Steatite offers superior electrical insulation and thermal stability compared to terracotta, making it ideal for high-performance electronic components. Terracotta, while cost-effective, lacks the durability and dielectric strength required for advanced electronic applications.
Table of Comparison
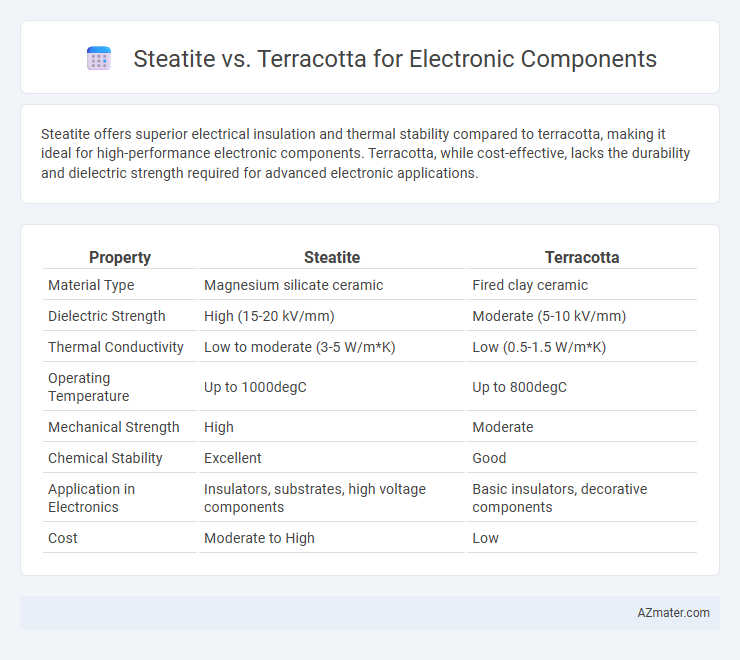
| Property | Steatite | Terracotta |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Magnesium silicate ceramic | Fired clay ceramic |
| Dielectric Strength | High (15-20 kV/mm) | Moderate (5-10 kV/mm) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to moderate (3-5 W/m*K) | Low (0.5-1.5 W/m*K) |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1000degC | Up to 800degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent | Good |
| Application in Electronics | Insulators, substrates, high voltage components | Basic insulators, decorative components |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low |
Introduction to Steatite and Terracotta in Electronics
Steatite, a dense ceramic composed primarily of magnesium silicate, offers excellent electrical insulation, high thermal stability, and low dielectric loss, making it ideal for electronic components such as insulators and substrates. Terracotta, a porous ceramic made from fired clay, exhibits moderate electrical insulation but lower mechanical strength and thermal resistance compared to steatite, limiting its use in high-performance electronic applications. The superior dielectric properties and mechanical durability of steatite provide a significant advantage over terracotta for electronic components requiring reliable insulation and heat management.
Material Composition and Properties
Steatite, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, offers excellent electrical insulation, high mechanical strength, and outstanding thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature electronic components. Terracotta, made from natural clay rich in iron oxide and alumina, provides moderate electrical insulation but lacks the thermal and mechanical robustness required for advanced electronic applications. The superior dielectric strength and resistance to thermal shock of steatite make it the preferred choice over terracotta for reliable, high-performance electronic insulators.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Steatite and terracotta differ significantly in manufacturing processes for electronic components due to their material properties; steatite is produced through powder pressing and sintering at high temperatures, resulting in dense, low-porosity ceramics ideal for insulation and thermal stability. Terracotta involves shaping clay and firing it at lower temperatures, creating a porous, less dense structure that limits its electrical insulating capabilities and mechanical strength. The precision and performance demands of electronic components favor steatite's advanced sintering process, enabling superior dielectric properties and dimensional consistency.
Thermal and Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Steatite offers superior thermal conductivity and excellent electrical insulation, making it ideal for high-power electronic components requiring efficient heat dissipation and dielectric stability. Terracotta, while providing good electrical insulation, has lower thermal conductivity, limiting its effectiveness in applications with significant heat generation. The choice between steatite and terracotta depends on the device's thermal load and insulation requirements, with steatite preferred for high-temperature environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Steatite exhibits higher mechanical strength and superior durability compared to terracotta, making it ideal for electronic components exposed to mechanical stress and thermal cycling. Its dense, non-porous structure resists cracking and deformation under load, while terracotta is more brittle and prone to chipping due to its porous composition. Steatite's enhanced wear resistance and thermal stability ensure longer lifespan and reliability in demanding electrical insulation applications.
Cost and Availability
Steatite offers a cost-effective solution for electronic components due to its widespread availability and ease of mass production, making it suitable for high-volume manufacturing. Terracotta, although less common and typically more expensive, provides superior thermal insulation and dielectric properties that justify its higher cost in specialized applications. The choice between steatite and terracotta depends largely on budget constraints and performance requirements within the electronics industry.
Suitability for High-Frequency Applications
Steatite offers superior dielectric properties and low dielectric loss, making it highly suitable for high-frequency electronic components compared to terracotta. Terracotta's porous structure and higher dielectric constant cause signal attenuation and increased loss at elevated frequencies. Steatite's high mechanical strength and thermal stability further enhance its performance in demanding high-frequency applications.
Environmental Sustainability
Steatite offers superior environmental sustainability compared to terracotta due to its high durability and resistance to thermal shock, reducing material waste and extending component lifespan. Terracotta, being a natural clay product, has lower embodied energy but is more prone to degradation, which can lead to more frequent replacements and increased resource consumption. Choosing steatite over terracotta supports sustainable electronics manufacturing by minimizing environmental impact through enhanced performance and longevity.
Common Applications in Electronic Components
Steatite is widely used in electronic components such as insulators, substrates, and capacitors due to its excellent thermal stability, high dielectric strength, and low loss tangent, making it ideal for high-frequency applications. Terracotta, with its porous and less uniform structure, is less common but is occasionally utilized in low-cost, non-critical insulation components or as a substrate in prototype circuits where high-performance dielectric properties are not essential. The choice between steatite and terracotta in electronic component manufacturing primarily depends on the specific thermal and electrical performance requirements of the application.
Summary: Choosing Between Steatite and Terracotta
Steatite offers superior electrical insulation and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-performance electronic components where durability and heat resistance are critical. Terracotta, while more cost-effective and environmentally friendly, typically exhibits lower mechanical strength and dielectric properties, limiting its use to less demanding applications. Selecting between steatite and terracotta depends on balancing performance requirements with budget constraints and environmental considerations.
Infographic: Steatite vs Terracotta for Electronic Component
 azmater.com
azmater.com