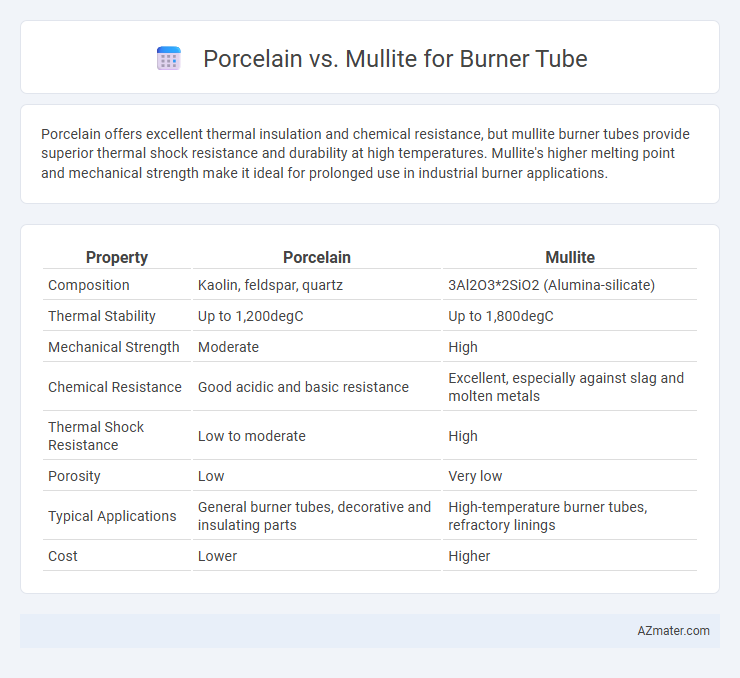
Porcelain offers excellent thermal insulation and chemical resistance, but mullite burner tubes provide superior thermal shock resistance and durability at high temperatures. Mullite's higher melting point and mechanical strength make it ideal for prolonged use in industrial burner applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Alumina-silicate) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1,200degC | Up to 1,800degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good acidic and basic resistance | Excellent, especially against slag and molten metals |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
| Porosity | Low | Very low |
| Typical Applications | General burner tubes, decorative and insulating parts | High-temperature burner tubes, refractory linings |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Burner Tube Materials
Burner tube materials like porcelain and mullite are critical for high-temperature applications due to their thermal stability and resistance to corrosion. Porcelain offers excellent insulating properties and durability in moderate heat environments, making it suitable for residential burner tubes. Mullite, characterized by its superior mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock, is preferred in industrial burners operating under extreme conditions.
Importance of Material Selection in Burner Tubes
Material selection in burner tubes significantly impacts durability, thermal resistance, and chemical stability under high-temperature combustion environments. Porcelain offers excellent insulating properties and corrosion resistance but is prone to brittleness and thermal shock, whereas mullite provides superior thermal shock resistance, mechanical strength, and longevity in harsh conditions due to its high alumina content. Choosing mullite enhances burner tube performance by reducing maintenance costs and downtime, ensuring efficient combustion and safety in industrial applications.
Overview of Porcelain Burner Tubes
Porcelain burner tubes are highly valued for their excellent thermal insulation and resistance to high temperatures, making them ideal for combustion systems. Their smooth, non-porous surface minimizes fuel residue buildup, enhancing burner efficiency and longevity. Compared to mullite, porcelain offers superior electrical insulation properties but has lower mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance.
Overview of Mullite Burner Tubes
Mullite burner tubes are engineered from a unique aluminosilicate ceramic known for exceptional thermal shock resistance and high-temperature durability up to 1800degC, making them ideal for industrial burning applications. Compared to porcelain, mullite offers superior mechanical strength and chemical stability under harsh combustion conditions, reducing the risk of cracking and extending service life. These attributes enhance combustion efficiency and operational reliability in burner systems across petrochemical, glass manufacturing, and power generation sectors.
Thermal Resistance: Porcelain vs Mullite
Mullite exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to porcelain, withstanding temperatures up to 1800degC, making it ideal for high-temperature burner tube applications. Porcelain typically endures temperatures around 1200degC but offers excellent electrical insulation properties. The enhanced thermal stability and mechanical strength of mullite contribute to longer service life and reliability in harsh burner environments.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Mullite burner tubes exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to porcelain, with higher resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress due to their crystalline structure and enhanced toughness. Porcelain, while cost-effective and corrosion-resistant, tends to be more brittle and prone to cracking under rapid temperature fluctuations and mechanical impact. The inherent durability of mullite makes it a preferred choice for high-stress applications requiring long service life and reliability in burner tube components.
Chemical Stability Under High Temperatures
Porcelain burner tubes offer moderate chemical stability but are prone to degradation in acidic or alkaline environments at elevated temperatures above 1200degC. Mullite burner tubes exhibit superior chemical stability under high temperatures up to 1600degC, resisting thermal shock and corrosion from combustion gases due to their high alumina content and low thermal expansion. The enhanced durability of mullite makes it ideal for industrial burner applications requiring long service life and consistent performance in aggressive chemical atmospheres.
Cost-Effectiveness and Longevity Analysis
Porcelain burner tubes offer a lower initial cost and moderate durability, making them suitable for applications with budget constraints and less demanding thermal cycles. Mullite burner tubes, while more expensive upfront, provide superior thermal shock resistance and longer service life, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs. Choosing mullite enhances cost-effectiveness over time in high-temperature, high-stress environments due to its exceptional longevity and reliability.
Common Applications for Porcelain and Mullite Tubes
Porcelain burner tubes are commonly used in residential heating systems and gas fireplaces due to their excellent insulating properties and resistance to thermal shock. Mullite tubes, favored in industrial furnaces and high-temperature kilns, provide superior strength and durability under extreme thermal cycling and corrosive environments. Both materials serve critical roles in burner assemblies, with porcelain preferred for moderate temperatures and aesthetics, while mullite excels in high-temperature, heavy-duty applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material for Burner Tubes
Porcelain offers excellent thermal insulation and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it suitable for low to moderate temperature burner tubes. Mullite, with superior high-temperature stability and mechanical strength, is ideal for demanding industrial burners that operate at elevated temperatures. Selecting the best material depends on operational temperature, mechanical stress, and chemical exposure, with mullite preferred for durability and performance in harsh conditions.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Mullite for Burner Tube
 azmater.com
azmater.com