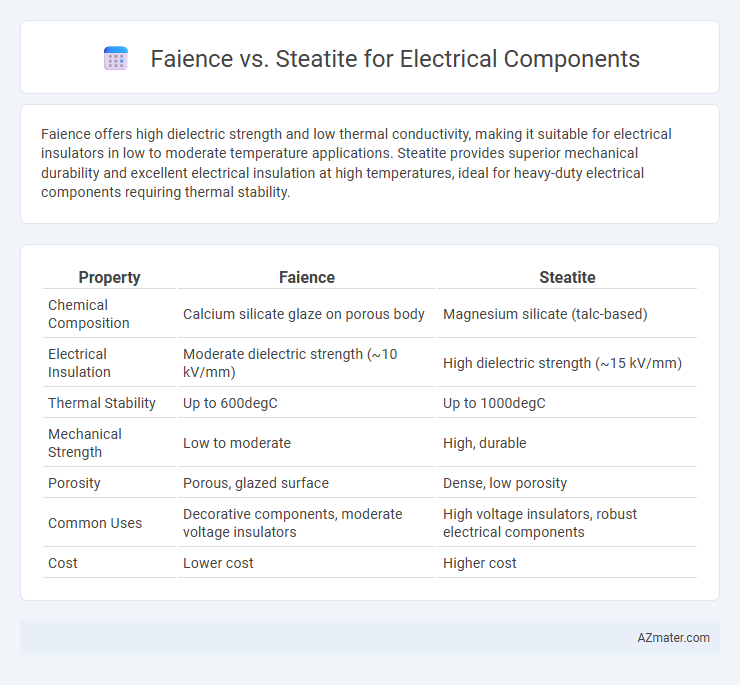
Faience offers high dielectric strength and low thermal conductivity, making it suitable for electrical insulators in low to moderate temperature applications. Steatite provides superior mechanical durability and excellent electrical insulation at high temperatures, ideal for heavy-duty electrical components requiring thermal stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Faience | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Calcium silicate glaze on porous body | Magnesium silicate (talc-based) |
| Electrical Insulation | Moderate dielectric strength (~10 kV/mm) | High dielectric strength (~15 kV/mm) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 600degC | Up to 1000degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate | High, durable |
| Porosity | Porous, glazed surface | Dense, low porosity |
| Common Uses | Decorative components, moderate voltage insulators | High voltage insulators, robust electrical components |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Electrical Insulating Materials
Faience and steatite are ceramic materials commonly used as electrical insulating components due to their excellent dielectric properties. Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic, offers high electrical resistance and thermal stability, making it suitable for applications requiring moisture resistance. Steatite, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, provides superior mechanical strength, low dielectric loss, and high temperature tolerance, ideal for insulators and substrates in electronic devices.
Defining Faience: Composition and Properties
Faience is a non-clay ceramic material primarily composed of finely ground quartz or sand mixed with small amounts of sodium carbonate and other fluxes, which melt during firing to form a glassy surface. Its high dielectric strength and excellent electrical insulation properties make it ideal for electrical components such as insulators and capacitors. The material's smooth, vitrified surface provides resistance to moisture and chemical corrosion, enhancing durability in electrical applications.
Understanding Steatite: Structure and Features
Steatite, a dense, ceramic material primarily composed of talc, exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties and high thermal stability, making it ideal for electrical components. Its microstructure features fine-grained crystals that contribute to superior mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock compared to faience, which is more brittle and porous. Steatite's low dielectric loss and high dielectric strength ensure reliable performance in high-frequency and high-voltage applications, distinguishing it as a preferred choice in electronic insulation and substrates.
Historical Uses of Faience and Steatite in Electrical Engineering
Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic material rich in silica, was historically valued for its insulating properties in early electrical components before synthetic materials became prevalent. Steatite, a dense form of talc with excellent dielectric strength and thermal stability, found extensive use in electrical engineering for insulators, spark plugs, and circuit boards throughout the 20th century. Both materials enabled the development of durable, heat-resistant electrical parts, but steatite's superior mechanical strength ultimately made it more dominant in industrial applications.
Dielectric Strength Comparison
Faience exhibits a dielectric strength typically ranging between 15 to 20 kV/mm, making it suitable for moderate electrical insulation applications. In contrast, steatite offers a higher dielectric strength often exceeding 25 kV/mm, providing superior performance in high-voltage environments. The enhanced dielectric properties of steatite result from its dense microstructure and low porosity, which minimize electrical breakdown risks compared to the more porous faience material.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Dissipation
Steatite exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to faience, making it more effective in high-temperature electrical component applications. Its excellent heat dissipation properties help prevent overheating, ensuring component reliability and longevity. Faience, while ceramic-based, generally has lower thermal conductivity and is less suitable for environments requiring rapid heat dispersion.
Mechanical Strength and Durability in Electrical Applications
Faience exhibits lower mechanical strength compared to steatite, making steatite more suitable for electrical components exposed to mechanical stress. Steatite's superior durability and resistance to thermal shock enhance its performance in high-stress electrical environments. The combination of excellent insulating properties and robust mechanical strength positions steatite as the preferred material in demanding electrical applications.
Cost Analysis: Faience vs Steatite
Faience typically offers lower manufacturing costs compared to steatite due to its less complex firing process and abundant raw materials, making it a cost-effective choice for mass production of electrical components. Steatite, while more expensive owing to its superior electrical insulation properties and higher mechanical strength, reduces long-term costs by enhancing durability and performance in high-stress applications. Businesses must weigh initial material expenses against lifecycle savings when choosing between faience and steatite for electrical component manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Faience components, made from glazed non-clay ceramic materials, typically involve higher energy consumption and emissions due to firing temperatures exceeding 1000degC, impacting environmental sustainability negatively compared to steatite. Steatite, a natural magnesium silicate mineral, demonstrates lower processing temperatures around 900degC and offers excellent dielectric properties with minimal environmental footprint during extraction and manufacturing. The biodegradability and recyclability of steatite-based electrical components further enhance their sustainability profile compared to the less eco-friendly disposal challenges of faience materials.
Choosing the Right Material for Modern Electrical Components
Faience offers excellent electrical insulation and thermal resistance, making it ideal for components subjected to high voltage and heat. Steatite, with its superior mechanical strength and lower dielectric loss, suits applications requiring robust durability and minimal signal interference. Selecting between faience and steatite depends on the specific electrical properties and mechanical demands of modern devices, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Faience vs Steatite for Electrical Component
 azmater.com
azmater.com