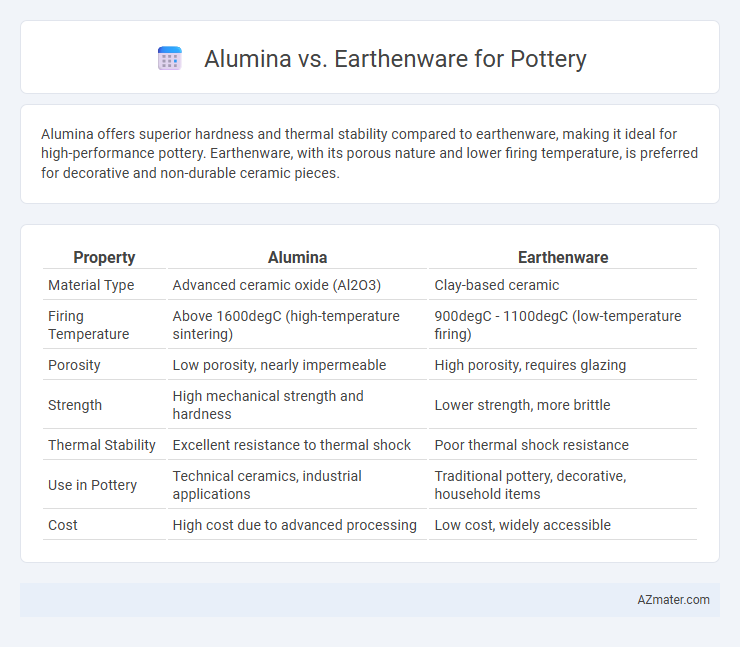
Alumina offers superior hardness and thermal stability compared to earthenware, making it ideal for high-performance pottery. Earthenware, with its porous nature and lower firing temperature, is preferred for decorative and non-durable ceramic pieces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced ceramic oxide (Al2O3) | Clay-based ceramic |
| Firing Temperature | Above 1600degC (high-temperature sintering) | 900degC - 1100degC (low-temperature firing) |
| Porosity | Low porosity, nearly impermeable | High porosity, requires glazing |
| Strength | High mechanical strength and hardness | Lower strength, more brittle |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent resistance to thermal shock | Poor thermal shock resistance |
| Use in Pottery | Technical ceramics, industrial applications | Traditional pottery, decorative, household items |
| Cost | High cost due to advanced processing | Low cost, widely accessible |
Introduction: Alumina vs Earthenware Pottery
Alumina pottery, known for its high alumina content, offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to heat compared to traditional earthenware, which is more porous and fragile. Earthenware pottery, typically fired at lower temperatures, retains a rustic aesthetic and is more absorbent, making it suitable for decorative purposes rather than functional dinnerware. The contrasting properties between alumina and earthenware influence their applications, firing processes, and finish quality within the pottery industry.
Material Composition and Structure
Alumina pottery contains a high percentage of aluminum oxide, making it dense, strong, and heat-resistant, ideal for industrial and technical ceramics. Earthenware consists mainly of clay and other natural materials like quartz and feldspar, resulting in a porous and less durable structure that requires glazing for waterproofing. The microscopic crystalline structure of alumina provides superior mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to the open-pore, less compact matrix of earthenware.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
Alumina exhibits superior thermal properties and high heat resistance, making it ideal for pottery that requires durability under extreme temperatures. Earthenware, composed primarily of clay fired at lower temperatures, has lower thermal conductivity and is more prone to thermal shock and cracking under rapid temperature changes. Choosing alumina-based pottery ensures greater stability and longevity in high-heat applications compared to the more porous and less heat-resistant earthenware.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Alumina pottery exhibits significantly higher strength and durability compared to earthenware, owing to its dense, vitrified structure and higher alumina content. Earthenware is more porous and prone to chipping or cracking under stress due to its lower firing temperature and less compact composition. The superior mechanical properties of alumina make it ideal for functional ceramics requiring enhanced wear resistance and longevity.
Porosity and Water Absorption
Alumina ceramics exhibit significantly lower porosity compared to earthenware, resulting in minimal water absorption rates typically below 1%, which enhances their durability and resistance to moisture-related damage. Earthenware, characterized by high porosity levels often exceeding 20%, absorbs water readily, making it less suitable for functional pottery exposed to liquids. The reduced porosity of alumina also contributes to its superior strength and thermal resistance, distinguishing it from the more porous and fragile earthenware materials.
Glazing and Surface Finishes
Alumina in pottery provides a durable, smooth surface that enhances glaze adhesion and results in a high-gloss finish resistant to chipping. Earthenware, being more porous, often requires a thicker glaze coat to prevent absorption, which can lead to varied textures from matte to glossy based on firing temperature. The choice between alumina and earthenware significantly impacts the final surface finish qualities, including hardness, glossiness, and resistance to wear.
Suitability for Pottery Techniques
Alumina offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature firing and intricate sculptural pottery techniques. Earthenware, characterized by its porous nature and lower firing temperature, suits hand-building and decorative glazing but requires careful handling to avoid cracks. Potters prioritize alumina for wheel throwing and functional ware needing strength, while earthenware excels in decorative and traditional craft applications.
Applications in Functional and Decorative Ware
Alumina pottery exhibits superior strength and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for functional ware such as cookware and laboratory ceramics that require durability and heat endurance. Earthenware, known for its porous and softer texture, is preferred in decorative items and traditional pottery where aesthetic appeal and ease of shaping take precedence. Functional applications favor alumina for longevity and performance, while earthenware suits ornamental uses due to its rustic charm and versatility in glazing.
Cost and Availability
Alumina pottery typically incurs higher costs due to its advanced raw materials and manufacturing processes, making it less accessible for casual pottery enthusiasts. Earthenware is widely available and budget-friendly, as it uses abundant natural clay and simpler production methods, ideal for beginners and large-scale pottery projects. The choice between these materials often hinges on balancing price constraints with desired durability and finish quality.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Alumina and Earthenware
Alumina offers superior strength, durability, and high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for industrial and functional pottery applications. Earthenware provides a rustic aesthetic, easier workability, and lower firing temperatures, suited for decorative and everyday pottery. Selecting between alumina and earthenware depends on the desired balance between durability and artistic expression, as well as firing capabilities and functional requirements.
Infographic: Alumina vs Earthenware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com