Refractory materials offer superior heat resistance and durability for kiln linings compared to standard ceramic tiles, which may crack under high temperatures. Using specialized refractory bricks ensures prolonged kiln lifespan and efficient thermal insulation during high-temperature operations.
Table of Comparison
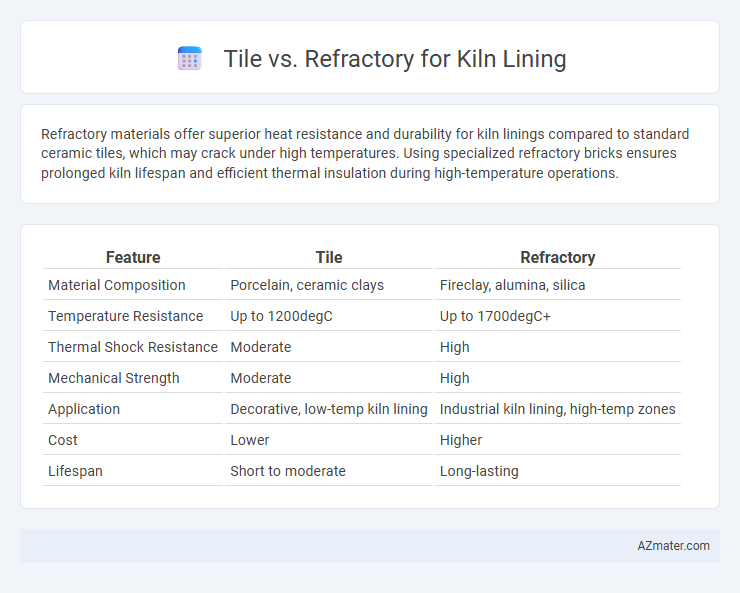
| Feature | Tile | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Porcelain, ceramic clays | Fireclay, alumina, silica |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1700degC+ |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Application | Decorative, low-temp kiln lining | Industrial kiln lining, high-temp zones |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Lifespan | Short to moderate | Long-lasting |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Materials
Kiln lining materials, crucial for thermal insulation and structural integrity, typically include tiles and refractories designed to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments. Tiles offer easier installation and replacement with good thermal performance, while refractories provide superior durability and resistance to thermal shock. Selecting the appropriate kiln lining depends on operational temperature, mechanical stress, and maintenance needs, directly impacting kiln efficiency and lifespan.
Understanding Tile Linings: Composition and Uses
Tile linings for kiln interiors typically consist of high-alumina or silicon carbide materials, prized for their thermal shock resistance and chemical stability at temperatures up to 1600degC. These tiles offer a modular and easy-to-maintain surface suitable for environments where abrasion and corrosion occur moderately. Their composition allows for rapid installation and replacement, making tile linings an efficient choice for kilns with variable operating cycles and maintenance schedules.
What Are Refractory Linings? Key Features and Types
Refractory linings are heat-resistant materials designed to protect kilns from extreme temperatures and thermal stress, ensuring structural integrity and energy efficiency. Key features include high melting points, thermal shock resistance, chemical inertness, and mechanical strength, essential for withstanding prolonged exposure to intense heat. Types of refractory linings commonly used in kiln applications consist of firebrick, castable refractories, ceramic fiber, and insulating bricks, each selected based on specific temperature requirements and thermal conductivity.
Heat Resistance: Tile vs. Refractory Performance
Refractory materials offer superior heat resistance for kiln lining, withstanding temperatures above 3000degF compared to typical kiln tiles rated up to 2500degF. Their dense structure provides better thermal shock resistance and durability under repeated heating cycles. Tiles, while easier to install and replace, generally exhibit lower thermal conductivity and faster degradation in extreme heat environments.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Refractory materials used for kiln lining exhibit superior durability, withstanding extreme temperatures above 1700degC and thermal shock without significant degradation. Tiles, particularly ceramic or fireclay variants, offer good resistance but generally have a shorter lifespan due to susceptibility to cracking and spalling under repeated heating cycles. In industrial kiln applications, high-quality refractories can maintain structural integrity for 5 to 10 years or more, whereas tile linings often require replacement every 2 to 4 years depending on operating conditions.
Installation Process: Tile vs. Refractory
Kiln lining installation involves distinct processes for tile and refractory materials; tile installation requires precise cutting and fitting of ceramic or fireclay tiles using specialized adhesives or mortar, ensuring a uniform and durable thermal barrier. Refractory lining installation entails pouring, casting, or stacking refractory bricks or castables that must be carefully cured and sintered to withstand extreme kiln temperatures and thermal cycling. Both methods demand expert handling to optimize kiln efficiency and longevity, but refractory linings typically offer more versatile shapes and repair options compared to tile linings.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Refractory linings for kilns typically require higher initial investment but offer superior durability and thermal resistance, reducing long-term maintenance frequency and associated costs. Tile linings, while generally less expensive upfront, demand more frequent inspections and repairs due to lower resistance to thermal shock and mechanical wear, resulting in higher cumulative maintenance expenses. Choosing refractory materials optimizes kiln operational efficiency by minimizing downtime and maintenance interventions over the lifespan of the kiln lining.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Tile lining in kilns offers enhanced safety by providing superior resistance to thermal shock and reducing the risk of structural failure, while refractory linings excel in high-temperature durability but may contain materials posing health hazards such as silica dust. Environmentally, tile linings tend to have lower embodied energy and generate less dust during installation and maintenance, contributing to improved air quality and worker safety. Choosing tile over traditional refractory materials can mitigate exposure to harmful particulates, ensuring compliance with stringent workplace safety regulations and reducing environmental impact.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Lining
Tile kiln linings offer excellent thermal shock resistance and are ideal for low to medium temperature applications such as ceramic firing or glass annealing. Refractory linings provide superior high-temperature stability and chemical resistance, making them suitable for industrial furnaces and metal melting processes. Selecting the right kiln lining depends on the kiln's operating temperature, atmosphere, and the specific thermal and chemical stresses expected during use.
Conclusion: Which Kiln Lining Is Best for Your Needs?
Choosing between tile and refractory kiln lining depends on factors such as temperature range, durability, and maintenance requirements. Refractory linings offer superior heat resistance and longevity for high-temperature operations, while tile linings provide cost-effective solutions for moderate heat and easier replacement. Evaluating kiln usage and thermal demands ensures selecting the optimal lining to enhance performance and lifespan.
Infographic: Tile vs Refractory for Kiln Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com