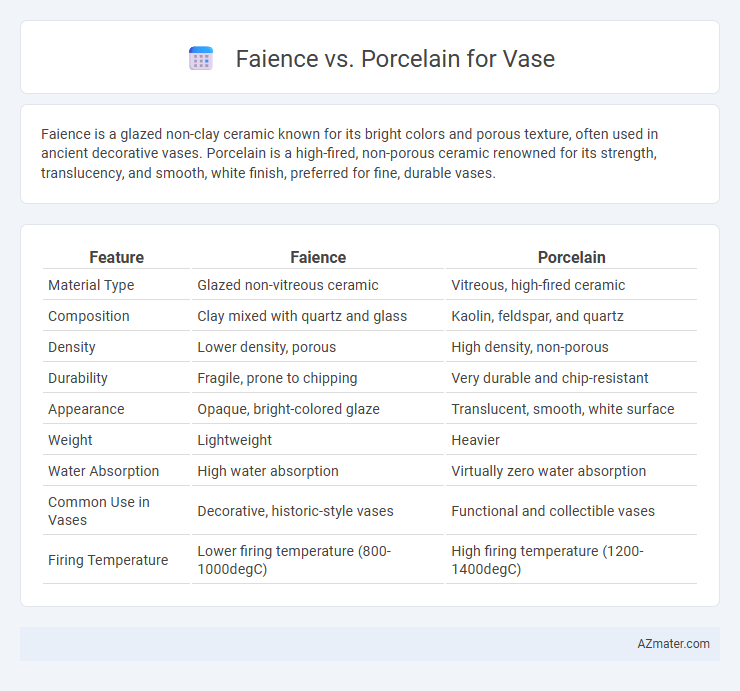
Faience is a glazed non-clay ceramic known for its bright colors and porous texture, often used in ancient decorative vases. Porcelain is a high-fired, non-porous ceramic renowned for its strength, translucency, and smooth, white finish, preferred for fine, durable vases.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Faience | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed non-vitreous ceramic | Vitreous, high-fired ceramic |
| Composition | Clay mixed with quartz and glass | Kaolin, feldspar, and quartz |
| Density | Lower density, porous | High density, non-porous |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to chipping | Very durable and chip-resistant |
| Appearance | Opaque, bright-colored glaze | Translucent, smooth, white surface |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Water Absorption | High water absorption | Virtually zero water absorption |
| Common Use in Vases | Decorative, historic-style vases | Functional and collectible vases |
| Firing Temperature | Lower firing temperature (800-1000degC) | High firing temperature (1200-1400degC) |
Introduction to Faience and Porcelain
Faience is a type of tin-glazed pottery known for its opaque, brightly colored surface, originating in ancient Egypt and later popularized in Europe, often used for decorative vases with intricate designs. Porcelain, made from refined kaolin clay fired at high temperatures, is valued for its strength, translucency, and smooth, white surface, making it ideal for both functional and ornamental vases. The distinct composition and firing techniques create faience's vibrant, opaque finish versus porcelain's delicate, translucent quality in vase craftsmanship.
Historical Origins of Faience and Porcelain
Faience originated in ancient Egypt and the Near East around 4000 BCE, characterized by its tin-glazed earthenware with vibrant colors and intricate designs often reflecting cultural and religious symbolism. Porcelain was first developed in China during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE), refined significantly in the Song Dynasty, and is known for its high-fired, translucent, and durable quality, often associated with fine artistry and imperial use. Both materials have distinct historical contexts: faience embodies ancient craft techniques and spiritual significance, while porcelain represents technological innovation and artistic refinement in East Asia.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Faience vases are crafted from earthenware clay mixed with quartz and coated with a brightly colored tin glaze, offering a porous body that requires glazing to be watertight. Porcelain vases, made from refined kaolin clay and fired at higher temperatures above 1200degC, achieve a dense, non-porous structure with a smooth, white, and translucent finish. The manufacturing process of faience involves low firing and glazing techniques that emphasize vibrant colors, whereas porcelain demands precise high-temperature kiln firing to develop its strength and delicate aesthetic.
Visual Characteristics and Aesthetic Appeal
Faience vases offer vibrant, glossy surfaces with intricate painted designs often inspired by historical and cultural motifs, creating a rich, tactile visual appeal. Porcelain vases exhibit a smooth, translucent quality with a refined, delicate finish that enhances minimalist and elegant aesthetics. The choice between faience and porcelain hinges on desired color intensity and texture versus sleekness and subtlety in vase decor.
Durability and Functional Differences
Faience vases, made from glazed earthenware, exhibit moderate durability but are more prone to chipping and cracking compared to porcelain. Porcelain vases, crafted from refined kaolin clay fired at higher temperatures, offer superior strength, resistance to thermal shock, and a denser, non-porous surface ideal for holding water without leaking. The functional differences highlight porcelain's suitability for long-term use and practical applications, while faience often serves decorative purposes due to its delicate glaze.
Common Uses in Vase Production
Faience vases are commonly used for decorative purposes, featuring vibrant glazes and intricate patterns ideal for ornamental display. Porcelain vases offer durability and a fine, translucent finish, making them popular for both functional uses and high-end decorative pieces. Both materials are favored in vase production for their unique aesthetic qualities and ability to be molded into diverse shapes.
Price and Market Value Comparison
Faience vases typically command lower prices in the market due to their less durable, earthenware composition and more affordable production process, making them accessible for budget-conscious collectors. Porcelain vases, valued for their strength, translucence, and intricate craftsmanship, often fetch higher market prices and are considered more prestigious among collectors and investors. The significant price gap reflects porcelain's superior material quality and its historical demand in high-end decorative arts markets.
Collectibility and Cultural Significance
Faience vases, known for their glazed earthenware finish, hold significant cultural value in ancient Egyptian and Middle Eastern art collections, symbolizing early ceramic craftsmanship and vibrant decorative traditions. Porcelain vases, prized for their translucency and refined texture, are highly collectible due to their association with East Asian artistry, particularly Chinese Ming and Qing dynasties, reflecting centuries of sophisticated ceramic technology and royal patronage. Collectors value faience for its historical and ethnographic significance, while porcelain is esteemed for its artistic finesse and durability, making each material uniquely appealing in the antique vase market.
Care, Cleaning, and Maintenance Tips
Faience vases require gentle handling and cleaning with mild soap and warm water to preserve their glazed surface and avoid chipping. Porcelain vases are more durable but should still be cleaned using a soft cloth and non-abrasive cleaner to maintain their smooth finish and intricate designs. Both materials benefit from avoidance of harsh chemicals and sudden temperature changes to ensure longevity and preserve aesthetic quality.
Choosing the Right Vase: Faience or Porcelain
Choosing between faience and porcelain for a vase involves considering durability, appearance, and intended use. Faience offers vibrant, hand-painted designs with a porous texture ideal for decorative purposes, while porcelain provides a smooth, translucent finish known for strength and resistance to chipping. Selecting the right vase depends on balancing aesthetic preferences with functional needs such as water retention and longevity.
Infographic: Faience vs Porcelain for Vase
 azmater.com
azmater.com