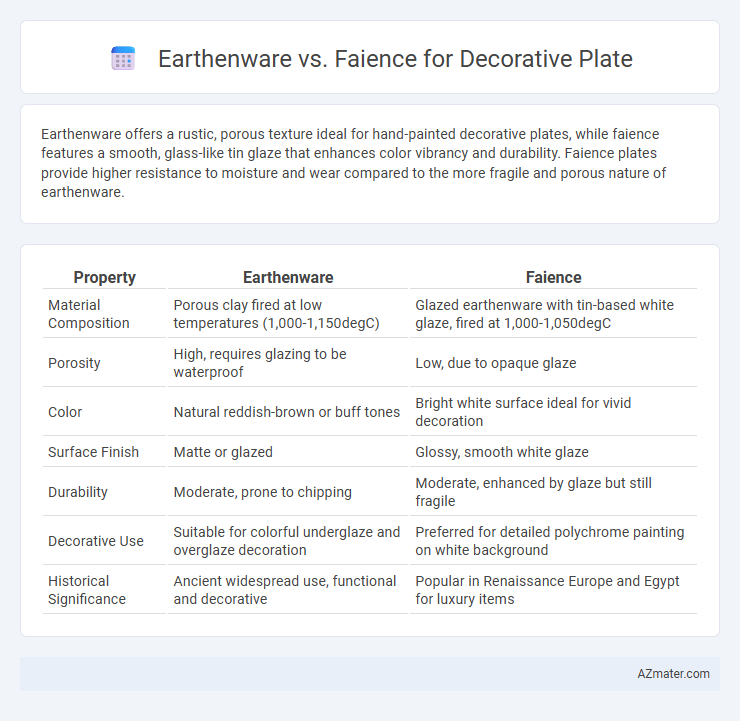
Earthenware offers a rustic, porous texture ideal for hand-painted decorative plates, while faience features a smooth, glass-like tin glaze that enhances color vibrancy and durability. Faience plates provide higher resistance to moisture and wear compared to the more fragile and porous nature of earthenware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Earthenware | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Porous clay fired at low temperatures (1,000-1,150degC) | Glazed earthenware with tin-based white glaze, fired at 1,000-1,050degC |
| Porosity | High, requires glazing to be waterproof | Low, due to opaque glaze |
| Color | Natural reddish-brown or buff tones | Bright white surface ideal for vivid decoration |
| Surface Finish | Matte or glazed | Glossy, smooth white glaze |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping | Moderate, enhanced by glaze but still fragile |
| Decorative Use | Suitable for colorful underglaze and overglaze decoration | Preferred for detailed polychrome painting on white background |
| Historical Significance | Ancient widespread use, functional and decorative | Popular in Renaissance Europe and Egypt for luxury items |
Introduction to Decorative Plates
Decorative plates crafted from earthenware and faience showcase distinct qualities essential for collectors and interior designers. Earthenware, a porous ceramic fired at lower temperatures, offers a rustic appeal with its earthy textures and vibrant glazes. Faience, a type of fine tin-glazed pottery, provides a smooth, glossy surface ideal for intricate, colorful designs that elevate the aesthetic value of decorative plates.
What Is Earthenware?
Earthenware is a porous, non-vitreous ceramic material fired at relatively low temperatures, typically between 1,000 to 1,150degC, resulting in a dense, opaque body that is often glazed for durability and aesthetic appeal. Unlike faience, which is a type of tin-glazed earthenware known for its bright, opaque surface, standard earthenware possesses a more rustic texture and earthy color palette, making it popular for decorative plates with a traditional or artisanal look. The versatility of earthenware allows for various glazing techniques, enabling vibrant color application and intricate designs that enhance the visual impact of decorative plates.
Understanding Faience
Faience, a type of glazed ceramic ware, features a distinctive opaque tin glaze that creates a bright, glossy surface ideal for decorative plates. Compared to earthenware, faience offers enhanced durability and vibrant color retention due to its unique glazing process, making it highly valued for ornamental use. Its origins trace back to ancient Mediterranean cultures, where the technique evolved to combine artistic expression with practical functionality in household items.
Historical Origins of Earthenware and Faience
Earthenware, dating back to ancient Mesopotamia around 6000 BCE, is one of the oldest pottery types characterized by its porous texture and firing at relatively low temperatures. Faience, originating in ancient Egypt around 4000 BCE, is a glazed non-clay ceramic made primarily from crushed quartz or sand, renowned for its bright blue-green finish symbolizing fertility and rebirth. Both materials played significant roles in historical decorative plate production, with earthenware favored for its durability and faience prized for its vibrant, glass-like surface.
Material Composition and Techniques
Earthenware decorative plates consist primarily of porous clay fired at lower temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, resulting in a more fragile and absorbent material often sealed with a glaze for durability. Faience plates are made from finely ground quartz mixed with a clay body, then coated with a tin-based opaque glaze that provides a glossy, white surface ideal for detailed painting, typically fired at a slightly higher temperature around 1,100degC. The production of faience involves an intricate glazing technique that creates vibrant colors and a smooth finish, distinguishing it from the more rustic texture and finish of traditional earthenware.
Visual Differences and Aesthetic Appeal
Earthenware plates typically feature a rustic, matte finish with earthy tones and visible texture variations, emphasizing a handcrafted, traditional aesthetic. Faience plates are characterized by their glossy, smooth surface with vibrant, intricate painted designs often in blue, green, and yellow hues, reflecting a more refined and decorative appeal. The visual distinction lies in earthenware's organic, muted palette versus faience's polished, colorful artistry, influencing their decorative use and aesthetic impact.
Durability and Functionality Comparison
Earthenware decorative plates tend to be more porous and less durable due to their lower firing temperature, making them susceptible to chipping and moisture absorption. Faience plates, crafted from tin-glazed earthenware, offer enhanced functionality with a more vitrified surface that increases resistance to scratches and stains while maintaining vivid color retention. For long-term decorative use combined with occasional functionality, faience provides a superior balance of durability and aesthetic vibrancy compared to standard earthenware.
Suitability for Artistic Designs
Earthenware offers a porous, matte surface ideal for rustic and traditional artistic designs, allowing vibrant glazes to enhance handcrafted details. Faience, a tin-glazed earthenware, provides a smooth, glossy finish that supports intricate, colorful patterns with sharp definition and durability. For decorative plates emphasizing detailed and vibrant artistic designs, faience is more suitable due to its enhanced surface for fine brushwork and color retention.
Cost and Collectibility
Earthenware decorative plates generally offer a lower cost option due to their porous composition and less labor-intensive production, making them accessible for casual collectors. Faience plates, featuring a tin-glazed surface and intricate designs, command higher prices reflecting their craftsmanship and historical significance. Collectors prioritize faience for its vibrant colors and durability, often resulting in greater long-term value compared to the more common earthenware pieces.
Choosing Between Earthenware and Faience for Decorative Plates
Choosing between earthenware and faience for decorative plates depends on the desired aesthetic and durability. Earthenware, characterized by its porous and slightly coarse texture, offers rustic charm and is often glazed for added protection, making it ideal for decorative use with vibrant, earth-toned designs. Faience, a type of tin-glazed earthenware, provides a glossy, opaque surface that enhances intricate patterns and bright colors, perfect for detailed artistic plates requiring a smooth, polished finish.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Faience for Decorative Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com