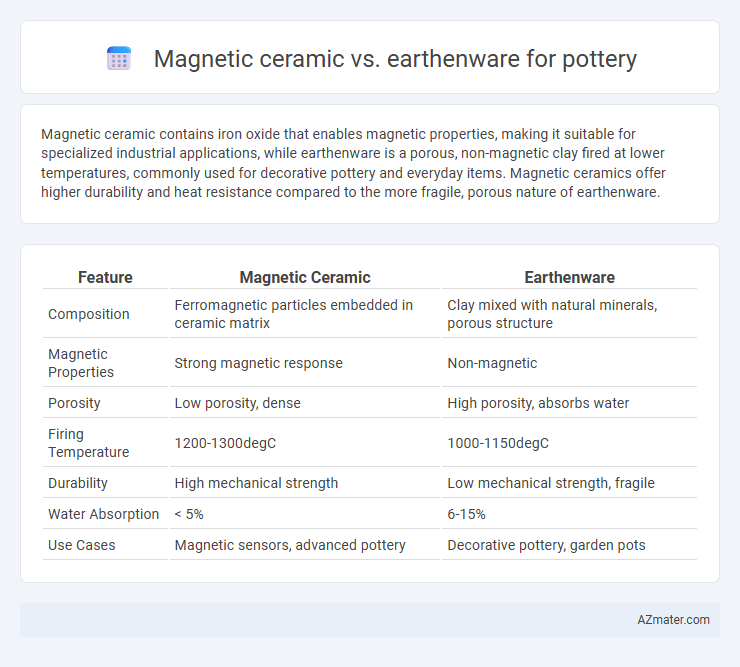
Magnetic ceramic contains iron oxide that enables magnetic properties, making it suitable for specialized industrial applications, while earthenware is a porous, non-magnetic clay fired at lower temperatures, commonly used for decorative pottery and everyday items. Magnetic ceramics offer higher durability and heat resistance compared to the more fragile, porous nature of earthenware.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Magnetic Ceramic | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Ferromagnetic particles embedded in ceramic matrix | Clay mixed with natural minerals, porous structure |
| Magnetic Properties | Strong magnetic response | Non-magnetic |
| Porosity | Low porosity, dense | High porosity, absorbs water |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1300degC | 1000-1150degC |
| Durability | High mechanical strength | Low mechanical strength, fragile |
| Water Absorption | < 5% | 6-15% |
| Use Cases | Magnetic sensors, advanced pottery | Decorative pottery, garden pots |
Introduction to Pottery Materials
Magnetic ceramic and earthenware represent two distinct categories of pottery materials, each characterized by unique clay compositions and firing temperatures. Magnetic ceramics, typically made with iron-rich clays, exhibit strong magnetic properties and are fired at higher temperatures, resulting in greater durability and density. Earthenware, composed of more porous clay and fired at lower temperatures, is softer and more porous, making it ideal for decorative pottery and traditional ceramics with a rustic aesthetic.
What Are Magnetic Ceramics?
Magnetic ceramics are advanced materials composed of ferrite compounds like barium or strontium ferrite, exhibiting strong magnetic properties used in electronic and industrial applications. Unlike traditional earthenware, which is porous and fired at lower temperatures, magnetic ceramics are sintered at high temperatures to achieve enhanced hardness and electromagnetic functionality. Their unique composition allows magnetic ceramics to serve in specialized pottery applications requiring durability and magnetic responsiveness beyond the aesthetic and functional limits of earthenware.
Understanding Earthenware in Pottery
Earthenware in pottery is a porous, low-fire ceramic known for its warm, rustic appearance and ease of shaping. Magnetic ceramic, a high-tech variant, typically offers enhanced durability and responsiveness to magnetic fields, unlike traditional earthenware. Understanding earthenware involves recognizing its vulnerability to water absorption and its requirement for glazing to achieve functional use in pottery.
Material Composition and Properties
Magnetic ceramic contains ferrite or iron oxide particles that provide magnetic properties, making it suitable for specialized applications requiring electromagnetic interference shielding or induction heating. Earthenware is primarily composed of natural clay mixed with minerals like quartz and feldspar, resulting in a porous and less dense material that is more fragile but easier to shape and glaze in low-temperature firing. While magnetic ceramics exhibit higher durability and thermal stability due to their inorganic magnetic components, earthenware offers greater aesthetic versatility and traditional appeal in pottery.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Magnetic ceramic exhibits superior strength and durability compared to traditional earthenware due to its dense molecular structure and enhanced thermal resistance, making it less prone to cracking or chipping. Earthenware, while more porous and less dense, tends to be more fragile and susceptible to damage under mechanical stress or temperature fluctuations. For pottery applications requiring long-lasting performance and robustness, magnetic ceramics offer a more reliable material choice.
Firing Temperatures and Techniques
Magnetic ceramic pottery generally requires higher firing temperatures between 1,200degC and 1,400degC, utilizing electric or gas kilns to achieve dense, vitrified surfaces with strong magnetic properties. Earthenware typically fires at lower temperatures around 1,000degC to 1,150degC, often employing traditional pit or wood-fired kilns that yield porous, softer textures ideal for decorative or functional ware. The choice of firing technique and temperature directly influences the durability, porosity, and magnetic responsiveness of the final ceramic product.
Aesthetic Differences in Finished Pieces
Magnetic ceramic pottery exhibits a smooth, glass-like surface with vibrant, consistent colors due to its high-temperature firing, enhancing its visual appeal for contemporary designs. Earthenware, fired at lower temperatures, often features a rustic, porous texture with earthy tones and natural imperfections that contribute to a handcrafted, traditional aesthetic. The aesthetic differences make magnetic ceramics ideal for sleek, modern pieces, while earthenware suits organic, artisanal styles.
Suitability for Functional vs. Decorative Pieces
Magnetic ceramic offers superior durability and heat resistance, making it highly suitable for functional pottery such as cookware and tableware that require frequent use and washing. In contrast, earthenware is more porous and less durable, often favored for decorative pieces like vases and ornamental objects where aesthetic appeal is prioritized over everyday utility. The choice between these materials hinges on the intended use, with magnetic ceramic excelling in practical applications and earthenware enriching artistic expression.
Cost and Accessibility of Materials
Magnetic ceramic often involves advanced raw materials like ferrites and requires precise manufacturing processes, resulting in higher costs compared to traditional earthenware made from readily available clay and natural minerals. Earthenware's wide accessibility and lower material expenses make it a cost-effective choice for pottery, especially in regions with abundant natural clay deposits. While magnetic ceramics offer specialized properties, their expense and limited material availability restrict widespread use compared to the economical and easily sourced components used in earthenware production.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Pottery Project
Magnetic ceramic, known for its durability and resistance to thermal shock, offers excellent strength and a sleek finish, making it ideal for functional pottery pieces that require longevity. Earthenware, characterized by its porous nature and lower firing temperature, provides a rustic look perfect for decorative items and traditional pottery but requires glazing to avoid water absorption. Choosing between magnetic ceramic and earthenware depends on the pottery project's purpose, with magnetic ceramic favored for practicality and durability, while earthenware suits aesthetic and artisanal pieces.
Infographic: Magnetic ceramic vs Earthenware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com