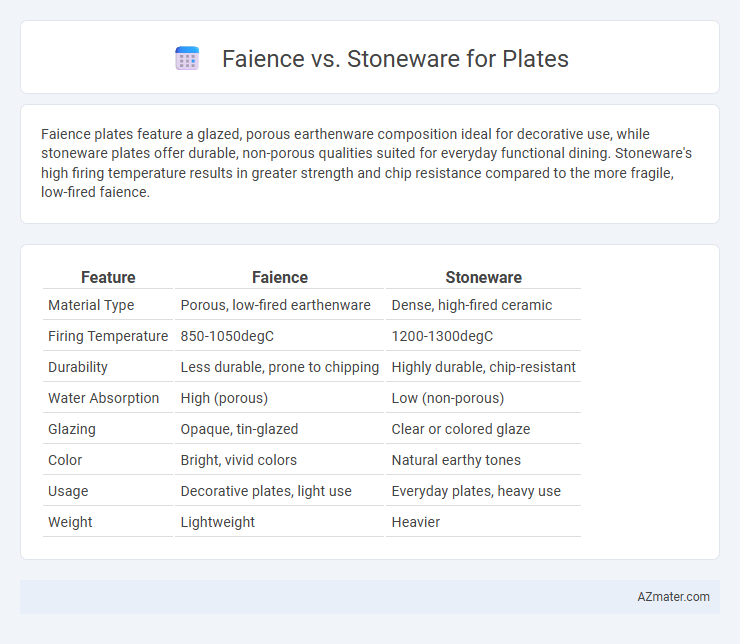
Faience plates feature a glazed, porous earthenware composition ideal for decorative use, while stoneware plates offer durable, non-porous qualities suited for everyday functional dining. Stoneware's high firing temperature results in greater strength and chip resistance compared to the more fragile, low-fired faience.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Faience | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous, low-fired earthenware | Dense, high-fired ceramic |
| Firing Temperature | 850-1050degC | 1200-1300degC |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to chipping | Highly durable, chip-resistant |
| Water Absorption | High (porous) | Low (non-porous) |
| Glazing | Opaque, tin-glazed | Clear or colored glaze |
| Color | Bright, vivid colors | Natural earthy tones |
| Usage | Decorative plates, light use | Everyday plates, heavy use |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
Introduction to Faience and Stoneware Plates
Faience plates are characterized by their tin-glazed, brightly colored surfaces, originating from ancient Mediterranean pottery traditions that emphasize decorative artistry and lightweight durability. Stoneware plates, made from dense, vitrified clay fired at higher temperatures, offer robust strength, chip resistance, and practicality for everyday use. The choice between faience and stoneware plates involves balancing aesthetic appeal with functional durability, catering to varied dining and decorative preferences.
What is Faience? Origin and Characteristics
Faience is a type of tin-glazed pottery originating in the Middle East and later popularized in Europe during the Renaissance, characterized by its opaque white glaze and vibrant painted designs. Typically made from a porous earthenware clay body, faience offers a glossy, decorative surface that enhances intricate patterns and colors. Unlike the dense and durable stoneware, faience is more fragile and primarily valued for its artistic appeal rather than its functional strength.
What is Stoneware? Definition and Features
Stoneware is a durable, non-porous ceramic material fired at high temperatures between 1,100degC and 1,300degC, resulting in a dense and vitrified body that resists chipping and moisture absorption. Its features include a sturdy, opaque texture with a slightly grainy finish, making it ideal for everyday use and dishwasher safety. Stoneware plates are valued for their strength, heat retention, and ability to withstand temperature fluctuations compared to more delicate ceramics like faience.
Visual Differences: Appearance and Aesthetics
Faience plates exhibit a glossy, brightly colored glaze often decorated with intricate hand-painted designs, creating a vibrant and ornamental appearance. Stoneware plates have a more muted, earthy tone with a matte or satin finish, emphasizing natural textures and a rustic, sturdy aesthetic. The visual contrast lies in faience's vivid patterns and sheen versus stoneware's subdued, organic look.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Faience plates offer a delicate and decorative finish but tend to be less durable and more prone to chipping compared to stoneware. Stoneware plates boast high strength and resistance to impact due to their dense, vitrified composition, making them ideal for everyday use. The superior durability of stoneware ensures long-lasting performance in both domestic and commercial settings.
Porosity and Water Resistance
Faience plates exhibit higher porosity due to their low-temperature firing, making them more absorbent and less water-resistant compared to stoneware. Stoneware undergoes high-temperature firing, resulting in a dense, non-porous surface that offers superior water resistance and durability. The low porosity of stoneware enhances its suitability for everyday use and frequent washing, whereas faience requires careful maintenance to prevent moisture absorption and staining.
Suitability for Daily Use
Faience plates, made from tin-glazed earthenware, offer vibrant colors and intricate designs but tend to be more porous and fragile, making them less suitable for heavy daily use. Stoneware plates, crafted from dense, fired clay, provide superior durability, resistance to chipping, and are typically microwave and dishwasher safe, enhancing their practicality for everyday meals. For frequent use, stoneware is the preferred choice due to its robust nature and low maintenance compared to the more decorative and delicate faience.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Faience plates require gentle cleaning with mild soap and avoid abrasive scrubbers to prevent surface damage due to their porous and glazed nature. Stoneware plates offer greater durability and resist stains, allowing for easier maintenance with dishwasher-safe cleaning and robust scrubbing. Both materials benefit from prompt drying to prevent moisture absorption and preserve longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Faience plates, made from glazed earthenware, typically involve lower firing temperatures compared to stoneware, resulting in reduced energy consumption and a smaller carbon footprint during production. Stoneware, known for its durability and higher firing temperatures, offers longer lifespan and resistance to chipping, which contributes to reduced waste over time and less frequent replacement. The environmental impact of both materials depends heavily on sourcing and manufacturing practices, but sustainable production of either can minimize resource extraction and emissions.
Which is Better: Faience or Stoneware for Plates?
Stoneware offers exceptional durability and chip resistance, making it ideal for everyday plates that withstand frequent use and dishwasher cycles. Faience, known for its decorative glazes and intricate designs, excels in aesthetic appeal but is more porous and fragile compared to stoneware. For practical, long-lasting dinnerware, stoneware outperforms faience in strength and maintenance.
Infographic: Faience vs Stoneware for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com