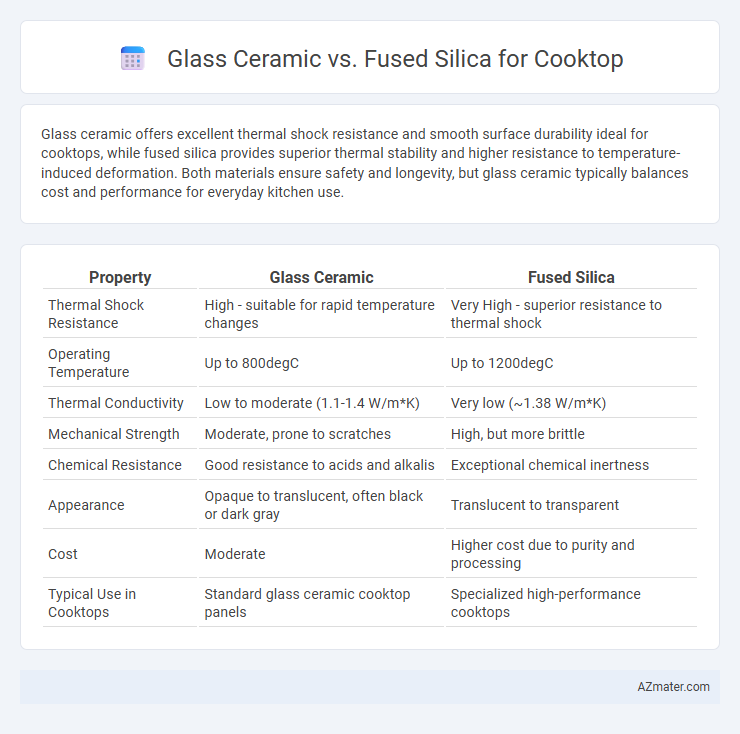
Glass ceramic offers excellent thermal shock resistance and smooth surface durability ideal for cooktops, while fused silica provides superior thermal stability and higher resistance to temperature-induced deformation. Both materials ensure safety and longevity, but glass ceramic typically balances cost and performance for everyday kitchen use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Ceramic | Fused Silica |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High - suitable for rapid temperature changes | Very High - superior resistance to thermal shock |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 800degC | Up to 1200degC |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to moderate (1.1-1.4 W/m*K) | Very low (~1.38 W/m*K) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, prone to scratches | High, but more brittle |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Exceptional chemical inertness |
| Appearance | Opaque to translucent, often black or dark gray | Translucent to transparent |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher cost due to purity and processing |
| Typical Use in Cooktops | Standard glass ceramic cooktop panels | Specialized high-performance cooktops |
Introduction to Cooktop Surface Materials
Glass ceramic and fused silica are two prominent cooktop surface materials known for their durability and heat resistance. Glass ceramic offers excellent thermal shock resistance and smooth aesthetics, making it a popular choice for induction and radiant cooktops. Fused silica, with its superior thermal stability and high purity, provides enhanced heat distribution and resistance to thermal stress, often favored in high-performance cooking appliances.
Understanding Glass Ceramic: Properties and Composition
Glass ceramic cooktops feature a unique composition of crystalline and glassy phases that create a durable, heat-resistant surface ideal for cooking. These materials exhibit low thermal expansion, allowing rapid temperature changes without cracking or warping, and provide excellent thermal shock resistance. Engineered from controlled crystallization of glass, glass ceramic surfaces combine strength, smoothness, and transparency tailored for efficient heat conduction and aesthetic appeal in modern cooktops.
What is Fused Silica? Key Features and Uses
Fused silica is a high-purity glass made from non-crystalline silicon dioxide with exceptional thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and high resistance to heat and chemical corrosion. Key features include its superior thermal shock resistance, optical transparency in ultraviolet to infrared wavelengths, and excellent electrical insulation properties. Common uses of fused silica in cooktops involve durable, heat-resistant surfaces that withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it ideal for high-performance cooking appliances.
Heat Resistance: Glass Ceramic vs Fused Silica
Glass ceramic cooktops exhibit excellent thermal shock resistance, handling rapid temperature changes up to approximately 750degC without cracking, making them ideal for household cooking. Fused silica, known for its superior heat resistance, tolerates temperatures above 1000degC and has an exceptionally low coefficient of thermal expansion, reducing the risk of thermal stress and deformation during intense heating. The choice between glass ceramic and fused silica hinges on the specific heat exposure and mechanical durability required for cooktop applications.
Thermal Shock Durability: Which Material Performs Better?
Glass ceramic cooktops exhibit superior thermal shock durability compared to fused silica, making them highly resistant to sudden temperature changes and rapid heating or cooling cycles. The crystalline structure in glass ceramics enhances their ability to withstand extreme temperature fluctuations without cracking or warping. Fused silica, while offering excellent thermal insulation, is more susceptible to thermal shock due to its amorphous nature, leading to potential damage under abrupt temperature shifts.
Scratch and Impact Resistance Comparison
Glass ceramic cooktops offer superior scratch resistance due to their crystalline structure, which hardens the surface and minimizes abrasions from cookware. Fused silica, known for its exceptional thermal shock resistance, exhibits better impact resistance but is generally more prone to scratches compared to glass ceramic. When balancing durability, glass ceramic provides a harder surface less susceptible to everyday scratches, while fused silica excels in absorbing impacts without cracking.
Aesthetic Options: Colors and Designs Available
Glass ceramic cooktops offer a wide range of color options and sleek, glossy finishes that enhance modern kitchen aesthetics. Fused silica cooktops typically feature a more limited palette, often in classic black or neutral tones, prioritizing durability over design variety. The advanced manufacturing process of glass ceramic allows for custom patterns and textures, making it a preferred choice for stylish, contemporary kitchen designs.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Glass ceramic cooktops require gentle cleaning with non-abrasive cleaners and soft cloths to prevent scratches and maintain smooth surfaces, while fused silica cooktops offer superior thermal shock resistance and can withstand more aggressive cleaning agents without damage. Both materials resist stains effectively, but glass ceramics may show smudges and require frequent wiping, whereas fused silica surfaces tend to retain a clearer finish with less upkeep. Regular maintenance of glass ceramic involves timely removal of spills to avoid etching, while fused silica's durability reduces the frequency of deep cleaning.
Cost Considerations for Glass Ceramic and Fused Silica Cooktops
Glass ceramic cooktops generally offer a more cost-effective option due to their lower manufacturing expenses and widespread availability, making them popular in both mid-range and budget kitchen appliances. Fused silica cooktops, known for superior thermal shock resistance and durability, tend to be priced higher, reflecting the advanced material technology and enhanced performance characteristics. When budgeting for a cooktop, consumers should weigh the upfront cost of glass ceramic against the long-term benefits and potential savings associated with fused silica's longevity and thermal efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Cooktop
Glass ceramic cooktops offer superior thermal shock resistance and aesthetic versatility, making them ideal for modern kitchens with rapid temperature changes. Fused silica provides exceptional durability and higher resistance to scratches and abrasion, suitable for heavy-duty cooking environments. Selecting the right material depends on your cooking style, durability needs, and budget, with glass ceramic favored for everyday use and fused silica preferred for long-term resilience.
Infographic: Glass Ceramic vs Fused Silica for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com