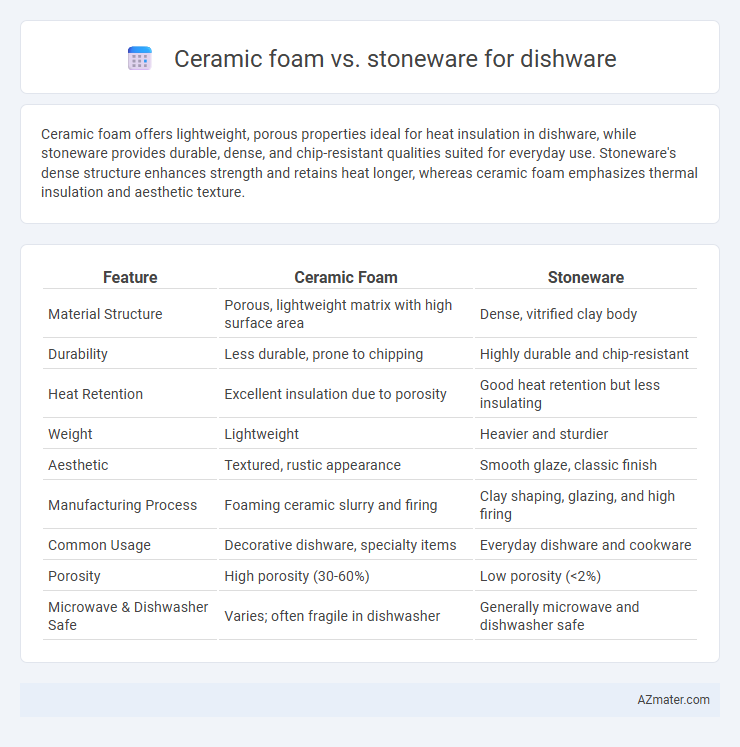
Ceramic foam offers lightweight, porous properties ideal for heat insulation in dishware, while stoneware provides durable, dense, and chip-resistant qualities suited for everyday use. Stoneware's dense structure enhances strength and retains heat longer, whereas ceramic foam emphasizes thermal insulation and aesthetic texture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Foam | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Structure | Porous, lightweight matrix with high surface area | Dense, vitrified clay body |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to chipping | Highly durable and chip-resistant |
| Heat Retention | Excellent insulation due to porosity | Good heat retention but less insulating |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier and sturdier |
| Aesthetic | Textured, rustic appearance | Smooth glaze, classic finish |
| Manufacturing Process | Foaming ceramic slurry and firing | Clay shaping, glazing, and high firing |
| Common Usage | Decorative dishware, specialty items | Everyday dishware and cookware |
| Porosity | High porosity (30-60%) | Low porosity (<2%) |
| Microwave & Dishwasher Safe | Varies; often fragile in dishwasher | Generally microwave and dishwasher safe |
Introduction to Ceramic Foam and Stoneware
Ceramic foam, made from porous materials with a lightweight structure, offers superior insulation and thermal shock resistance compared to traditional stoneware. Stoneware, a dense and durable type of pottery fired at high temperatures, provides excellent strength and chip resistance ideal for daily dishware use. Both materials differ fundamentally in composition and functional properties, influencing their suitability for various culinary applications.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Ceramic foam dishware features a porous structure created by introducing gas or foaming agents into the clay mixture before firing, resulting in lightweight, insulating properties ideal for heat retention. Stoneware is crafted from dense, non-porous clay composed primarily of kaolinite, feldspar, and quartz, fired at high temperatures (usually 1200-1300degC) to achieve durability and water resistance. The manufacturing process of ceramic foam involves specialized foaming techniques and controlled firing to maintain voids, whereas stoneware relies on traditional molding and high-temperature vitrification for strength and chip resistance.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Ceramic foam dishware offers lightweight properties with moderate durability, making it resistant to chipping but less strong under heavy impact compared to stoneware. Stoneware boasts superior strength and heavier construction, providing enhanced resistance to cracking and breakage from daily use and thermal stress. In terms of longevity, stoneware outperforms ceramic foam due to its dense structure and higher resistance to wear and tear in kitchen environments.
Weight and Handling Differences
Ceramic foam dishware is notably lighter than traditional stoneware, making it easier to handle and less prone to accidental drops during daily use. The porous structure of ceramic foam reduces overall weight while maintaining reasonable durability, whereas stoneware's denser composition results in heavier plates and bowls that offer a more solid feel but can be cumbersome. Choosing ceramic foam enhances comfort and ease of handling, particularly for larger sets or when serving multiple dishes at once.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Ceramic foam dishware offers a unique, porous texture that enhances aesthetic appeal with its organic and lightweight design, making it ideal for modern and artistic table settings. Stoneware provides a more traditional, dense surface with rich, earthy tones and varied glazing options, allowing for durable and classic styles suited to rustic or elegant decor. Both materials support diverse design options, but ceramic foam stands out for innovative, sculptural forms while stoneware excels in timeless versatility.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Performance
Ceramic foam exhibits superior heat resistance compared to stoneware, withstanding temperatures above 1200degC due to its porous structure that enhances thermal insulation. Stoneware offers reliable thermal performance, typically resistant up to 1000degC, making it durable for everyday dishware but less effective in extreme heat scenarios. The porous nature of ceramic foam reduces heat conductivity, ensuring dishes retain temperature longer while preventing heat transfer to surfaces.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Ceramic foam dishware offers excellent heat resistance and non-toxic properties, ensuring safe use with hot or acidic foods without leaching harmful substances. Stoneware is highly durable and non-porous after glazing, making it resistant to bacteria and safe for everyday food contact. Both materials meet FDA food safety standards but ceramic foam may provide enhanced thermal insulation, reducing risk of burns during handling.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Ceramic foam dishware offers a porous surface that can require gentle cleaning methods to avoid trapping food particles and stains, whereas stoneware features a denser, non-porous glaze that resists absorption and simplifies maintenance. Stoneware's smooth finish allows for easier dishwasher cleaning without risk of damage, in contrast to ceramic foam, which may degrade with harsh detergents or abrasive scrubbing. Regular hand washing with mild soap extends the lifespan of ceramic foam dishware, while stoneware withstands more frequent and intensive cleaning routines.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic foam dishware, made from porous materials with a lower firing temperature, generally consumes less energy and produces fewer emissions compared to dense stoneware, which requires higher temperatures and longer kiln times. Stoneware's durability and resistance to chipping extend product lifespan, reducing waste, while ceramic foam's lightweight nature decreases transportation emissions. Both materials are recyclable and non-toxic, but ceramic foam's lower resource intensity offers a more sustainable option for eco-conscious consumers.
Cost Analysis and Value for Money
Ceramic foam dishware typically incurs higher costs due to advanced manufacturing processes but offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties that enhance durability and usability. Stoneware is generally more affordable, providing excellent strength and chip resistance, making it a practical choice for everyday use without sacrificing quality. Evaluating cost against longevity and performance, ceramic foam presents better long-term value for premium users, while stoneware delivers economical benefits for budget-conscious consumers.
Infographic: Ceramic foam vs Stoneware for Dishware
 azmater.com
azmater.com