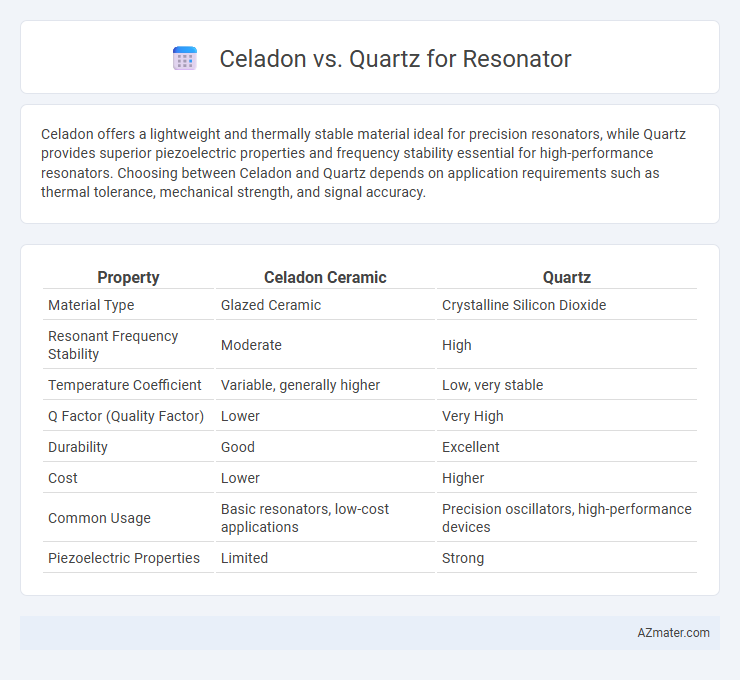
Celadon offers a lightweight and thermally stable material ideal for precision resonators, while Quartz provides superior piezoelectric properties and frequency stability essential for high-performance resonators. Choosing between Celadon and Quartz depends on application requirements such as thermal tolerance, mechanical strength, and signal accuracy.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Celadon Ceramic | Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed Ceramic | Crystalline Silicon Dioxide |
| Resonant Frequency Stability | Moderate | High |
| Temperature Coefficient | Variable, generally higher | Low, very stable |
| Q Factor (Quality Factor) | Lower | Very High |
| Durability | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Usage | Basic resonators, low-cost applications | Precision oscillators, high-performance devices |
| Piezoelectric Properties | Limited | Strong |
Introduction to Resonators: Celadon vs Quartz
Resonators, essential components in electronic circuits, determine signal frequency stability and accuracy, with Celadon and Quartz being popular material choices. Quartz resonators exhibit superior frequency precision and temperature stability due to their crystalline structure, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Celadon resonators offer cost-effective solutions with moderate frequency stability, often favored in budget-sensitive or less critical frequency control devices.
Material Composition: Celadon and Quartz Explained
Celadon is a ceramic material composed primarily of feldspar, silica, and clay, known for its smooth, glass-like surface that enhances resonance with warm, mellow tones. Quartz is a crystalline mineral made of silicon dioxide, prized for its high purity and ability to produce clear, vibrant sound with excellent sustain. The differing molecular structures of celadon ceramics and quartz crystals result in unique acoustic properties, influencing the resonator's tonal quality and response.
Resonator Functionality: How Material Influences Performance
Resonators composed of Celadon exhibit superior thermal stability and mechanical resonance due to the ceramic's low thermal expansion and high Q-factor, which enhances signal clarity and reduces energy loss. Quartz resonators outperform in frequency precision and temperature compensation properties, leveraging quartz's piezoelectric effect to maintain stable oscillations in varying environmental conditions. Material choice directly impacts resonator functionality, with Celadon favored for robustness in harsh environments and Quartz preferred for high-precision timing and filtering applications.
Sound Quality Comparison: Celadon vs Quartz
Celadon resonators produce a warm, rich tone with smooth midrange frequencies and a slightly mellow resonance, ideal for blues and folk styles requiring depth and character. Quartz resonators offer a brighter, more focused sound with enhanced clarity and sustain, making them suitable for genres demanding sharp attack and articulate note separation. Comparing Celadon to Quartz, Celadon provides a more vintage, rounded sound profile, while Quartz excels in delivering precise, cutting tonal quality.
Durability and Longevity Insights
Quartz resonators exhibit superior durability due to their inorganic crystalline structure, which provides resistance against environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress. Celadon resonators, typically made from ceramic materials, may experience faster degradation and reduced lifespan under harsh operating conditions. The longevity of quartz resonators often surpasses celadon varieties, ensuring more stable frequency performance and minimal maintenance over extended periods.
Aesthetic Appeal: Visual Differences
Celadon resonators feature a soft, muted green glaze with subtle variations in tone, creating a serene and timeless aesthetic that complements rustic and traditional decor styles. Quartz resonators offer a clean, translucent appearance with a sparkling clarity that enhances modern and minimalist interiors by adding a crisp, luminous accent. The choice between Celadon's earthy, organic finish and Quartz's bright, crystalline look directly influences the visual impact and ambiance of the resonator's setting.
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
Celadon resonators generally offer a more affordable price point compared to Quartz, making them accessible for budget-conscious buyers seeking effective performance. Quartz resonators, while typically more expensive, provide superior stability and durability, appealing to professional applications that justify the higher cost. Availability of Celadon components tends to be wider in general markets, whereas Quartz may require sourcing from specialized suppliers, impacting overall accessibility.
User Preference: Musicians’ Perspectives
Musicians often prefer Celadon quartz for resonators due to its superior tonal clarity and warm resonance, which enhances acoustic projection and dynamic response. Quartz resonators, valued for their durability and stability, provide consistent sound quality, making them ideal for studio recording and live performance reliability. User preference ultimately depends on the desired tonal character and playing context, with Celadon favored for expressive nuances and Quartz for precision and longevity.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Celadon resonators require minimal maintenance due to their smooth, non-porous surface that resists stains and corrosion, making regular wiping with a damp cloth sufficient. Quartz resonators demand more careful handling to avoid scratches and often benefit from periodic professional cleaning to maintain their clarity and performance. Both materials require avoiding harsh chemicals, but quartz's sensitivity to abrasive cleaners makes celadon a more durable choice for low-maintenance upkeep.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Celadon and Quartz Resonators
Celadon resonators provide superior tonal warmth and vintage aesthetics, making them ideal for blues and jazz musicians seeking rich, expressive sound. Quartz resonators excel in durability and frequency stability, preferred by players who require consistent performance across varied environments. Choosing between Celadon and Quartz depends on whether tonal character or reliability is the priority for your resonator needs.
Infographic: Celadon vs Quartz for Resonator
 azmater.com
azmater.com