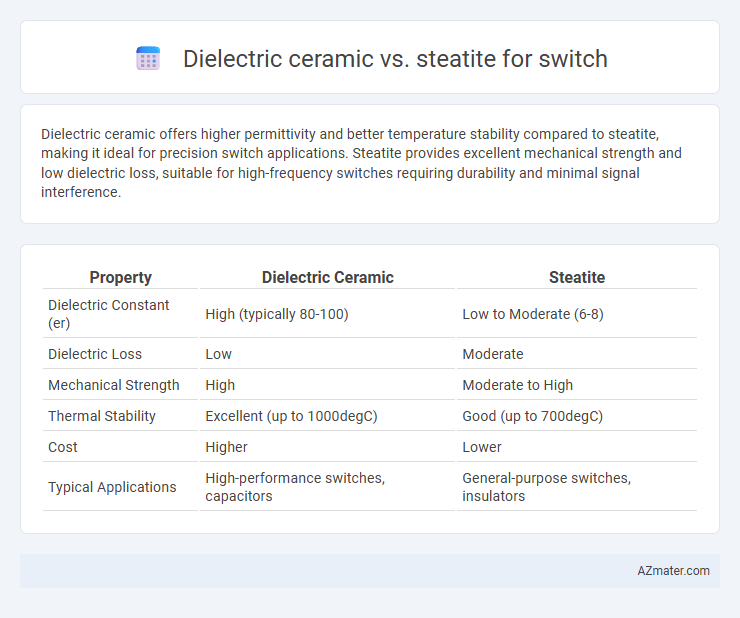
Dielectric ceramic offers higher permittivity and better temperature stability compared to steatite, making it ideal for precision switch applications. Steatite provides excellent mechanical strength and low dielectric loss, suitable for high-frequency switches requiring durability and minimal signal interference.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dielectric Ceramic | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant (er) | High (typically 80-100) | Low to Moderate (6-8) |
| Dielectric Loss | Low | Moderate |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate to High |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent (up to 1000degC) | Good (up to 700degC) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Applications | High-performance switches, capacitors | General-purpose switches, insulators |
Introduction to Dielectric Ceramic and Steatite
Dielectric ceramic materials exhibit high permittivity and excellent insulation properties, making them ideal for high-frequency switch applications where stable electrical performance and thermal resistance are critical. Steatite, a magnesium silicate ceramic, offers moderate dielectric strength and superior mechanical robustness, often chosen for switches requiring cost-effective solutions with reliable wear resistance. Comparing dielectric ceramic and steatite highlights trade-offs in electrical characteristics, thermal stability, and durability essential for optimizing switch design.
Key Properties of Dielectric Ceramics
Dielectric ceramics exhibit high permittivity, excellent insulation resistance, and low dielectric loss, making them ideal for switch applications requiring reliable electrical performance and minimal energy dissipation. Their superior thermal stability and mechanical strength ensure consistent operation under varying temperatures and mechanical stress. Compared to steatite, dielectric ceramics provide faster response times and better frequency stability, essential for high-precision switching devices.
Key Properties of Steatite Ceramics
Steatite ceramics exhibit excellent electrical insulation with a dielectric constant typically ranging from 6 to 7, making them suitable for switch applications requiring stable performance under high voltage. Their high mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock ensure durability and reliability in varying operational environments. Unlike dielectric ceramics with higher permittivity, steatite offers lower dielectric loss, contributing to improved efficiency and longevity in electrical switches.
Thermal Stability Comparison
Dielectric ceramic materials exhibit superior thermal stability compared to steatite, maintaining consistent electrical properties across a wider temperature range, typically from -55degC to 200degC. Steatite, composed mainly of magnesium silicate, shows greater susceptibility to thermal expansion and can experience degradation in dielectric strength at elevated temperatures above 150degC. This makes dielectric ceramics more reliable for high-temperature switch applications requiring stable dielectric constants and low loss tangents.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Dielectric ceramic offers superior electrical insulation performance due to its high dielectric strength and low dielectric loss, enabling it to withstand higher voltages and minimize leakage currents in switches. Steatite, composed mainly of magnesium silicate, provides moderate insulation properties with good thermal stability but lower dielectric strength compared to advanced dielectric ceramics. Consequently, dielectric ceramics are preferred in high-performance switch applications requiring enhanced electrical insulation and reliability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Dielectric ceramic exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to steatite, making it more resistant to mechanical stress and thermal cycling in switch applications. Its higher fracture toughness and stability under high voltage enable longer operational life and reduced risk of failure. Steatite, while cost-effective and electrically insulating, tends to have lower mechanical strength and is more prone to cracking under impact or repeated mechanical load.
Applications in Electrical Switches
Dielectric ceramic materials in electrical switches provide high permittivity and excellent insulation, enabling efficient signal transmission and reliable performance in high-frequency or sensitive electronic applications. Steatite, a magnesium silicate ceramic, offers superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and dielectric properties suitable for heavy-duty switches and high-voltage insulation components. The choice between dielectric ceramics and steatite depends on the switch's required electrical properties, operating environment, and mechanical demands.
Cost Analysis: Dielectric Ceramic vs Steatite
Dielectric ceramic switches generally incur higher material and manufacturing costs due to their superior electrical insulation and thermal stability compared to steatite. Steatite switches offer a more cost-effective solution, especially in large-scale applications, because of cheaper raw materials and simpler processing techniques. However, the long-term reliability and performance benefits of dielectric ceramic can justify the initial investment in high-precision or high-voltage switching devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages Summary
Dielectric ceramic offers higher dielectric constant and better insulation properties, making it ideal for high-frequency switches with low signal loss, but it tends to be more brittle and costly. Steatite provides excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability, and is more cost-effective, yet it has a lower dielectric constant and higher signal attenuation, limiting its use in high-frequency applications. Selecting between dielectric ceramic and steatite depends on specific switch requirements such as frequency performance, durability, and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Material for Switches
Dielectric ceramic offers superior insulating properties and higher thermal stability, making it ideal for high-frequency and high-voltage switch applications where consistent performance is critical. Steatite, with its excellent mechanical strength and lower cost, suits switches operating under moderate electrical stress and mechanical wear conditions. Selecting the right material depends on specific switch requirements such as voltage rating, thermal load, mechanical durability, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Dielectric ceramic vs Steatite for Switch
 azmater.com
azmater.com