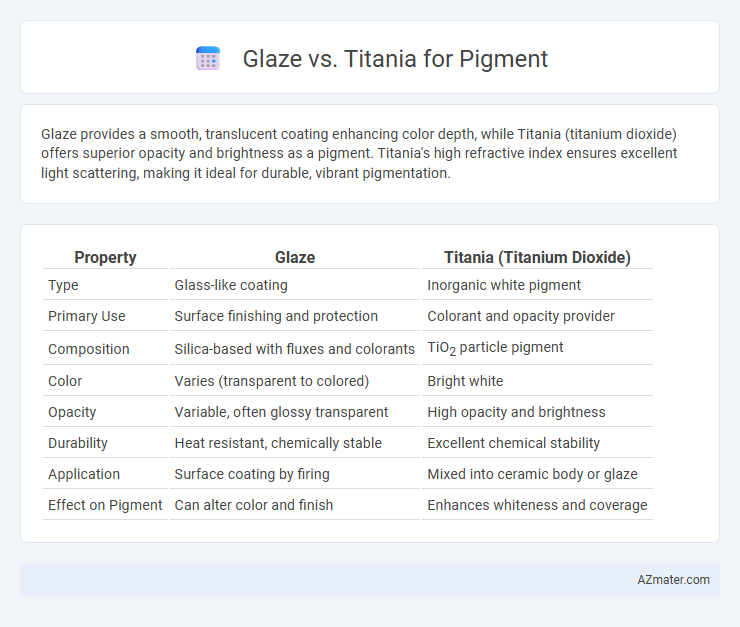
Glaze provides a smooth, translucent coating enhancing color depth, while Titania (titanium dioxide) offers superior opacity and brightness as a pigment. Titania's high refractive index ensures excellent light scattering, making it ideal for durable, vibrant pigmentation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glaze | Titania (Titanium Dioxide) |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Glass-like coating | Inorganic white pigment |
| Primary Use | Surface finishing and protection | Colorant and opacity provider |
| Composition | Silica-based with fluxes and colorants | TiO2 particle pigment |
| Color | Varies (transparent to colored) | Bright white |
| Opacity | Variable, often glossy transparent | High opacity and brightness |
| Durability | Heat resistant, chemically stable | Excellent chemical stability |
| Application | Surface coating by firing | Mixed into ceramic body or glaze |
| Effect on Pigment | Can alter color and finish | Enhances whiteness and coverage |
Understanding Glaze and Titania: Definitions and Uses
Glaze and Titania serve distinct roles in pigment applications, with glaze referring to a transparent or semi-transparent coating that enhances color depth and surface texture in ceramics and paints. Titania, chemically known as titanium dioxide, is a highly effective white pigment valued for its opacity, brightness, and UV resistance, extensively used in paints, coatings, and plastics. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate material in artistic and industrial pigment formulations.
Composition Differences: Glaze vs Titania
Glaze pigments consist primarily of finely ground glass particles combined with metal oxides, providing a translucent and glossy finish. Titania pigments are composed mainly of titanium dioxide (TiO2), known for their high opacity and strong light-scattering properties. The key composition difference lies in Glaze's glass-based matrix that imparts shine, whereas Titania's inorganic TiO2 particles deliver superior whiteness and coverage.
Optical Effects: How Glaze and Titania Impact Color
Glaze enhances pigment depth by adding a translucent layer that intensifies color saturation and creates subtle light diffusion, resulting in richer and more vibrant hues. Titania, or titanium dioxide, functions as a powerful whiteness and opacity modifier that reflects and scatters light, significantly increasing brightness and altering the pigment's visual perception. Both materials modify optical properties--glaze through layering and translucency effects, titan dioxide by high refractive index and light scattering--but glaze preserves underlying color nuance while titania shifts overall color tone towards opacity and luminosity.
Pigment Performance: Durability and Stability
Glaze pigments offer superior durability with excellent resistance to UV radiation and chemical exposure, making them ideal for long-lasting color retention in outdoor applications. Titania pigments, primarily composed of titanium dioxide, provide exceptional stability due to their strong opacity and resistance to discoloration under harsh environmental conditions. Both pigments exhibit robust performance, but Titania often leads in maintaining color integrity over extended periods, especially in high-exposure settings.
Application Methods for Glaze and Titania in Pigment
Glaze application for pigment typically involves thin, translucent layers brushed or sprayed onto surfaces, enhancing color depth and creating a luminous finish through light refraction. Titania pigments are applied using dispersions in coatings and paints, often requiring high shear mixing to achieve uniform particle distribution for optimal opacity and brightness. Both application methods demand precise control of pigment concentration and medium compatibility to maximize durability and visual impact.
Environmental Impact: Glaze vs Titania Pigments
Glaze pigments typically have a lower environmental impact due to their natural mineral composition and minimal processing requirements, resulting in reduced carbon emissions and waste production. Titania pigments, known for their high opacity and brightness, often require energy-intensive manufacturing processes and can contribute to air and water pollution through the release of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Sustainable pigment producers prioritize eco-friendly Glazes over conventional Titania to minimize ecological footprints and promote safer, biodegradable alternatives.
Cost Comparison: Economic Considerations
Glaze pigments typically incur lower initial costs compared to Titania pigments, making them more budget-friendly for large-scale projects. Titania pigments, derived from titanium dioxide, offer higher durability and opacity but carry a premium price due to raw material and processing expenses. Evaluating the long-term benefits against upfront costs is crucial, as Titania's longevity can reduce maintenance expenses despite its higher initial investment.
Industry Preferences: Glaze or Titania in Modern Pigments
Industry preferences favor Titania in modern pigments due to its superior opacity, brightness, and UV resistance, making it ideal for coatings, plastics, and paints. Glaze pigments, while offering unique aesthetic effects with translucency and subtle color shifts, are less commonly used in large-scale industrial applications where durability and coverage are critical. Manufacturers prioritize Titania for consistent quality and performance in high-demand environments.
Health and Safety Implications of Each Pigment
Glaze pigments typically contain fewer hazardous substances but may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during application, impacting indoor air quality and posing inhalation risks. Titania (titanium dioxide) is widely used for its non-toxic profile but has raised concerns regarding inhalation of fine particulate forms, classified as a possible carcinogen by IARC when airborne nanoparticles are involved. Proper ventilation, respiratory protection, and adherence to occupational exposure limits are essential safety measures when handling both glaze and titania pigments to minimize health risks.
Choosing the Right Pigment: Glaze or Titania?
Choosing the right pigment between Glaze and Titania depends on the desired finish and application requirements. Glaze pigments provide a transparent, glossy effect ideal for layering and enhancing depth in ceramic or paint surfaces, while Titania pigments offer high opacity and brilliance, delivering strong coverage and vibrant white hues. Consider the project's need for translucency versus opacity to determine whether Glaze's subtle sheen or Titania's intense brightness best suits your artistic or industrial goals.
Infographic: Glaze vs Titania for Pigment
 azmater.com
azmater.com