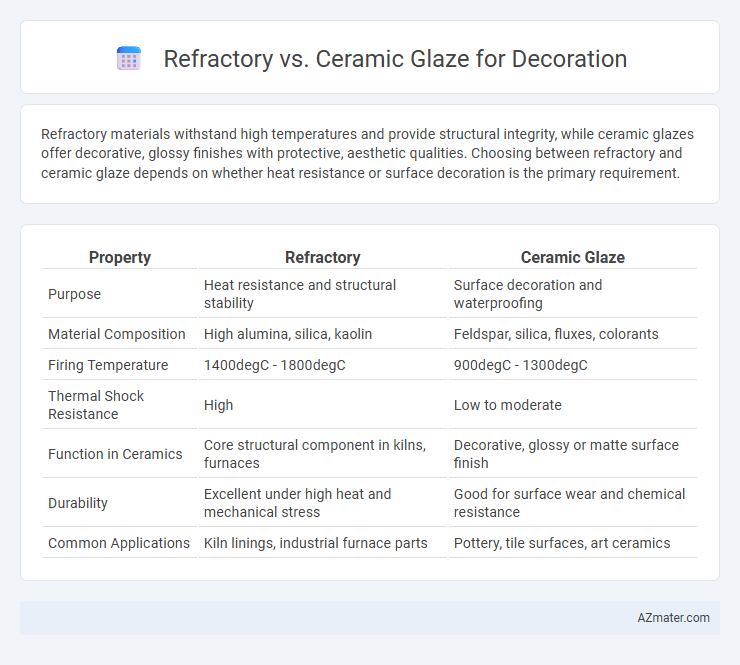
Refractory materials withstand high temperatures and provide structural integrity, while ceramic glazes offer decorative, glossy finishes with protective, aesthetic qualities. Choosing between refractory and ceramic glaze depends on whether heat resistance or surface decoration is the primary requirement.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Refractory | Ceramic Glaze |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Heat resistance and structural stability | Surface decoration and waterproofing |
| Material Composition | High alumina, silica, kaolin | Feldspar, silica, fluxes, colorants |
| Firing Temperature | 1400degC - 1800degC | 900degC - 1300degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High | Low to moderate |
| Function in Ceramics | Core structural component in kilns, furnaces | Decorative, glossy or matte surface finish |
| Durability | Excellent under high heat and mechanical stress | Good for surface wear and chemical resistance |
| Common Applications | Kiln linings, industrial furnace parts | Pottery, tile surfaces, art ceramics |
Introduction to Decorative Glazes
Decorative glazes transform ceramic surfaces with vibrant colors and textures, enhancing both aesthetics and durability. Refractory glazes are formulated to withstand extreme heat, making them ideal for functional pottery exposed to high temperatures, while ceramic glazes prioritize visual appeal with diverse finishes such as glossy, matte, or textured effects. Understanding glaze chemistry and firing temperatures is crucial for achieving desired decorative outcomes and ensuring long-lasting surface quality.
What is Refractory Glaze?
Refractory glaze is a specialized coating designed to withstand high temperatures without degrading, making it ideal for industrial applications such as kiln linings and furnace components. Unlike ceramic glazes, which prioritize aesthetic appeal and smooth finishes for pottery and tiles, refractory glazes emphasize thermal resistance, chemical stability, and durability under extreme heat conditions. These glazes are formulated with materials like alumina and silica to ensure they maintain integrity and protect substrates during prolonged exposure to temperatures often exceeding 1200degC.
What is Ceramic Glaze?
Ceramic glaze is a glassy coating applied to pottery and ceramics to create a smooth, often colorful, decorative finish that also enhances durability and water resistance. Unlike refractory materials designed to withstand high temperatures and thermal stress, ceramic glazes primarily serve aesthetic purposes while providing a protective layer. These glazes are composed of silica, fluxes, and colorants, which melt during firing to form a hardened surface that can be glossy, matte, or textured.
Key Differences Between Refractory and Ceramic Glazes
Refractory glazes are designed to withstand extremely high temperatures without melting or deforming, making them ideal for use in industrial furnaces, kilns, and heat-resistant components. Ceramic glazes, on the other hand, primarily enhance the aesthetic appeal and surface durability of pottery, providing a smooth, glass-like finish that varies in texture and color. The key differences lie in their thermal resistance, chemical composition, and intended function: refractory glazes prioritize heat resistance and chemical stability, while ceramic glazes focus on decoration and surface protection.
Surface Effects and Aesthetics
Refractory glazes offer a durable and matte surface effect ideal for high-heat applications, providing subtle textures and earthy tones that enhance rustic aesthetics. Ceramic glazes deliver a wide range of vibrant colors and glossy finishes, creating smooth, reflective surfaces that elevate visual appeal and artistic detail. The choice between refractory and ceramic glazes significantly influences the final decorative impact, balancing heat resistance with color intensity and surface texture.
Application Techniques in Decoration
Refractory glazes are formulated to withstand high temperatures and are primarily used in industrial ceramics requiring durability and thermal resistance, making them ideal for kiln linings and heat exchangers. Ceramic glazes, on the other hand, offer a wide variety of colors and textures suitable for decorative surfaces, applied through techniques like brushing, dipping, spraying, or airbrushing to achieve artistic effects. Application methods for ceramic glazes emphasize uniform coverage and precise layering to enhance aesthetic appeal, while refractory glazes focus on consistent thickness to ensure thermal and mechanical performance.
Thermal Durability and Firing Temperatures
Refractory glazes offer superior thermal durability, able to withstand higher firing temperatures typically ranging from 1400degC to 1600degC, making them ideal for industrial and high-heat applications. Ceramic glazes, while decorative, generally fire at lower temperatures between 1000degC and 1300degC, providing less resistance to thermal shock and heat stress. Choosing between these glazes depends on the required thermal performance and the specific firing processes used in ceramic decoration.
Suitability for Artistic vs. Functional Pieces
Refractory glazes excel in functional ceramic pieces, offering high thermal resistance essential for cookware and industrial applications, whereas ceramic glazes are preferred for artistic decorations due to their wide color range and surface finish options. The chemical composition of refractory glazes allows them to withstand extreme temperatures without cracking or degrading, making them ideal for utilitarian objects requiring durability. Conversely, ceramic glazes provide superior aesthetic versatility, enabling artists to achieve intricate designs and vibrant visual effects suitable for decorative art pieces.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Refractory glazes generally exhibit higher cost due to their specialized materials and limited suppliers, making them less accessible for large-scale decorative applications compared to ceramic glazes. Ceramic glazes benefit from widespread availability and a diverse range of formulations, which often results in lower price points and easier procurement from multiple vendors. Cost-efficiency and availability make ceramic glazes preferable for decorative projects with budget constraints or tight supply timelines.
Choosing the Right Glaze for Your Project
Choosing the right glaze for your project involves understanding the differences between refractory and ceramic glazes in terms of heat resistance and surface finish. Refractory glazes are ideal for high-temperature applications such as kiln interiors and industrial ceramics due to their durability and ability to withstand rapid temperature changes. Ceramic glazes offer a broader palette of decorative finishes and colors, making them suitable for artistic and functional pieces where aesthetic appeal is the priority.
Infographic: Refractory vs Ceramic glaze for Decoration
 azmater.com
azmater.com