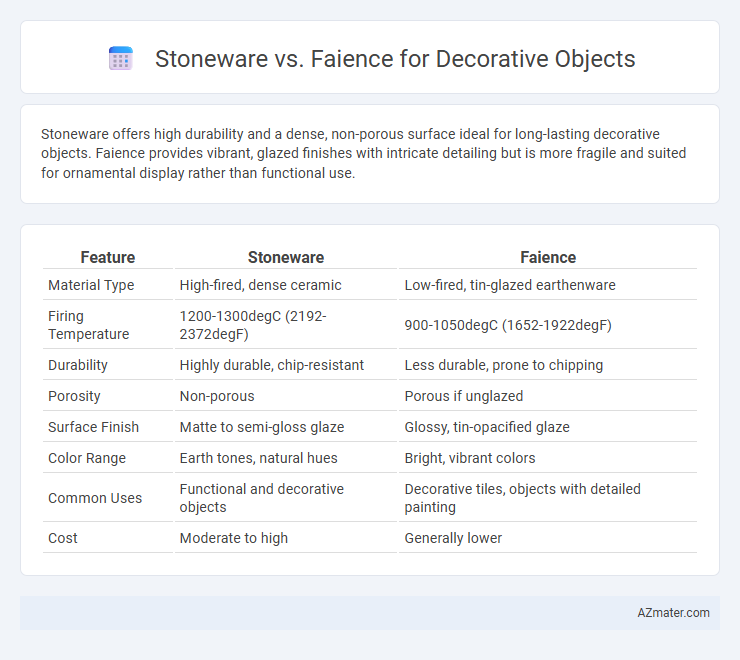
Stoneware offers high durability and a dense, non-porous surface ideal for long-lasting decorative objects. Faience provides vibrant, glazed finishes with intricate detailing but is more fragile and suited for ornamental display rather than functional use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stoneware | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-fired, dense ceramic | Low-fired, tin-glazed earthenware |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1300degC (2192-2372degF) | 900-1050degC (1652-1922degF) |
| Durability | Highly durable, chip-resistant | Less durable, prone to chipping |
| Porosity | Non-porous | Porous if unglazed |
| Surface Finish | Matte to semi-gloss glaze | Glossy, tin-opacified glaze |
| Color Range | Earth tones, natural hues | Bright, vibrant colors |
| Common Uses | Functional and decorative objects | Decorative tiles, objects with detailed painting |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower |
Introduction: Understanding Stoneware and Faience
Stoneware is a durable, non-porous ceramic fired at high temperatures, known for its strength and resistance to chipping, making it ideal for decorative objects requiring longevity. Faience, a glazed earthenware, features a vibrant glassy surface created by applying a tin or lead oxide-based glaze over a porous ceramic body, prized for its intricate designs and bright colors. Understanding the material properties and firing techniques of stoneware and faience helps in selecting the suitable medium for decorative art that balances durability with aesthetic appeal.
Historical Overview of Stoneware and Faience
Stoneware, originating in ancient China around 1600 BCE, is known for its dense, durable composition achieved through high-temperature firing, making it ideal for both utilitarian and decorative objects. Faience, developed in ancient Egypt as early as 4000 BCE, is a glazed non-clay ceramic composed primarily of crushed quartz, notable for its bright colors and intricate designs used extensively in decorative artifacts and jewelry. Both materials illustrate distinct historical advancements in ceramic technology, reflecting diverse cultural aesthetics and functional purposes across civilizations.
Composition and Material Differences
Stoneware is a dense, non-porous ceramic made from refined clay fired at high temperatures (1200degC-1300degC), resulting in durability and water resistance ideal for decorative objects. Faience, traditionally composed of glazed earthenware with a porous body made from silica, quartz, and clay, is fired at lower temperatures (900degC-1050degC), giving it a lighter, more fragile structure often adorned with vibrant tin-based glazes. The primary material differences lie in stoneware's vitrified, hard nature versus faience's softer, porous body with a distinct opaque, glossy surface.
Production Techniques Compared
Stoneware is fired at high temperatures between 1,200degC and 1,300degC, resulting in a dense, non-porous, and durable ceramic ideal for long-lasting decorative objects. Faience uses a lower firing temperature around 950degC to 1,050degC and incorporates a tin-opacified glaze, producing its distinctive bright, opaque surface with intricate painted designs. The production of faience requires precise glazing and controlled firing to achieve its vibrant finish, whereas stoneware emphasizes high-temperature vitrification for strength and subtle surface texture.
Durability and Longevity
Stoneware offers superior durability and longevity compared to faience due to its dense, non-porous composition fired at high temperatures, making it highly resistant to chipping, cracking, and water absorption. Faience, a glazed earthenware, is more porous and less robust, prone to crazing and damage over time when exposed to moisture or mechanical stress. For decorative objects requiring lasting structural integrity, stoneware is the preferred choice for enduring performance.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finishes
Stoneware offers a dense, non-porous surface with rich, earthy tones and a natural matte or glazed finish that enhances rustic and traditional decorative objects. Faience, characterized by its vibrant tin-glazed surface, provides a glossy, brightly colored aesthetic often featuring intricate painted designs that create a striking visual impact. The contrast in surface textures and color vibrancy between stoneware and faience directly influences their suitability for different decorative styles and artistic expressions.
Color and Glazing Possibilities
Stoneware offers a wide palette of earthy, muted tones enhanced by its dense, non-porous body that supports durable, glossy or matte glazing styles. Faience, characterized by its porous ceramic base, facilitates vibrant, opaque glazes in luminous blues, greens, and whites, making it ideal for richly colored decorations. The glazing on stoneware typically results in a more subdued, natural finish, whereas faience allows for intricate painted designs and bright, crackled surfaces that emphasize ornamental details.
Decorative Applications in Modern Design
Stoneware offers durability and a rustic, earthy texture ideal for modern decorative objects that require both functionality and aesthetic appeal. Faience, characterized by its vibrant, glossy glaze and intricate patterns, excels in creating visually striking decorative pieces that enhance contemporary interior designs. Both materials provide distinct tactile and visual qualities, with stoneware favoring robustness and subtlety, while faience prioritizes color richness and ornamental detail.
Care, Maintenance, and Preservation
Stoneware's dense, non-porous composition ensures high durability and resistance to moisture, making it easier to clean with mild soap and water without risk of damage. Faience, a glazed earthenware, requires gentler care due to its more delicate glaze that can crack or craze if exposed to sudden temperature changes or harsh chemicals. To preserve faience decorative objects, avoid abrasive cleaners and handle them carefully to prevent chipping, while stoneware objects can generally withstand more rigorous cleaning and handling.
Choosing the Right Material: Stoneware or Faience?
Stoneware offers exceptional durability and a natural, earthy finish ideal for decorative objects exposed to wear, while faience provides vibrant, glossy glazes with intricate designs suited for ornamental displays. Choosing stoneware ensures resistance to chipping and a matte texture that enhances rustic aesthetics, whereas faience allows for more vivid color palettes and detailed artistry but requires careful handling due to its fragility. Prioritize stoneware for functional decor or high-traffic areas and select faience when vibrant visual impact and fine craftsmanship are the main goals.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Faience for Decorative Object
 azmater.com
azmater.com