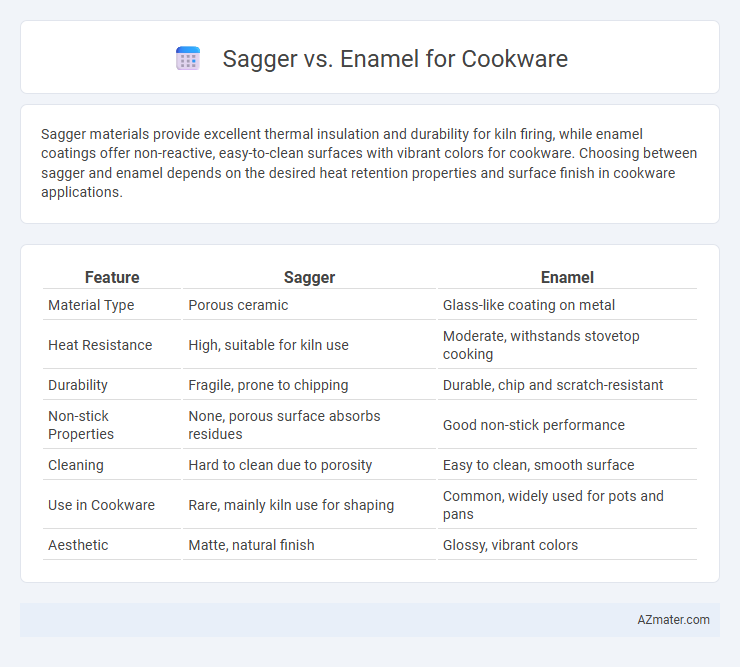
Sagger materials provide excellent thermal insulation and durability for kiln firing, while enamel coatings offer non-reactive, easy-to-clean surfaces with vibrant colors for cookware. Choosing between sagger and enamel depends on the desired heat retention properties and surface finish in cookware applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sagger | Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous ceramic | Glass-like coating on metal |
| Heat Resistance | High, suitable for kiln use | Moderate, withstands stovetop cooking |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to chipping | Durable, chip and scratch-resistant |
| Non-stick Properties | None, porous surface absorbs residues | Good non-stick performance |
| Cleaning | Hard to clean due to porosity | Easy to clean, smooth surface |
| Use in Cookware | Rare, mainly kiln use for shaping | Common, widely used for pots and pans |
| Aesthetic | Matte, natural finish | Glossy, vibrant colors |
Introduction to Sagger and Enamel Cookware
Sagger cookware, crafted from heat-resistant clay or ceramic, provides uniform heat distribution and retains moisture effectively, making it ideal for slow-cooking and baking traditional recipes. Enamel cookware features a durable, non-reactive coating fused to metal, usually cast iron or steel, offering easy cleanup and resistance to rust and stains. Both materials enhance cooking performance by combining heat retention with user-friendly maintenance, but their distinct compositions cater to different culinary preferences.
What is Sagger Cookware?
Sagger cookware is crafted from high-fired clay that undergoes a protective firing process inside a sagger box, preventing direct flame contact and enhancing durability. This traditional method results in porous, natural cookware ideal for slow cooking and heat retention. Compared to enamel cookware coated with glass-like ceramic, sagger pots offer a rustic, chemical-free option prized for its natural breathability and unique flavor development in dishes.
What is Enamel Cookware?
Enamel cookware consists of a metal core, typically cast iron or steel, coated with a layer of smooth, durable enamel made from fused glass particles. This enamel coating provides a non-reactive surface that resists rust, prevents food from sticking, and allows for easy cleaning without the need for seasoning. Enamel cookware combines the heat retention and even distribution properties of metal with the convenience and aesthetic appeal of a colorful, protective enamel finish.
Material Composition: Sagger vs Enamel
Sagger cookware is typically crafted from fireclay or ceramic materials that offer high heat resistance and natural thermal retention, ideal for slow cooking and baking. Enamel cookware features a metal core, usually cast iron or steel, coated with a glassy enamel layer that provides durability, non-reactivity, and easy cleaning without compromising heat distribution. The material composition of sagger emphasizes natural clay minerals, while enamel combines a robust metal base with a chemically inert, smooth surface for versatile cooking performance.
Heat Retention and Distribution Comparisons
Sagger cookware, often made from unglazed clay or ceramic, excels in heat retention due to its porous structure, allowing it to hold warmth evenly over extended periods, ideal for slow cooking and simmering. Enamel cookware, coated with a smooth, glass-like finish, provides superior heat distribution by efficiently transferring heat across the cooking surface, reducing hotspots and enabling precise temperature control. While sagger cookware retains heat longer, enamel pans respond faster to temperature changes, making each suitable for different cooking methods based on their thermal properties.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Sagger cookware offers exceptional durability due to its thick, heat-resistant clay composition that withstands high temperatures and resists cracking over time. Enamel cookware, while providing a smooth, non-reactive surface, can chip or crack with heavy use, reducing its longevity despite being corrosion-resistant. For long-term use, sagger cookware generally outlasts enamel, especially in rigorous cooking environments.
Maintenance and Cleaning Differences
Sagger cookware requires careful handling during cleaning due to its porous surface, which can absorb water and residue, leading to potential staining and odors if not dried thoroughly. Enamel cookware features a smooth, non-porous coating that resists stains and simplifies maintenance, allowing for easy cleanup with mild detergents and less risk of corrosion. While saggers may need gentle scrubbing and oiling to maintain their integrity, enamel cookware is dishwasher safe and generally more resistant to chipping under regular use.
Cooking Performance: Flavor and Food Safety
Sagger cookware provides excellent heat retention and even distribution, enhancing flavor development through precise temperature control and minimizing hotspots, which reduces the risk of food burning. Enamel cookware offers a non-reactive cooking surface that prevents metallic taste transfer and supports safe cooking with acidic ingredients, ensuring food safety without leaching harmful substances. Both materials contribute to optimal cooking performance, but choose sagger for superior heat management and enamel for ease of maintenance and chemical inertness.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Sagger cookware offers a rustic, artisanal aesthetic with earthy textures and handcrafted designs that appeal to those seeking a natural, organic look in their kitchen. Enamel cookware provides a smooth, glossy finish available in a wide array of vibrant colors and patterns, allowing for versatile design options that complement modern and classic kitchen styles. Both materials enhance visual appeal, but enamel excels in customization and color variety, while sagger highlights unique, tactile craftsmanship.
Which to Choose: Sagger or Enamel Cookware?
Sagger cookware offers superior heat retention and natural non-stick properties due to its clay composition, ideal for slow cooking and roasting, while enamel cookware provides a durable, non-reactive surface easy to clean and resistant to rust, making it versatile for various cooking methods. Choosing between sagger and enamel depends on cooking style: select sagger for traditional, slow-cooked recipes requiring moisture retention and enamel for everyday use with acidic ingredients. Both materials offer unique durability advantages, but enamel excels in low-maintenance care, whereas sagger enhances flavor development through its porous texture.
Infographic: Sagger vs Enamel for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com