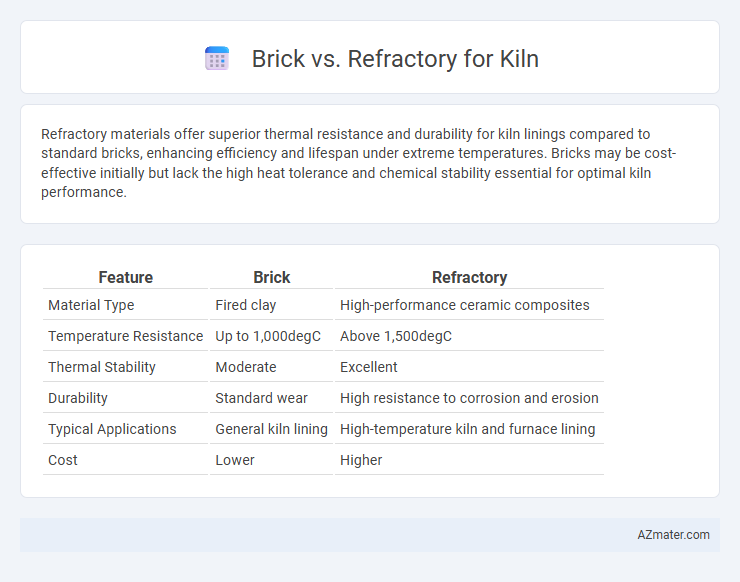
Refractory materials offer superior thermal resistance and durability for kiln linings compared to standard bricks, enhancing efficiency and lifespan under extreme temperatures. Bricks may be cost-effective initially but lack the high heat tolerance and chemical stability essential for optimal kiln performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Brick | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Fired clay | High-performance ceramic composites |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1,000degC | Above 1,500degC |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | Excellent |
| Durability | Standard wear | High resistance to corrosion and erosion |
| Typical Applications | General kiln lining | High-temperature kiln and furnace lining |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Kiln Construction Materials
Kiln construction materials primarily include bricks and refractory, each offering distinct thermal properties and durability essential for high-temperature applications. Bricks, often made from fireclay or other heat-resistant clays, provide structural stability and moderate heat retention, while refractory materials composed of specialized ceramics endure extreme temperatures and chemical wear, ensuring longer lifespan and efficiency. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the kiln's operating temperature, fuel type, and specific industrial processes requiring optimal heat management and insulation.
Understanding Brick Types for Kilns
Firebrick and refractory brick are essential materials for kiln construction, each offering unique thermal properties suited to high-temperature environments. Firebricks, typically made from alumina and silica, provide excellent insulation and withstand temperatures up to 1800degC, making them ideal for preserving heat in kiln linings. Refractory bricks, composed of materials like magnesite and chromite, offer superior structural strength and chemical resistance, suitable for areas exposed to intense heat and corrosive atmospheres in industrial kilns.
What Are Refractory Materials?
Refractory materials are heat-resistant substances designed to withstand high temperatures in kilns and furnaces without melting or breaking down. Unlike standard bricks, they possess superior thermal stability, chemical inertness, and mechanical strength, making them essential for lining kiln interiors. Common refractory materials include fireclay, alumina, silica, and magnesia, each tailored to specific temperature ranges and chemical environments.
Thermal Properties: Brick vs Refractory
Bricks used in kilns typically have lower thermal conductivity, providing effective insulation that helps maintain stable temperatures and reduce energy consumption. Refractory materials offer superior thermal resistance and can withstand much higher temperatures without degradation, making them ideal for extreme heat environments. The choice between brick and refractory depends on specific kiln operating temperatures and insulation efficiency requirements.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Refractory materials offer superior durability and lifespan compared to standard bricks when used in kilns due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal cycling without cracking or deteriorating. High-quality refractories maintain structural integrity over thousands of heating and cooling cycles, significantly extending kiln service life and reducing maintenance costs. Standard bricks often degrade faster under kiln conditions, leading to more frequent replacements and potential operational disruptions.
Heat Retention and Insulation Efficiency
Refractory materials offer superior heat retention and insulation efficiency compared to traditional brick due to their high melting points and low thermal conductivity, enabling kilns to maintain stable internal temperatures with less energy consumption. Bricks, especially firebricks, provide good heat resistance but typically lack the advanced thermal insulation properties found in specialized refractory ceramics, resulting in higher heat loss. Selecting refractory linings designed for kiln environments improves overall energy efficiency and durability by minimizing heat transfer and protecting structural integrity under extreme thermal conditions.
Cost Analysis: Brick vs Refractory
Bricks generally offer lower initial costs compared to refractory materials when constructing kilns, making them a budget-friendly option for small to medium-scale operations. Refractory linings, though more expensive upfront, provide superior thermal resistance and durability, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating long-term operational costs highlights refractory as a cost-effective choice for high-temperature industrial kilns despite the higher initial investment.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Refractory materials provide superior heat resistance and thermal insulation compared to traditional bricks, reducing heat loss during kiln operation. Installation of refractory linings requires skilled labor and precise application to ensure durability and prevent cracks under high-temperature cycles. Maintenance involves regular inspections for erosion or spalling, with targeted repairs essential to preserve kiln efficiency and prevent costly downtime.
Safety and Performance Factors
Refractory bricks are specially designed to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal cycling, providing superior safety by minimizing the risk of structural failure in kilns compared to regular clay bricks. Their high thermal insulation properties enhance energy efficiency and maintain consistent kiln performance, reducing heat loss and operational costs. Safety factors include resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal shock, which ensure long-term durability and reliable kiln operation under harsh firing conditions.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Kiln
Selecting the right material for your kiln hinges on understanding the differences between standard brick and refractory brick; refractory bricks are engineered to withstand higher temperatures and thermal shock, making them ideal for intense firing processes. These bricks offer superior insulating properties and chemical stability, essential for maintaining consistent kiln temperatures and protecting structural integrity. Cost and application requirements should guide the choice, as refractory bricks provide long-term durability in industrial settings while ordinary bricks may suffice for less demanding, hobbyist kilns.
Infographic: Brick vs Refractory for Kiln
 azmater.com
azmater.com