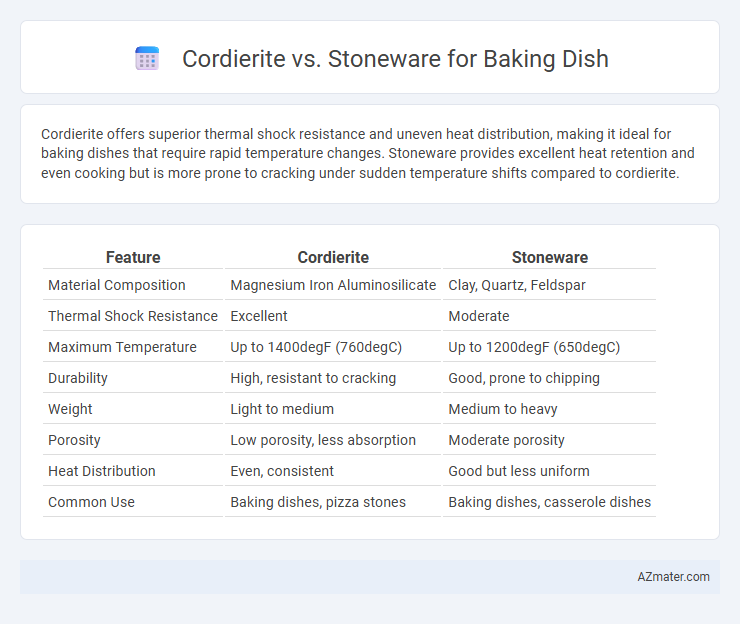
Cordierite offers superior thermal shock resistance and uneven heat distribution, making it ideal for baking dishes that require rapid temperature changes. Stoneware provides excellent heat retention and even cooking but is more prone to cracking under sudden temperature shifts compared to cordierite.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cordierite | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Magnesium Iron Aluminosilicate | Clay, Quartz, Feldspar |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Maximum Temperature | Up to 1400degF (760degC) | Up to 1200degF (650degC) |
| Durability | High, resistant to cracking | Good, prone to chipping |
| Weight | Light to medium | Medium to heavy |
| Porosity | Low porosity, less absorption | Moderate porosity |
| Heat Distribution | Even, consistent | Good but less uniform |
| Common Use | Baking dishes, pizza stones | Baking dishes, casserole dishes |
Introduction to Cordierite and Stoneware
Cordierite is a dense, heat-resistant ceramic known for its superior thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for baking dishes that undergo rapid temperature changes. Stoneware, composed of fired clay, offers durability and even heat distribution, retaining heat well for consistent cooking. Both materials excel in oven use, but cordierite provides enhanced longevity under extreme thermal conditions.
Composition and Material Properties
Cordierite baking dishes are made from a mineral-based ceramic known for exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability, making them ideal for sudden temperature changes in the oven. Stoneware, composed primarily of clay fired at high temperatures, offers excellent heat retention and even cooking but is more prone to cracking under rapid temperature shifts. Both materials provide non-reactive surfaces suitable for baking, but cordierite's unique composition gives it superior resilience and longevity in high-heat applications.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Shock
Cordierite baking dishes offer superior heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 2,200degF, making them ideal for high-temperature baking and grilling. Stoneware, while durable, generally endures lower heat levels around 1,200degF to 1,500degF and is more prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Cordierite's outstanding thermal shock resistance ensures it handles sudden transitions from oven to countertop without damage, whereas stoneware requires gradual temperature changes to prevent breakage.
Baking Performance Comparison
Cordierite baking dishes offer excellent thermal shock resistance and evenly distribute heat, preventing hot spots and ensuring consistent baking results, making them ideal for high-temperature cooking like pizza and bread. Stoneware provides superior heat retention, maintaining even oven temperature over extended periods, which is beneficial for slow-cooked casseroles and delicate baked goods. While cordierite is more durable under rapid temperature changes, stoneware excels in moisture retention, enhancing the texture and flavor of baked dishes.
Durability and Longevity
Cordierite baking dishes offer superior thermal shock resistance and long-lasting durability, making them ideal for frequent oven use and rapid temperature changes. Stoneware, while providing excellent heat retention and even cooking, tends to be more prone to chipping and cracking over time with heavy use. Choosing cordierite ensures extended longevity and reliable performance in high-temperature baking environments.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Cordierite baking dishes offer exceptional resistance to thermal shock, making them easy to clean with minimal risk of cracking during temperature changes. Stoneware requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges to prevent surface scratches and preserve its glaze, which can be sensitive to harsh detergents. Both materials benefit from hand washing and avoiding sudden temperature shifts, but cordierite's durability simplifies maintenance over time.
Weight and Usability
Cordierite baking dishes are generally heavier and more durable, making them ideal for high-temperature baking and oven-to-table use, while stoneware is lighter and easier to handle but may be less resistant to thermal shock. Cordierite's superior heat retention offers even cooking, whereas stoneware provides moderate heat distribution suitable for everyday baking. The choice depends on whether weight durability or ease of handling is prioritized for baking tasks.
Cost Differences
Cordierite baking dishes typically cost more than stoneware due to their superior thermal shock resistance and durability, which extends their lifespan under high-temperature baking conditions. Stoneware offers a more budget-friendly option but may require replacement sooner due to its propensity for cracking under sudden temperature changes. Choosing between cordierite and stoneware depends on balancing initial cost with long-term performance and durability in baking applications.
Best Uses for Cordierite
Cordierite baking dishes excel in thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for recipes that require rapid temperature changes, such as baking casseroles or desserts that go from freezer to oven. Their superior heat retention and even heat distribution ensure consistent cooking and browning, perfect for bread baking and slow-cooked dishes. Unlike stoneware, cordierite is less prone to cracking under sudden heat exposure, providing durability for high-temperature baking and broiling tasks.
Best Uses for Stoneware
Stoneware baking dishes excel in even heat distribution and thermal retention, making them ideal for casseroles, gratins, and slow-cooked recipes. Their non-porous surface resists stains and odors, contributing to durability and ease of cleaning. Compared to cordierite, stoneware offers superior moisture retention, enhancing the texture and flavor of baked goods.
Infographic: Cordierite vs Stoneware for Baking Dish
 azmater.com
azmater.com