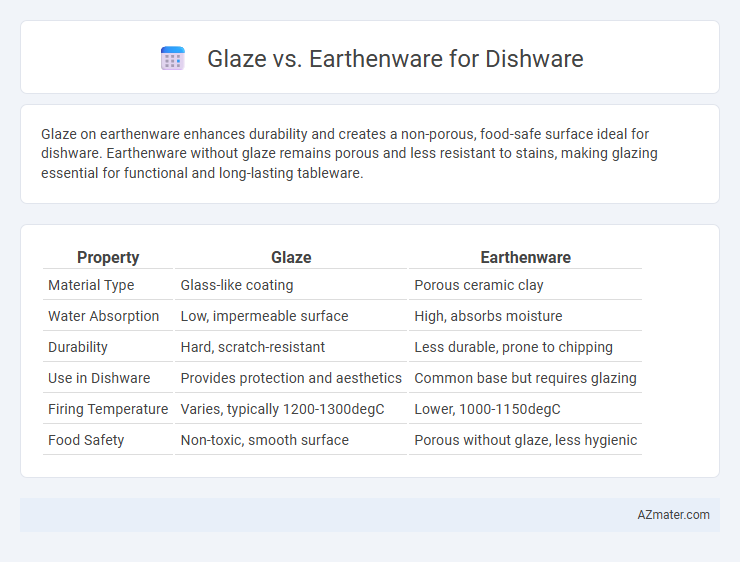
Glaze on earthenware enhances durability and creates a non-porous, food-safe surface ideal for dishware. Earthenware without glaze remains porous and less resistant to stains, making glazing essential for functional and long-lasting tableware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glaze | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glass-like coating | Porous ceramic clay |
| Water Absorption | Low, impermeable surface | High, absorbs moisture |
| Durability | Hard, scratch-resistant | Less durable, prone to chipping |
| Use in Dishware | Provides protection and aesthetics | Common base but requires glazing |
| Firing Temperature | Varies, typically 1200-1300degC | Lower, 1000-1150degC |
| Food Safety | Non-toxic, smooth surface | Porous without glaze, less hygienic |
Introduction to Dishware Materials
Glaze significantly enhances the durability and aesthetic appeal of earthenware, a common ceramic material used in dishware. Earthenware, characterized by its porous nature and lower firing temperature, benefits from the protective coating of glaze, which prevents water absorption and stains. This combination results in functional, attractive dishware suitable for everyday use and decorative purposes.
Understanding Glaze in Dishware
Glaze in dishware serves as a vitreous coating that enhances durability, prevents water absorption, and provides a smooth, non-porous surface crucial for earthenware. This glass-like layer protects the porous nature of earthenware, making it resistant to stains, scratches, and chemical corrosion while also allowing for vibrant colors and decorative finishes. Understanding glaze is essential for appreciating how earthenware dishware combines aesthetic appeal with functionality and longevity.
What is Earthenware?
Earthenware is a type of ceramic dishware made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, typically between 1,000degC and 1,150degC. It is often glazed to create a non-porous surface, enhancing durability and making it food-safe while retaining its rustic, traditional appearance. Commonly used for plates, bowls, and decorative items, earthenware is less durable than stoneware or porcelain but valued for its aesthetic warmth and affordability.
Key Differences: Glazed vs. Earthenware
Glazed dishware features a smooth, glass-like coating that enhances durability, prevents porosity, and resists stains, making it ideal for everyday use. Earthenware, made from porous clay, is more fragile and absorbent unless coated with glaze, which transforms it into a more practical option for dishware. The primary difference lies in glazing's ability to provide a non-porous, hygienic surface compared to the raw, porous nature of unglazed earthenware.
Durability and Longevity
Glazed dishware offers superior durability compared to unglazed earthenware due to its protective, non-porous coating that resists stains, scratches, and chipping. Earthenware, while aesthetically appealing with its porous and rustic texture, is more prone to cracking and absorbing moisture, which shortens its lifespan. For long-term use and resilience, glazed ceramics are the preferred choice in both everyday and specialty dishware collections.
Aesthetic Appeal and Customization
Glaze on earthenware enhances aesthetic appeal by providing a smooth, glossy finish available in a wide spectrum of colors and patterns, allowing for intricate designs and vibrant visual effects. Earthenware's porous nature requires glazing not only for durability but also for artistic customization, offering artisans flexibility in texture and finish, from matte to high gloss. Customization options include hand-painted details, decals, and layered glazes, enabling unique, personalized dishware that combines rustic warmth with refined beauty.
Safety and Non-Toxicity Factors
Glaze on dishware provides a protective, non-porous layer that prevents the absorption of harmful substances and enhances safety by reducing the risk of lead or cadmium leaching commonly found in low-quality earthenware. High-quality earthenware, when properly glazed with FDA-approved, non-toxic coatings, ensures safe use for food and beverages, while unglazed earthenware poses risks due to its porous nature harboring bacteria and contaminants. Selecting dishware with certified lead-free glazes and compliance with safety standards is crucial to maintain non-toxicity and prevent chemical exposure during everyday use.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Glazed dishware offers a smooth, non-porous surface that resists stains and makes cleaning easier, requiring only gentle hand washing or dishwasher use without special treatments. Earthenware is more porous and fragile, necessitating careful hand washing with mild detergents and avoiding prolonged soaking to prevent cracks or discoloration. Regular maintenance for earthenware includes drying thoroughly and occasionally reapplying a protective oil or sealant to maintain durability and appearance.
Cost Comparison: Glaze vs. Earthenware
Glazed dishware generally incurs higher production costs due to the additional kiln firing and materials required for the glossy, protective coating compared to unglazed earthenware. Earthenware, made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, offers a more budget-friendly option but may lack the durability and stain resistance of glazed pieces. Considering long-term value, glazed dishware often justifies its initial expense through enhanced longevity and easier maintenance.
Choosing the Right Dishware for Your Needs
Glaze provides a non-porous, durable finish for earthenware, enhancing its resistance to stains and making it ideal for everyday dishware that requires easy cleaning and long-term use. Earthenware, being more porous and fragile compared to stoneware or porcelain, suits decorative or occasional use but benefits significantly from a high-quality glaze to prevent moisture absorption and improve food safety. Selecting dishware depends on your priorities: choose glazed earthenware for affordable, attractive options with decent durability or consider alternatives for higher resistance and professional kitchen demands.
Infographic: Glaze vs Earthenware for Dishware
 azmater.com
azmater.com