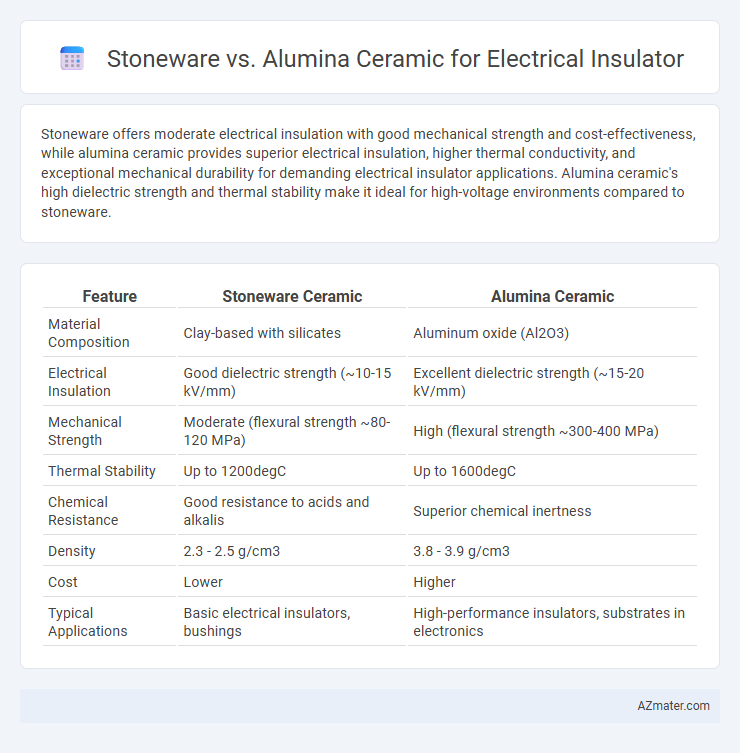
Stoneware offers moderate electrical insulation with good mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, while alumina ceramic provides superior electrical insulation, higher thermal conductivity, and exceptional mechanical durability for demanding electrical insulator applications. Alumina ceramic's high dielectric strength and thermal stability make it ideal for high-voltage environments compared to stoneware.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stoneware Ceramic | Alumina Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay-based with silicates | Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) |
| Electrical Insulation | Good dielectric strength (~10-15 kV/mm) | Excellent dielectric strength (~15-20 kV/mm) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate (flexural strength ~80-120 MPa) | High (flexural strength ~300-400 MPa) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1600degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Superior chemical inertness |
| Density | 2.3 - 2.5 g/cm3 | 3.8 - 3.9 g/cm3 |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | Basic electrical insulators, bushings | High-performance insulators, substrates in electronics |
Understanding Stoneware and Alumina Ceramic Materials
Stoneware and alumina ceramic are commonly used materials for electrical insulators, each offering distinct properties for specific applications. Stoneware is a dense, vitrified clay-based material known for its excellent mechanical strength, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for medium-voltage insulators in outdoor environments. Alumina ceramic, composed primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), provides superior electrical insulation, high thermal conductivity, and exceptional resistance to wear and chemical corrosion, ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability and reliability under extreme conditions.
Electrical Insulator Applications: Where Are They Used?
Stoneware electrical insulators, known for their high mechanical strength and moisture resistance, are widely used in power transmission and distribution systems, especially in outdoor environments such as substations and overhead lines. Alumina ceramic insulators offer superior dielectric properties, high thermal conductivity, and exceptional wear resistance, making them ideal for high-frequency, high-voltage applications and demanding industrial environments like semiconductor manufacturing and high-power electronic devices. Both materials play critical roles in ensuring reliable insulation performance in electrical infrastructure, with stoneware favored for cost-effective, heavy-duty uses and alumina chosen for precision and high-performance insulation needs.
Mechanical Strength Comparison: Stoneware vs Alumina
Alumina ceramic exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to stoneware, with flexural strength often exceeding 300 MPa, whereas stoneware typically ranges between 30-70 MPa. The superior strength of alumina results from its dense, homogenous microstructure and high purity aluminum oxide composition, making it ideal for high-stress electrical insulators. Stoneware's lower strength and higher porosity limit its use to less mechanically demanding applications where cost efficiency is prioritized over performance.
Electrical Properties: Which Material Performs Better?
Alumina ceramic exhibits superior electrical properties compared to stoneware, including higher dielectric strength and lower electrical conductivity, making it a better insulator in high-voltage applications. Stoneware typically has a dielectric strength range of 10-15 kV/mm, whereas alumina ceramics can reach up to 15-20 kV/mm or more, ensuring better resistance to electrical breakdown. The low dielectric loss and high resistivity of alumina make it the preferred choice for electrical insulators requiring reliability and durability in demanding environments.
Thermal Resistance: Durability in High-Temperature Environments
Stoneware offers moderate thermal resistance suitable for electrical insulators in standard high-temperature environments, with heat tolerance up to approximately 1200degC. Alumina ceramic exhibits superior thermal resistance, enduring temperatures above 1700degC while maintaining structural integrity and electrical insulation properties. This enhanced durability makes alumina ceramic ideal for demanding applications requiring prolonged exposure to extreme heat and thermal shock resistance.
Moisture Absorption and Weathering Effects
Stoneware exhibits higher moisture absorption rates compared to alumina ceramic, which significantly affects its electrical insulation properties under humid conditions. Alumina ceramic demonstrates superior resistance to weathering effects, maintaining its mechanical strength and dielectric integrity even in aggressive environmental exposures. Low porosity and dense microstructure of alumina ceramic contribute to its excellent performance in electrical insulators subjected to moisture and weather variations.
Manufacturing Processes for Stoneware and Alumina Ceramics
Stoneware electrical insulators are manufactured through a process involving shaping clay mixtures followed by firing at temperatures typically between 1200degC and 1300degC, which grants high mechanical strength and low porosity. Alumina ceramic insulators undergo a more complex manufacturing process including powder preparation, pressing, sintering at temperatures above 1600degC, and often hot isostatic pressing, resulting in superior dielectric strength and thermal conductivity. The high purity and controlled microstructure of alumina ceramics distinguish them from stoneware, making alumina preferable for high-performance electrical insulation applications.
Cost Analysis: Stoneware vs Alumina Electrical Insulators
Stoneware electrical insulators typically offer a lower initial cost compared to alumina ceramic insulators, making them attractive for budget-sensitive projects. Alumina ceramics provide superior electrical insulation properties and higher mechanical strength, justifying their higher price in high-performance or demanding environments. The long-term cost analysis often favors alumina due to its durability and lower maintenance, reducing total lifecycle expenses despite the upfront investment.
Lifespan and Reliability in Electrical Systems
Stoneware electrical insulators offer moderate lifespan with resistance to mechanical stress and environmental factors, but alumina ceramic insulators provide superior durability and reliability due to their high purity and excellent thermal stability. Alumina ceramics exhibit longer operational life under high voltage and temperature conditions, minimizing maintenance frequency and failure risk in electrical systems. The enhanced electrical insulation properties and resistance to wear make alumina ceramic the preferred material for critical and long-term electrical insulation applications.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors for Electrical Insulator Selection
Stoneware offers excellent mechanical strength and moderate electrical insulation but has higher porosity compared to alumina ceramic, which provides superior dielectric strength and thermal stability. Alumina ceramic is ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature applications due to its low electrical conductivity and exceptional resistance to wear and corrosion. Key factors in selecting the right material include operating voltage, thermal requirements, mechanical load, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal electrical insulation and durability.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Alumina ceramic for Electrical insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com