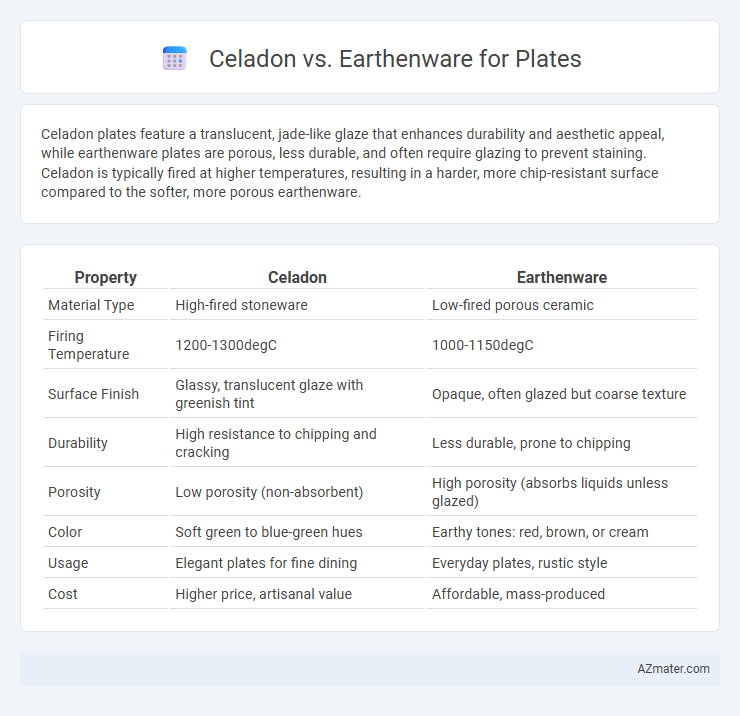
Celadon plates feature a translucent, jade-like glaze that enhances durability and aesthetic appeal, while earthenware plates are porous, less durable, and often require glazing to prevent staining. Celadon is typically fired at higher temperatures, resulting in a harder, more chip-resistant surface compared to the softer, more porous earthenware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Celadon | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-fired stoneware | Low-fired porous ceramic |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1300degC | 1000-1150degC |
| Surface Finish | Glassy, translucent glaze with greenish tint | Opaque, often glazed but coarse texture |
| Durability | High resistance to chipping and cracking | Less durable, prone to chipping |
| Porosity | Low porosity (non-absorbent) | High porosity (absorbs liquids unless glazed) |
| Color | Soft green to blue-green hues | Earthy tones: red, brown, or cream |
| Usage | Elegant plates for fine dining | Everyday plates, rustic style |
| Cost | Higher price, artisanal value | Affordable, mass-produced |
Introduction to Celadon and Earthenware Plates
Celadon plates are known for their translucent, pale green glaze derived from iron oxide, offering a smooth, glass-like surface that enhances both aesthetics and durability. Earthenware plates, crafted from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, typically feature a thicker, rustic texture and require glazing to hold liquids without seeping. Understanding the key differences in material composition and firing processes is essential for selecting the right plate for everyday use or decorative purposes.
Historical Background of Celadon and Earthenware
Celadon glaze originated during the Song Dynasty in China, prized for its jade-like, translucent green color and smooth texture, reflecting sophisticated ancient ceramic techniques. Earthenware, dating back to prehistoric times, represents one of the earliest forms of pottery made from clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous and less durable material compared to stoneware or porcelain. Both celadon and earthenware plates embody rich cultural heritages, with celadon symbolizing refined craftsmanship in East Asia and earthenware serving as a fundamental utilitarian pottery type worldwide.
Material Composition: Celadon vs Earthenware
Celadon plates are made from a refined porcelain clay fired at high temperatures, resulting in a durable, glass-like surface with a translucent pale green or blue glaze. Earthenware plates consist of a coarser clay fired at lower temperatures, producing a porous, opaque body that requires a glaze to prevent liquid absorption. The material composition of celadon offers superior strength and water resistance compared to the more porous and brittle earthenware.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Differences
Celadon plates showcase a signature translucent glaze with soft, muted green or blue hues that enhance intricate carved or molded designs, creating a refined, elegant aesthetic. Earthenware plates display warmer, earth-toned colors like terracotta, brown, or beige with a more rustic and matte finish, offering a cozy and artisanal charm. The color vibrancy in celadon is subtle and cool, contrasting with the rich, opaque, and warm palette typical of earthenware, making each suitable for distinct decorative preferences.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Celadon plates are known for their enhanced durability due to a higher firing temperature, which results in a denser, more vitrified ceramic body resistant to chipping and cracking. Earthenware plates, fired at lower temperatures, tend to be more porous and fragile, making them more susceptible to breakage and wear over time. This strength difference makes celadon a preferred choice for long-lasting dinnerware intended for frequent use.
Functional Uses in Modern Tableware
Celadon plates offer a non-porous, glazed surface that enhances durability and stain resistance, making them ideal for daily use and dishwasher cleaning in modern tableware. Earthenware plates, while more porous and prone to chipping, provide excellent heat retention, suitable for serving hot dishes and maintaining temperature. Both materials serve functional purposes in contemporary dining, with celadon favored for longevity and ease of maintenance, and earthenware preferred for rustic aesthetic and thermal properties.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Celadon plates require gentle handling and are best cleaned with mild soap and warm water to preserve their delicate glaze and prevent cracking. Earthenware plates demand careful maintenance due to their porous nature, needing thorough drying after washing to avoid moisture absorption and potential mold growth. Both types benefit from avoiding harsh abrasives and sudden temperature changes to extend their lifespan.
Price Point and Accessibility
Celadon plates typically command a higher price point due to their intricate glazing process and durability, making them less accessible for budget-conscious buyers. In contrast, earthenware plates are more affordable and widely available, offering a cost-effective option for everyday use despite being more porous and less durable. The accessibility of earthenware in mass-produced forms contributes to its popularity in both local markets and large retailers.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Celadon plates, crafted from high-fired clay with a glaze containing natural minerals, are durable and long-lasting, reducing waste compared to the more porous and fragile earthenware plates that often require frequent replacement. Earthenware, typically fired at lower temperatures, can contain lead-based glazes, raising environmental and health concerns, whereas celadon's non-toxic, natural mineral glazes offer a safer, eco-friendly alternative. Both materials are biodegradable, but celadon's enhanced durability and natural glazing process make it a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Choosing the Right Plate: Celadon or Earthenware
Choosing the right plate between celadon and earthenware depends on factors such as durability, aesthetic appeal, and use case. Celadon offers a smooth, translucent glaze with subtle green-blue hues, making it ideal for elegant table settings and delicate presentations, while earthenware provides a rustic, earthy texture with greater chip resistance and heat retention, suited for everyday use and casual dining. Consider the desired look, functionality, and maintenance requirements to select the plate that best fits your lifestyle and dining needs.
Infographic: Celadon vs Earthenware for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com